| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n , where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate”: the components are carbon (“carbo”) and the components of water (hence, “hydrate”). Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
One issue with carbohydrate chemistry is the nomenclature. Here are a few quick and simple rules:
These will be explained in detail below. For a short video on carbohydrate classification see the Khan academy video (10 minutes in length) by clicking here .
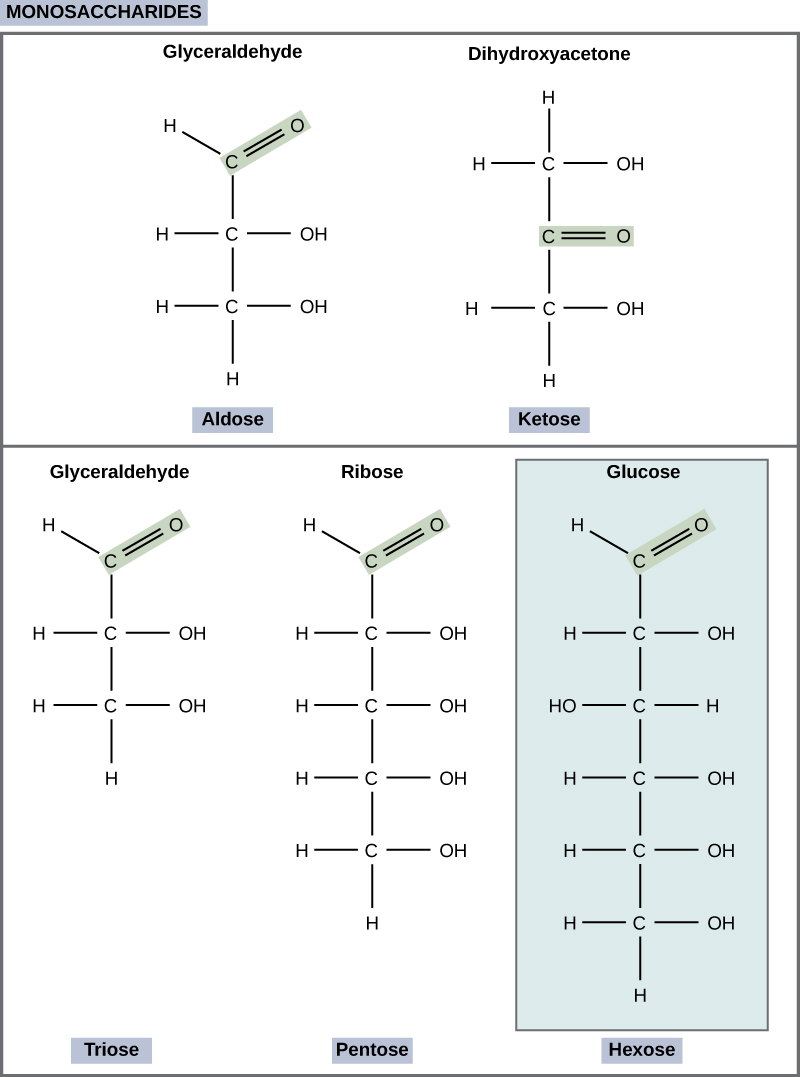
Monosaccharides (mono- = “one”; sacchar- = “sweet”) are simple sugars, the most common of which is glucose. In monosaccharides, the number of carbons usually ranges from three to seven. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix -ose. If the sugar has an aldehyde group (the functional group with the structure R-CHO), it is known as an aldose, and if it has a ketone group (the functional group with the structure RC(=O)R'), it is known as a ketose. Depending on the number of carbons in the sugar, they also may be known as trioses (three carbons), pentoses (five carbons), and or hexoses (six carbons). See [link] for an illustration of the monosaccharides.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cellular macromolecules: bis2a modules 3.0 to 3.5' conversation and receive update notifications?