| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The magnitude of this complex-valued function gives the ratio of the output to the inputof the filter for a sampled sinusoid at a frequency of in radians per seconds. The angle of is the phase shift between the output and input.
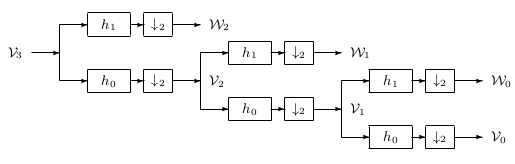
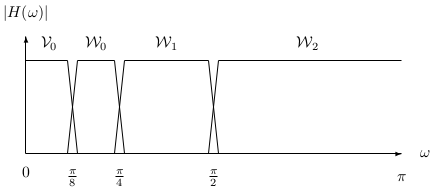
The first stage of two banks divides the spectrum of into a lowpass and highpass band, resulting in the scaling coefficients and wavelet coefficients at lower scale and . The second stage then divides that lowpass band into another lower lowpassband and a bandpass band. The first stage divides the spectrum into two equal parts. The second stage divides the lower half into quarters and soon. This results in a logarithmic set of bandwidths as illustrated in [link] . These are called “constant-Q" filters in filter bank language because the ratio of the band width to the center frequency ofthe band is constant. It is also interesting to note that a musical scale defines octaves in a similar way and that the ear responds to frequenciesin a similar logarithmic fashion.
For any practical signal that is bandlimited, there will be an upper scale , above which the wavelet coefficients, , are negligibly small [link] . By starting with a high resolution description of a signal in terms of the scaling coefficients , the analysis tree calculates the DWT
down to as low a resolution, , as desired by having stages. So, for , using [link] we have
which is a finite scale version of [link] . We will discuss the choice of and further in Chapter: Calculation of the Discrete Wavelet Transform .
As one would expect, a reconstruction of the original fine scale coefficients of the signal can be made from a combination of the scalingfunction and wavelet coefficients at a coarse resolution. This is derived by considering a signal in the scaling function space . This function can be written in terms of the scaling function as
or in terms of the next scale (which also requires wavelets) as
Substituting [link] and [link] into [link] gives
Because all of these functions are orthonormal, multiplying [link] and [link] by and integrating evaluates the coefficient as
For synthesis in the filter bank we have a sequence of first up-sampling or stretching, then filtering. This means that theinput to the filter has zeros inserted between each of the original terms. In other words,
where the input signal is stretched to twice its original length and zeros are inserted. Clearly this up-sampling or stretching couldbe done with factors other than two, and the two equation above could have the and 0 reversed. It is also clear that up-sampling does not lose any information. If you firstup-sample then down-sample, you are back where you started. However, if you first down-sample then up-sample, you are notgenerally back where you started.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wavelets and wavelet transforms' conversation and receive update notifications?