| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Power —the word conjures up many images: a professional football player muscling aside his opponent, a dragster roaring away from the starting line, a volcano blowing its lava into the atmosphere, or a rocket blasting off, as in [link] .
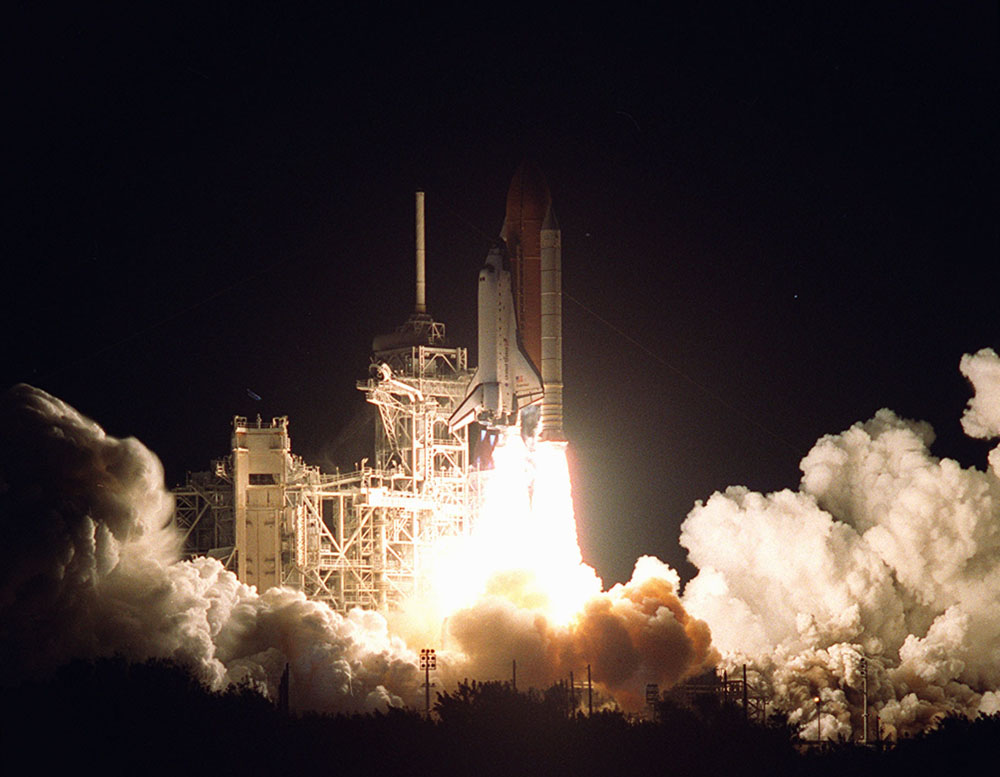

These images of power have in common the rapid performance of work, consistent with the scientific definition of power ( ) as the rate at which work is done.
Power is the rate at which work is done.
The SI unit for power is the watt ( ), where 1 watt equals 1 joule/second
Because work is energy transfer, power is also the rate at which energy is expended. A 60-W light bulb, for example, expends 60 J of energy per second. Great power means a large amount of work or energy developed in a short time. For example, when a powerful car accelerates rapidly, it does a large amount of work and consumes a large amount of fuel in a short time.
What is the power output for a 60.0-kg woman who runs up a 3.00 m high flight of stairs in 3.50 s, starting from rest but having a final speed of 2.00 m/s? (See [link] .)
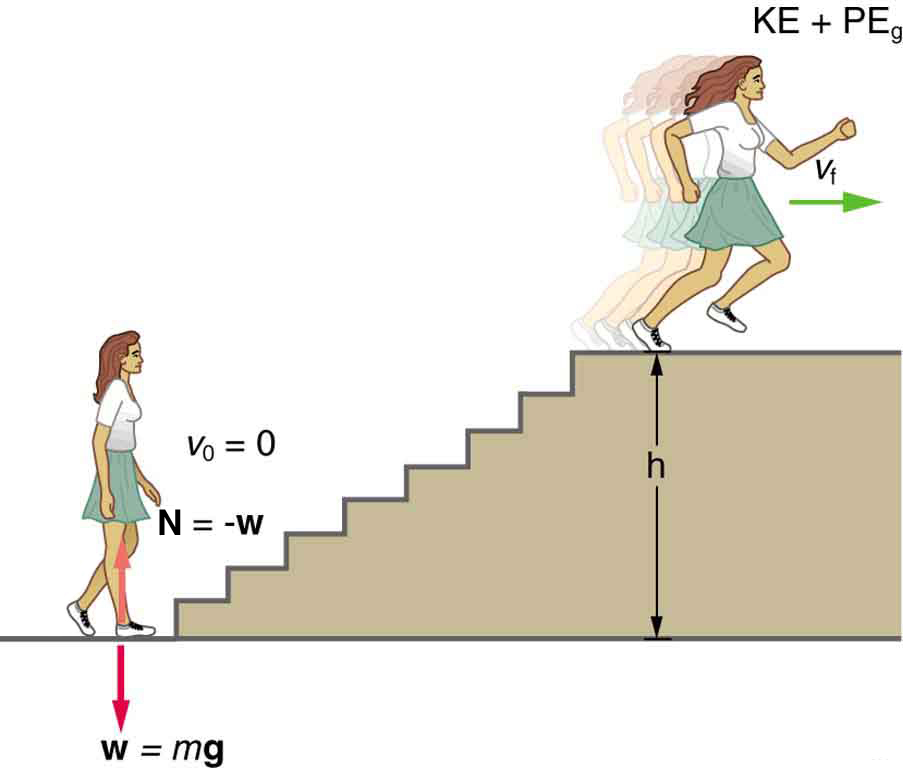
Strategy and Concept
The work going into mechanical energy is . At the bottom of the stairs, we take both and as initially zero; thus, , where is the vertical height of the stairs. Because all terms are given, we can calculate and then divide it by time to get power.
Solution
Substituting the expression for into the definition of power given in the previous equation, yields
Entering known values yields
Discussion
The woman does 1764 J of work to move up the stairs compared with only 120 J to increase her kinetic energy; thus, most of her power output is required for climbing rather than accelerating.
It is impressive that this woman’s useful power output is slightly less than 1 horsepower ! People can generate more than a horsepower with their leg muscles for short periods of time by rapidly converting available blood sugar and oxygen into work output. (A horse can put out 1 hp for hours on end.) Once oxygen is depleted, power output decreases and the person begins to breathe rapidly to obtain oxygen to metabolize more food—this is known as the aerobic stage of exercise. If the woman climbed the stairs slowly, then her power output would be much less, although the amount of work done would be the same.
Determine your own power rating by measuring the time it takes you to climb a flight of stairs. We will ignore the gain in kinetic energy, as the above example showed that it was a small portion of the energy gain. Don’t expect that your output will be more than about 0.5 hp.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Unit 5 - work and energy' conversation and receive update notifications?