| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have already studied transverse pulses and waves. In this chapter we look at another type of wave called longitudinal waves. In transverse waves, the motion of the particles in the medium were perpendicular to the direction of the wave. In longitudinal waves, the particles in the medium move parallel (in the same direction as) to the motion of the wave. Examples of transverse waves are water waves or light waves. An example of a longitudinal wave is a sound wave.
When we studied transverse waves we looked at two different motions: the motion of the particles of the medium and the motion of the wave itself. We will do the same for longitudinal waves.
The question is how do we construct such a wave?
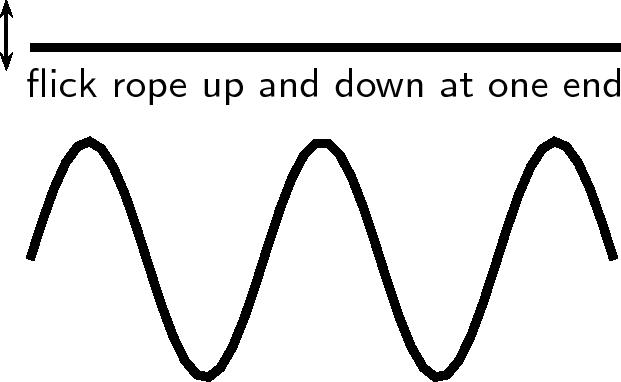
To create a transverse wave, we flick the end of for example a rope up and down. The particles move up and down and return to their equilibrium position. The wave moves from left to right and will be displaced.
A longitudinal wave is seen best in a spring that is hung from a ceiling. Do the following investigation to find out more about longitudinal waves.

From the investigation you will have noticed that the disturbance moves parallel to the direction in which the spring was pulled. The spring was pulled down and the wave moved up and down. The ribbon in the investigation represents one particle in the medium. The particles in the medium move in the same direction as the wave. The ribbon moves from rest upwards, then back to its original position, then down and then back to its original position.
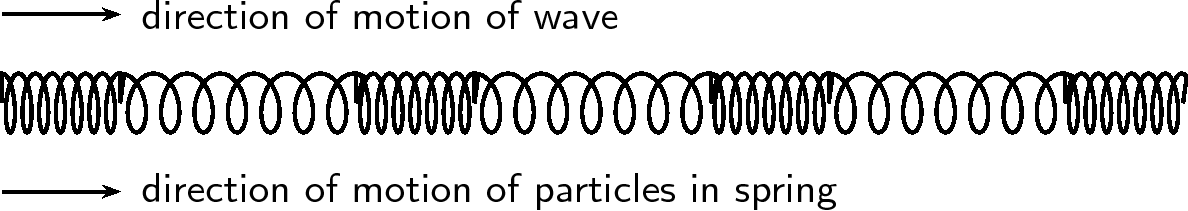
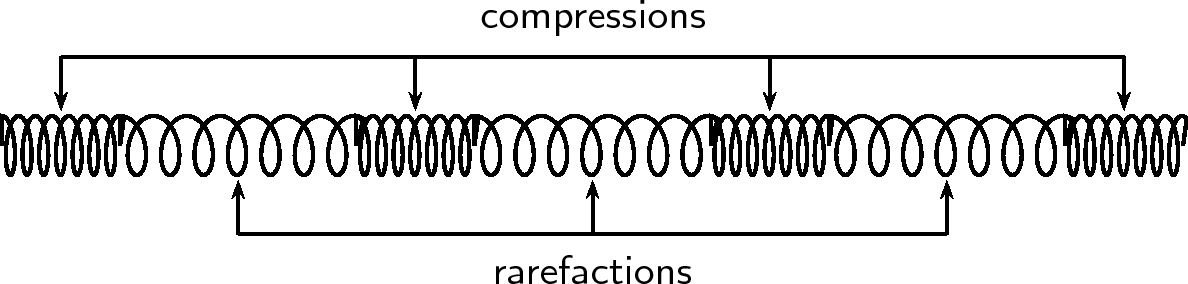
As in the case of transverse waves the following properties can be defined for longitudinal waves: wavelength, amplitude, period, frequency and wave speed. However instead of peaks and troughs, longitudinal waves have compressions and rarefactions .
As seen in [link] , there are regions where the medium is compressed and other regions where the medium is spread out in a longitudinal wave.
The region where the medium is compressed is known as a compression and the region where the medium is spread out is known as a rarefaction .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics - grade 10 [caps 2011]' conversation and receive update notifications?