| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
How can light be used to make food? When a person turns on a lamp, electrical energy becomes light energy. Like all other forms of kinetic energy, light can travel, change form, and be harnessed to do work. In the case of photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy, which photoautotrophs use to build carbohydrate molecules ( [link] ). However, autotrophs only use a few specific components of sunlight.

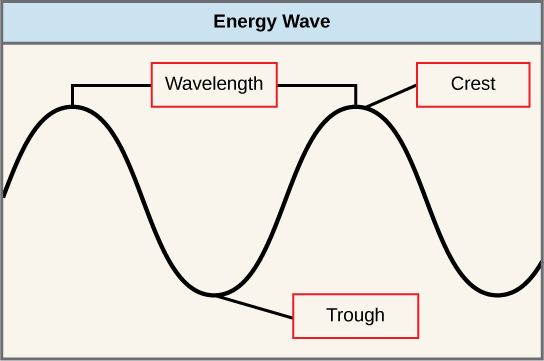
The sun emits an enormous amount of electromagnetic radiation (solar energy). Humans can see only a fraction of this energy, which portion is therefore referred to as “visible light.” The manner in which solar energy travels is described as waves. Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its wavelength , the distance between consecutive points of a wave. A single wave is measured from two consecutive points, such as from crest to crest or from trough to trough ( [link] ).
Visible light constitutes only one of many types of electromagnetic radiation emitted from the sun and other stars. Scientists differentiate the various types of radiant energy from the sun within the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of radiation ( [link] ). The difference between wavelengths relates to the amount of energy carried by them.
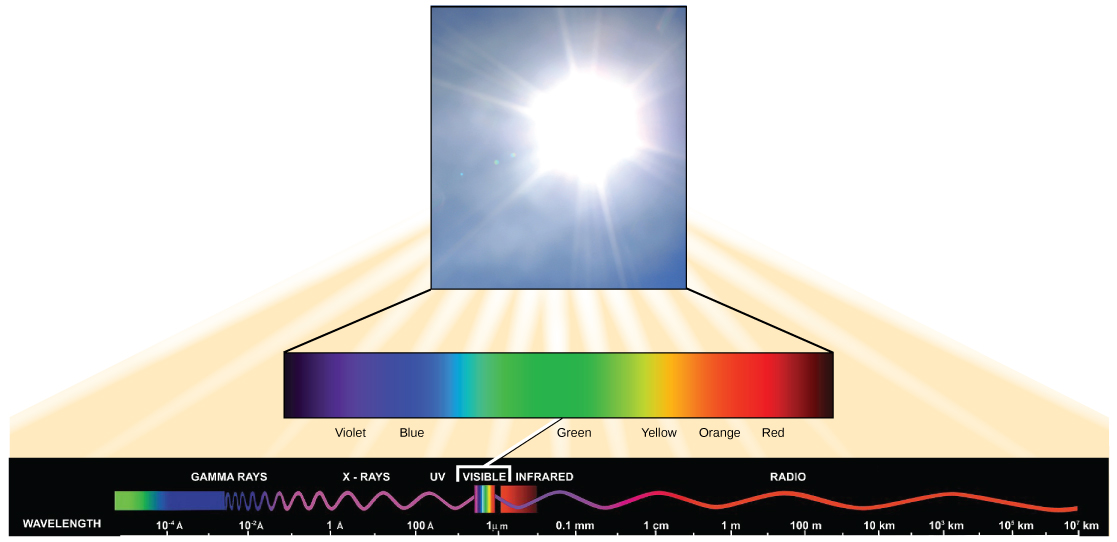
Each type of electromagnetic radiation travels at a particular wavelength. The longer the wavelength (or the more stretched out it appears in the diagram), the less energy is carried. Short, tight waves carry the most energy. This may seem illogical, but think of it in terms of a piece of moving a heavy rope. It takes little effort by a person to move a rope in long, wide waves. To make a rope move in short, tight waves, a person would need to apply significantly more energy.
The electromagnetic spectrum ( [link] ) shows several types of electromagnetic radiation originating from the sun, including X-rays and ultraviolet (UV) rays. The higher-energy waves can penetrate tissues and damage cells and DNA, explaining why both X-rays and UV rays can be harmful to living organisms.
Light energy initiates the process of photosynthesis when pigments absorb the light. Organic pigments, whether in the human retina or the chloroplast thylakoid, have a narrow range of energy levels that they can absorb. Energy levels lower than those represented by red light are insufficient to raise an orbital electron to a populatable, excited (quantum) state. Energy levels higher than those in blue light will physically tear the molecules apart, called bleaching. So retinal pigments can only “see” (absorb) 700 nm to 400 nm light, which is therefore called visible light. For the same reasons, plants pigment molecules absorb only light in the wavelength range of 700 nm to 400 nm; plant physiologists refer to this range for plants as photosynthetically active radiation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bio 351 university of texas' conversation and receive update notifications?