| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Now that we have studied the basics of longitudinal waves, we are ready to study sound waves in detail.
Have you ever thought about how amazing your sense of hearing is? It is actually pretty remarkable. There are many types of sounds: a car horn, a laughing baby, a barking dog, and somehow your brain can sort it all out. Though it seems complicated, it is rather simple to understand once you learn a very simple fact. Sound is a wave. So you can use everything you know about waves to explain sound.
Since sound is a wave, we can relate the properties of sound to the properties of a wave. The basic properties of sound are: pitch, loudness and tone.
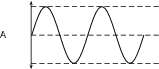
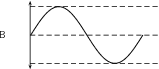
The frequency of a sound wave is what your ear understands as pitch. A higher frequency sound has a higher pitch, and a lower frequency sound has a lower pitch. In [link] sound A has a higher pitch than sound B. For instance, the chirp of a bird would have a high pitch, but the roar of a lion would have a low pitch.
The human ear can detect a wide range of frequencies. Frequencies from 20 to 20 000 Hz are audible to the human ear. Any sound with a frequency below 20 Hz is known as an infrasound and any sound with a frequency above 20 000 Hz is known as an ultrasound .
[link] lists the hearing ranges of some common animals compared to humans.
| lower frequency (Hz) | upper frequency (Hz) | |
| Humans | 20 | 20 000 |
| Dogs | 50 | 45 000 |
| Cats | 45 | 85 000 |
| Bats | 20 | 120 000 |
| Dolphins | 0,25 | 200 000 |
| Elephants | 5 | 10 000 |
Using the information given in [link] , calculate the lower and upper wavelengths that each species can hear. Assume the speed of sound in air is .
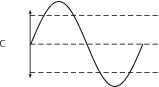
The amplitude of a sound wave determines its loudness or volume. A larger amplitude means a louder sound, and a smaller amplitude means a softer sound. In [link] sound C is louder than sound B. The vibration of a source sets the amplitude of a wave. It transmits energy into the medium through its vibration. More energetic vibration corresponds to larger amplitude. The molecules move back and forth more vigorously.
The loudness of a sound is also determined by the sensitivity of the ear. The human ear is more sensitive to some frequencies than to others. The volume we receive thus depends on both the amplitude of a sound wave and whether its frequency lies in a region where the ear is more or less sensitive.
Tone is a measure of the quality of the sound wave. For example, the quality of the sound produced in a particular musical instruments depends on which harmonics are superposed and in which proportions. The harmonics are determined by the standing waves that are produced in the instrument. For general interest see Physics of music , which explains the physics of music in greater detail.
The quality (timbre) of the sound heard depends on the pattern of the incoming vibrations, i.e. the shape of the sound wave. The more irregular the vibrations, the more jagged is the shape of the sound wave and the harsher is the sound heard.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics - grade 10 [caps 2011]' conversation and receive update notifications?