| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Chapter 2. Solid State of Matter.

We were taught in our high school that there are three states of matter:
Solid- it has a fixed volume and fixed shape.
Liquid- it has fixed volume but it takes the shape of the vessel it is kept in.
Gas-it has no fixed volume and no fixed shape. It takes the volume and shape of the vessel it is kept in.
From this we concluded that in Gaseous State inter-molecular distance is not fixed and the arrangement of the molecules is not fixed. Whereas in Liquid State inter-molecular distance is fixed but the arrangement of the molecules is not fixed. In contrast in Solid State inter-molecular distance is fixed and as well as the arrangement of the molecules is fixed. In fact every elemental or compound solid has a well defined crystalline structure. Every Solid has a characteristic Unit Cell and this is periodically repeated at an spatial distance known as Lattice Parameter.
The most commonly found Unit Cell structures are: Cubic Cell, FCC Cell and BCC Cell.
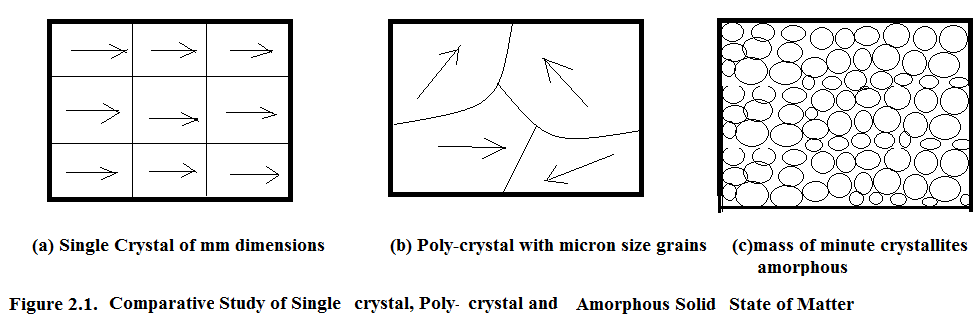
A large mm range spatial periodicity is called Single Crystal.
Micron range spatial periodicity is known as Poly-crystal.
Nanometer range spatial periodicity is known as Amorphous.
In Figure 2.1. single crystal, poly crystal and amorphous solids are shown .
We subsequently learnt that there was a FOURTH STATE of Matter namely PLASMA . Matter above 4000K is in plasma state. The whole Universe was in a state of plasma up to 380,000 years after the Big-Bang.
Now we know a FIFTH STATE of matter called Bose-Einstein Condensate at a fraction of Kelvin.
Section 2.1. Alloy- Solid Solutions.
Only a few elements are widely used commercially in their pure form. Generally, other elements are present to produce greater strength, to improve corrosion resistance, or simply as impurities left over from the refining process. The addition of other elements into a metal is called alloying and the resulting metal is called an alloy. Even if the added elements are nonmetals, alloys may still have metallic properties.
Copper alloys were produced very early in our history. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, was the first alloy known. It was easy to produce by simply adding tin to molten copper. Tools and weapons made of this alloy were stronger than pure copper ones. The typical alloying elements in some common metals are presented in the table below.
Table 2.1. Some Important Alloys and their constituent elements.
| Alloys | Composition |
|---|---|
| Brass | Copper,Zinc |
| Bronze | Copper, Zinc, Tin |
| Pewter | Tin, Copper, Bismuth,Antimony |
| Cast Iron | Iron, Carbon, Manganese, Silicon |
| Steel | Iron, Carbon(plus other elements) |
| Stailess Steel | Iron, Chromium, Nickel |
The properties of alloys can be manipulated by varying composition. For example steel formed from iron and carbon can vary substantially in hardness depending on the amount of carbon added and the way in which it was processed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Electrical and electronic materials science' conversation and receive update notifications?