| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
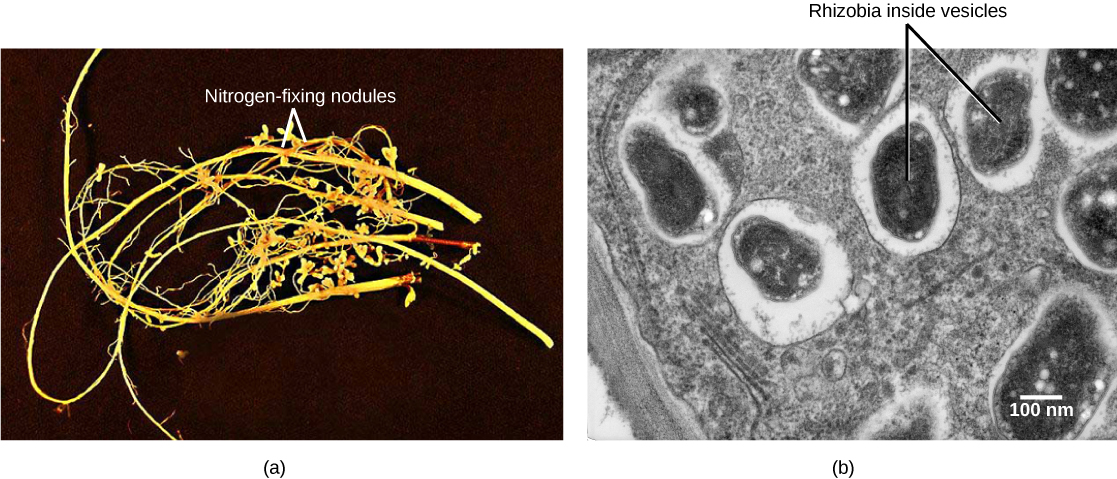
Soil bacteria, collectively called rhizobia , symbiotically interact with legume roots to form specialized structures called nodules , in which nitrogen fixation takes place. This process entails the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, by means of the enzyme nitrogenase . Therefore, using rhizobia is a natural and environmentally friendly way to fertilize plants, as opposed to chemical fertilization that uses a nonrenewable resource, such as natural gas. Through symbiotic nitrogen fixation, the plant benefits from using an endless source of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The process simultaneously contributes to soil fertility because the plant root system leaves behind some of the biologically available nitrogen. As in any symbiosis, both organisms benefit from the interaction: the plant obtains ammonia, and bacteria obtain carbon compounds generated through photosynthesis, as well as a protected niche in which to grow ( [link] ).
A nutrient depletion zone can develop when there is rapid soil solution uptake, low nutrient concentration, low diffusion rate, or low soil moisture. These conditions are very common; therefore, most plants rely on fungi to facilitate the uptake of minerals from the soil. Fungi form symbiotic associations called mycorrhizae with plant roots, in which the fungi actually are integrated into the physical structure of the root. The fungi colonize the living root tissue during active plant growth.
Through mycorrhization, the plant obtains mainly phosphate and other minerals, such as zinc and copper, from the soil. The fungus obtains nutrients, such as sugars, from the plant root ( [link] ). Mycorrhizae help increase the surface area of the plant root system because hyphae, which are narrow, can spread beyond the nutrient depletion zone. Hyphae can grow into small soil pores that allow access to phosphorus that would otherwise be unavailable to the plant. The beneficial effect on the plant is best observed in poor soils. The benefit to fungi is that they can obtain up to 20 percent of the total carbon accessed by plants. Mycorrhizae functions as a physical barrier to pathogens. It also provides an induction of generalized host defense mechanisms, and sometimes involves production of antibiotic compounds by the fungi.
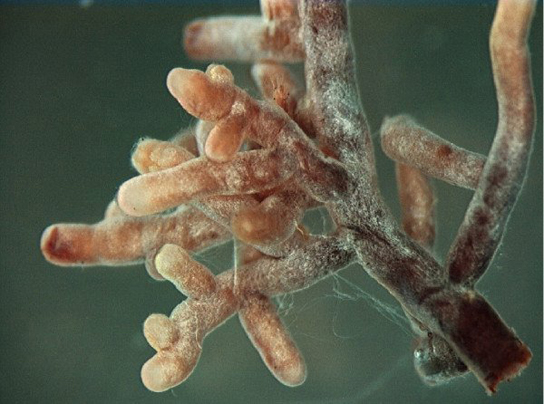
There are two types of mycorrhizae: ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae. Ectomycorrhizae form an extensive dense sheath around the roots, called a mantle. Hyphae from the fungi extend from the mantle into the soil, which increases the surface area for water and mineral absorption. This type of mycorrhizae is found in forest trees, especially conifers, birches, and oaks. Endomycorrhizae, also called arbuscular mycorrhizae, do not form a dense sheath over the root. Instead, the fungal mycelium is embedded within the root tissue. Endomycorrhizae are found in the roots of more than 80 percent of terrestrial plants.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bio 351 university of texas' conversation and receive update notifications?