| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A higher price for a good will cause the budget constraint to shift to the left, so that it is tangent to a lower indifference curve representing a reduced level of utility. Conversely, a lower price for a good will cause the opportunity set to shift to the right, so that it is tangent to a higher indifference curve representing an increased level of utility. Exactly how much a change in price will lead to the quantity demanded of each good will depend on personal preferences.
Anyone who faces a change in price will experience two interlinked motivations: a substitution effect and an income effect. The substitution effect is that when a good becomes more expensive, people seek out substitutes. If oranges become more expensive, fruit-lovers scale back on oranges and eat more apples, grapefruit, or raisins. Conversely, when a good becomes cheaper, people substitute toward consuming more. If oranges get cheaper, people fire up their juicing machines and ease off on other fruits and foods. The income effect refers to how a change in the price of a good alters the effective buying power of one’s income. If the price of a good that you have been buying falls, then in effect your buying power has risen—you are able to purchase more goods. Conversely, if the price of a good that you have been buying rises, then the buying power of a given amount of income is diminished. (One common source of confusion is that the “income effect” does not refer to a change in actual income. Instead, it refers to the situation in which the price of a good changes, and thus the quantities of goods that can be purchased with a fixed amount of income change. It might be more accurate to call the “income effect” a “buying power effect,” but the “income effect” terminology has been used for decades, and it is not going to change during this economics course.) Whenever a price changes, consumers feel the pull of both substitution and income effects at the same time.
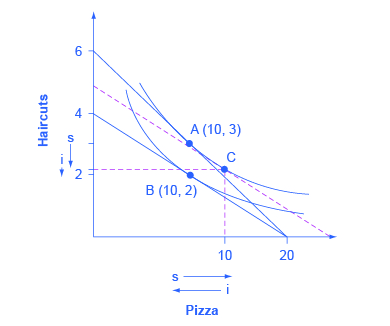
Using indifference curves, you can illustrate the substitution and income effects on a graph. In [link] , Ogden faces a choice between two goods: haircuts or personal pizzas. Haircuts cost $20, personal pizzas cost $6, and he has $120 to spend.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of microeconomics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?