| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase and the mitotic phase ( [link] ). During interphase , the cell grows and DNA is replicated. During the mitotic phase , the replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents are separated, and the cell divides.
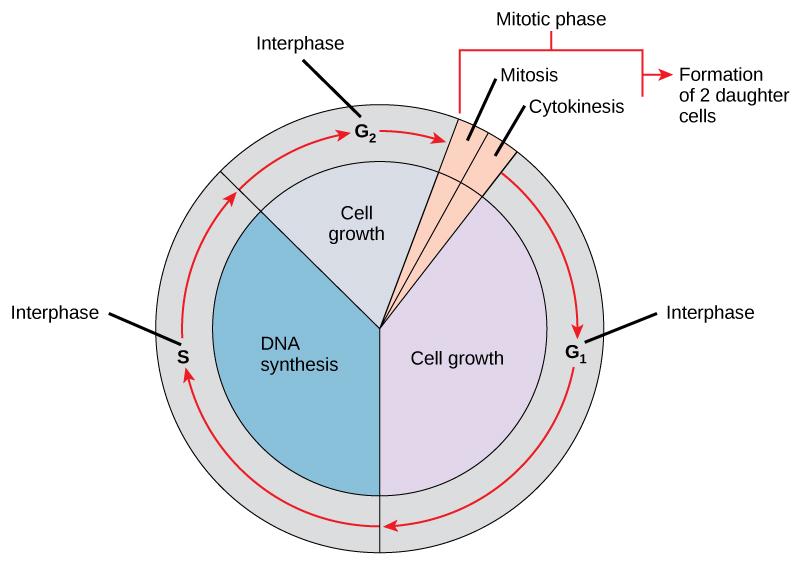
During interphase, the cell undergoes normal growth processes while also preparing for cell division. In order for a cell to move from interphase into the mitotic phase, many internal and external conditions must be met. The three stages of interphase are called G 1 , S, and G 2 .
The first stage of interphase is called the G 1 phase (first gap) because, from a microscopic aspect, little change is visible. However, during the G 1 stage, the cell is quite active at the biochemical level. The cell is accumulating the building blocks of chromosomal DNA and the associated proteins as well as accumulating sufficient energy reserves to complete the task of replicating each chromosome in the nucleus.
Throughout interphase, nuclear DNA remains in a semi-condensed chromatin configuration. In the S phase , DNA replication can proceed through the mechanisms that result in the formation of identical pairs of DNA molecules—sister chromatids—that are firmly attached to the centromeric region. The centrosome is duplicated during the S phase. The two centrosomes will give rise to the mitotic spindle , the apparatus that orchestrates the movement of chromosomes during mitosis. At the center of each animal cell, the centrosomes of animal cells are associated with a pair of rod-like objects, the centrioles , which are at right angles to each other. Centrioles help organize cell division. Centrioles are not present in the centrosomes of other eukaryotic species, such as plants and most fungi.
In the G 2 phase , the cell replenishes its energy stores and synthesizes proteins necessary for chromosome manipulation. Some cell organelles are duplicated, and the cytoskeleton is dismantled to provide resources for the mitotic phase. There may be additional cell growth during G 2 . The final preparations for the mitotic phase must be completed before the cell is able to enter the first stage of mitosis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cellular reproduction' conversation and receive update notifications?