| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Antibodies were the first part of the adaptive immune response to be discovered by scientists working on the immune system. It was already known that individuals who survived a bacterial infection were immune to re-infection with the same pathogen. Early microbiologists took blood from a patient who was already exposed to a certain pathogen and tested it. They learned that there was a substance in the blood, called an antibody which prevented the individual from getting sick from that pathogen. As studies continued, it was discovered that antibodies prevented the person from getting sick with the same illness a second time.
What is an antibody? An antibody protein is essentially a secreted from a plasma cell. which develops from B cell. There are five different classes of antibodies found in humans: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, and IgE. Each of these has specific functions in the immune response. As researchers learn about them, they are able to learn about the great variety of antibody functions critical to many adaptive immune responses.
B cells differentiate in the bone marrow. During the process of maturation, up to 100 trillion different clones of B cells are generated, which is similar to the diversity of antigen receptors seen in T cells.
B cells are activated by binding to antigen. They differentiate into plasma cells. Plasma cells often leave the lymphoid organs migrate back to the bone marrow, where the whole differentiation process started. After secreting antibodies for a specific period, the B cells die, as most of their energy is devoted to making antibodies and not to maintaining themselves.
The final B cell is the memory B cell , which results from exposure to a specific pathogen. Memory B cells function in a way similar to memory T cells. They lead to a stronger and faster secondary response when compared to the primary response. They "remember" the antibody for that pathogen which leads to quick production of antibodies. Often you do not experience any symptoms as the secondary response is so quick and effective.
Antibodies are proteins consisting of two chains with attached carbohydrates. The heavy chain and the light chain are the two proteins that form the antibody. The main differences between the classes of antibodies are in the differences between their heavy chains. There are 2 regions of the heavy chains known as the constant and variable regions .
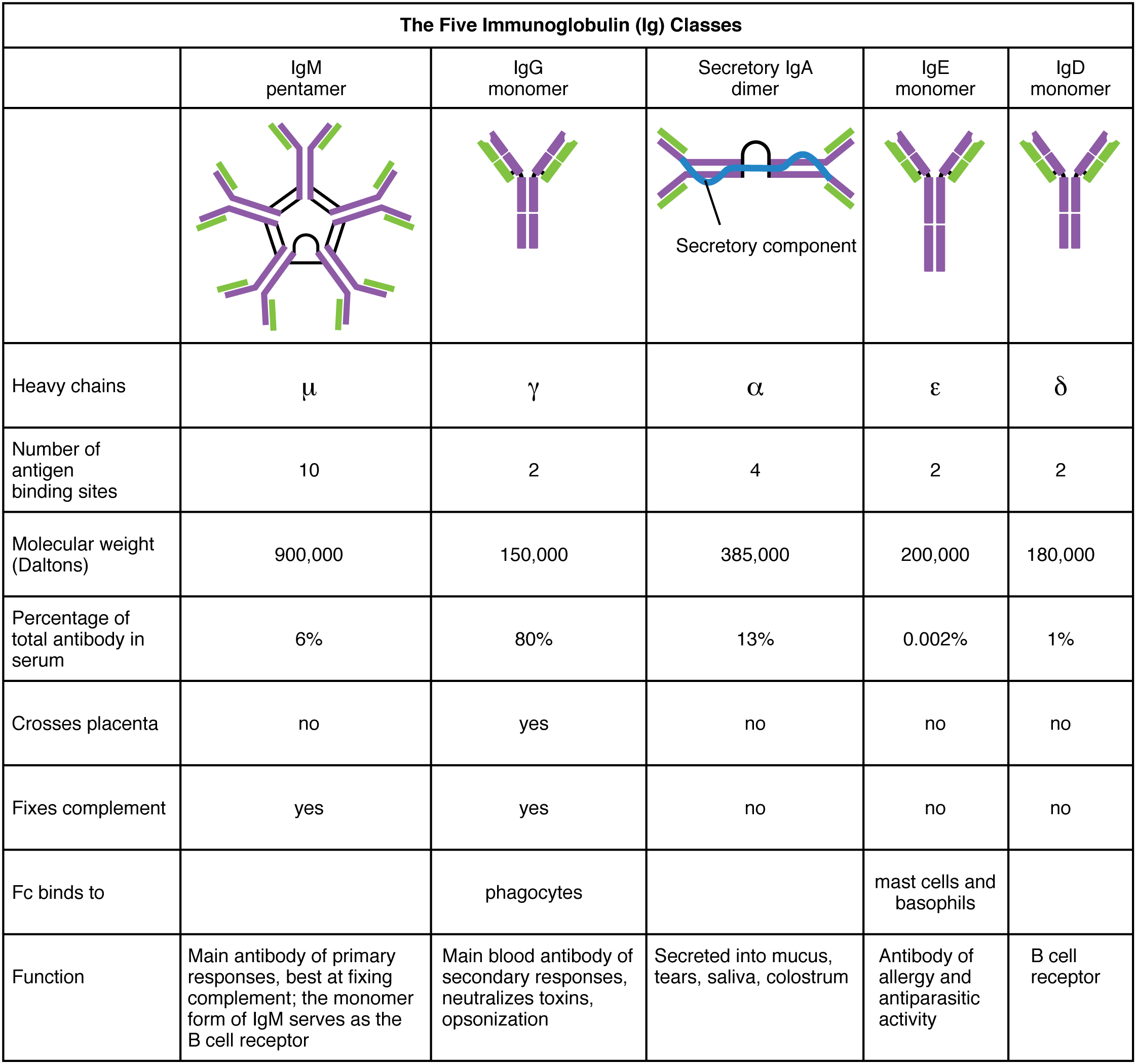
IgM is the largest of the antibody molecules. IgM is usually the first antibody made during a primary response. Its large shape allows it to bind well to many bacterial surfaces.Thus, it is a very effective antibody against bacteria at early stages of a primary antibody response.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mrs. browne's immune modules' conversation and receive update notifications?