| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Lake Huron contains about 79 species of fish, all of which are found in many other lakes in North America. What accounts for the difference in diversity between Lake Victoria and Lake Huron? Lake Victoria is a tropical lake, while Lake Huron is a temperate lake. Lake Huron in its present form is only about 7,000 years old, while Lake Victoria in its present form is about 15,000 years old. These two factors, latitude and age, are two of several hypotheses biogeographers have suggested to explain biodiversity patterns on Earth.
One of the oldest observed patterns in ecology is that biodiversity in almost every taxonomic group of organism increases as latitude declines. In other words, biodiversity increases closer to the equator ( [link] ).
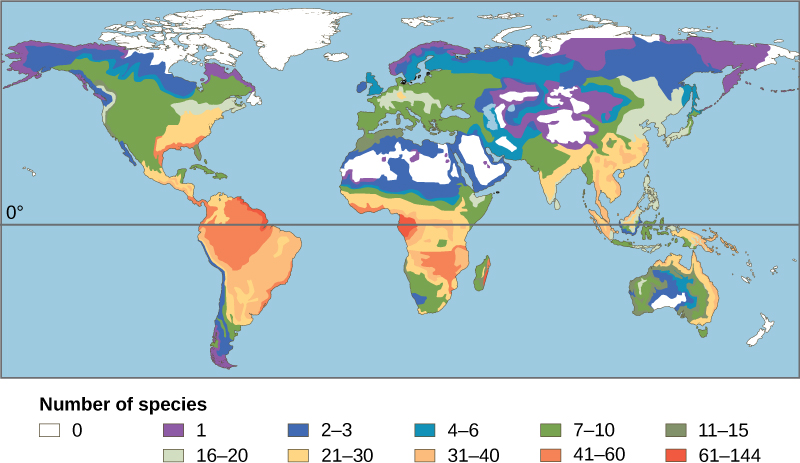
It is not yet clear why biodiversity increases closer to the equator, but hypotheses include the greater age of the ecosystems in the tropics versus temperate regions, which were largely devoid of life or drastically impoverished during the last ice age. The greater age provides more time for speciation. Another possible explanation is the greater energy the tropics receive from the sun versus the lesser energy input in temperate and polar regions. But scientists have not been able to explain how greater energy input could translate into more species. The complexity of tropical ecosystems may promote speciation by increasing the habitat heterogeneity , or number of ecological niches, in the tropics relative to higher latitudes. The greater heterogeneity provides more opportunities for coevolution, specialization, and perhaps greater selection pressures leading to population differentiation. However, this hypothesis suffers from some circularity—ecosystems with more species encourage speciation, but how did they get more species to begin with? The tropics have been perceived as being more stable than temperate regions, which have a pronounced climate and day-length seasonality. The tropics have their own forms of seasonality, such as rainfall, but they are generally assumed to be more stable environments and this stability might promote speciation.
Regardless of the mechanisms, it is certainly true that biodiversity is greatest in the tropics. The number of endemic species is higher in the tropics. The tropics also contain more biodiversity hotspots. At the same time, our knowledge of the species living in the tropics is lowest and because of recent, heavy human activity the potential for biodiversity loss is greatest.
Loss of biodiversity eventually threatens other species we do not impact directly because of their interconnectedness; as species disappear from an ecosystem other species are threatened by the changes in available resources. Biodiversity is important to the survival and welfare of human populations because it has impacts on our health and our ability to feed ourselves through agriculture and harvesting populations of wild animals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Environmental biology' conversation and receive update notifications?