| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
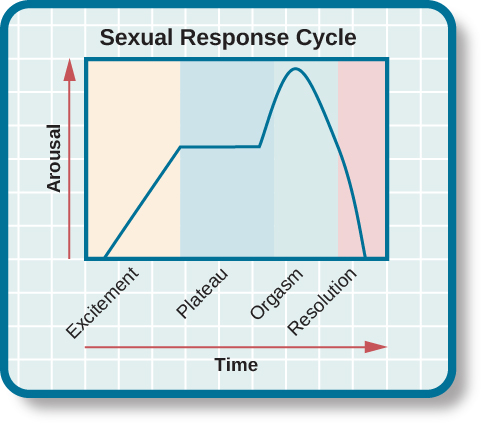
Based on these observations, Masters and Johnson divided the sexual response cycle into four phases that are fairly similar in men and women: excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution ( [link] ). The excitement phase is the arousal phase of the sexual response cycle, and it is marked by erection of the penis or clitoris and lubrication and expansion of the vaginal canal. During plateau , women experience further swelling of the vagina and increased blood flow to the labia minora, and men experience full erection and often exhibit pre-ejaculatory fluid. Both men and women experience increases in muscle tone during this time. Orgasm is marked in women by rhythmic contractions of the pelvis and uterus along with increased muscle tension. In men, pelvic contractions are accompanied by a buildup of seminal fluid near the urethra that is ultimately forced out by contractions of genital muscles, (i.e., ejaculation). Resolution is the relatively rapid return to an unaroused state accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and muscular relaxation. While many women can quickly repeat the sexual response cycle, men must pass through a longer refractory period as part of resolution. The refractory period is a period of time that follows an orgasm during which an individual is incapable of experiencing another orgasm. In men, the duration of the refractory period can vary dramatically from individual to individual with some refractory periods as short as several minutes and others as long as a day. As men age, their refractory periods tend to span longer periods of time.
In addition to the insights that their research provided with regards to the sexual response cycle and the multi-orgasmic potential of women, Masters and Johnson also collected important information about reproductive anatomy. Their research demonstrated the oft-cited statistic of the average size of a flaccid and an erect penis (3 and 6 inches, respectively) as well as dispelling long-held beliefs about relationships between the size of a man’s erect penis and his ability to provide sexual pleasure to his female partner. Furthermore, they determined that the vagina is a very elastic structure that can conform to penises of various sizes (Hock, 2008).
As mentioned earlier, a person’s sexual orientation is their emotional and erotic attraction toward another individual. While the majority of people identify as heterosexual, there is a sizable population of people within the United States who identify as either homosexual or bisexual. Research suggests that somewhere between 3% and 10% of the population identifies as homosexual (Kinsey, Pomeroy,&Martin, 1948; LeVay, 1996; Pillard&Bailey, 1995).
Issues of sexual orientation have long fascinated scientists interested in determining what causes one individual to be heterosexual while another is homosexual. For many years, people believed that these differences arose because of different socialization and familial experiences. However, research has consistently demonstrated that the family backgrounds and experiences are very similar among heterosexuals and homosexuals (Bell, Weinberg,&Hammersmith, 1981; Ross&Arrindell, 1988).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chapter 10: emotion and motivation sw' conversation and receive update notifications?