| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Activity 1
Forces and Structures
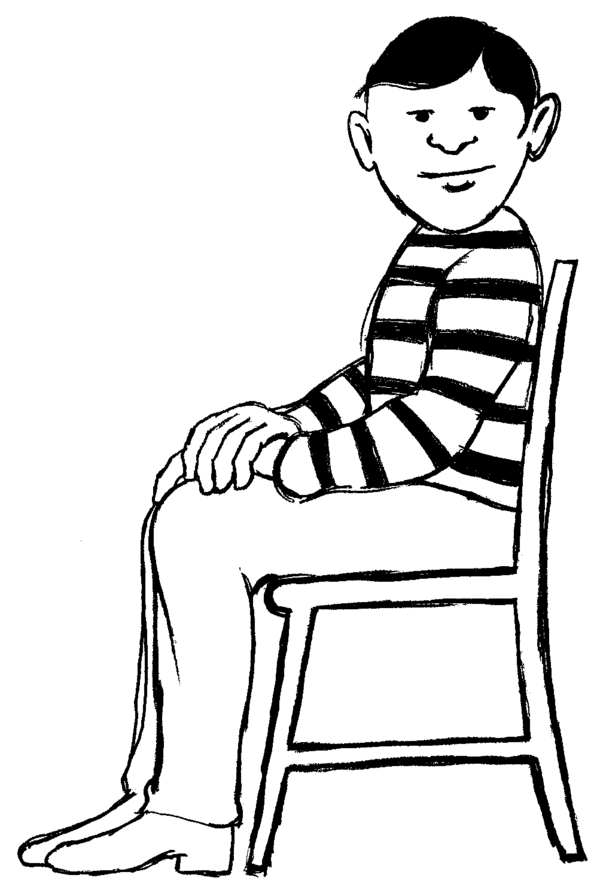

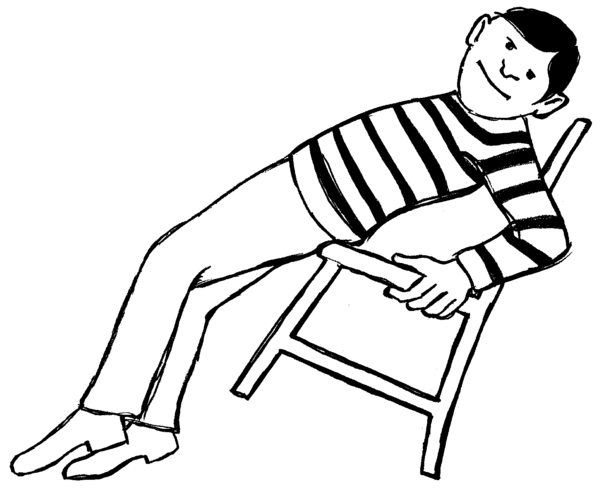
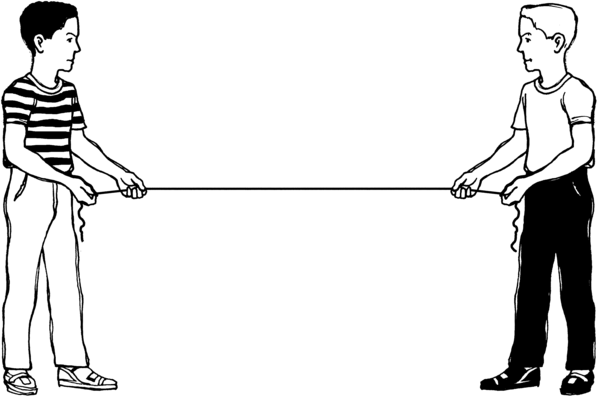
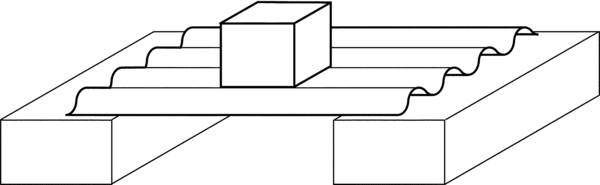
Stress
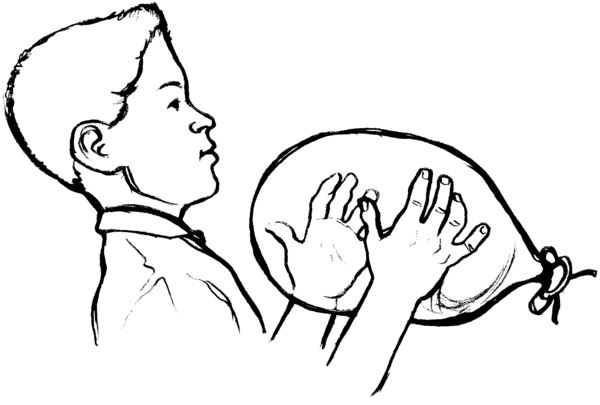

Compression
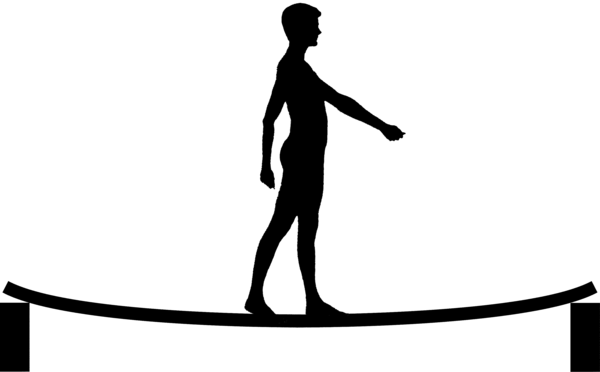
Flexure
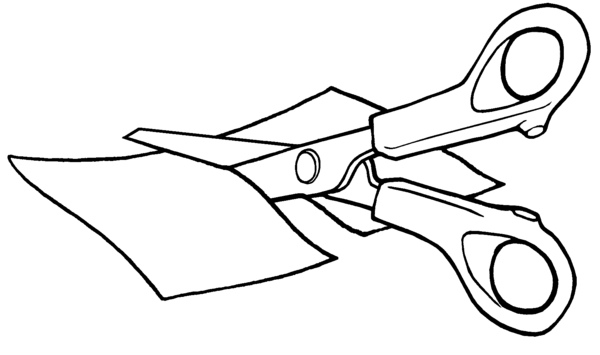
Shearing
Assignment 1

| LO 1.3 | ||||
| Learning Outcomes(LOs) |
| LO 1 |
| TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SKILLS The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technology. |
| This is demonstrated when the learner: |
| investigates:1.1 investigates the background context, the nature of the need, the environmental situation, and the people concerned when given a problem, need or opportunity set in a nationally relevant context; |
| 1.3 develops and performs practical tests in the technological areas (Structures, Processing, and Systems and Control); |
| 1.4 uses appropriate technologies and methods to: |
|
| designs:1.5 writes or communicates a short and clear statement or a design brief in response to a given identified situation for the development of a product or system; |
| 1.6 lists product and design specifications and constraints for a solution to an identified or given problem, need or opportunity based on most of the design key words listed below: |
|
| 1.7 generates several alternative solutions and writes notes, ideas that show some links to the design brief and specifications; |
| makes:1.9 develops a plan for making that outlines all of the following: |
|
ACTIVITY 1
Assignment 1

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?