| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Chosen Methods of Investigation
The limited timeframe of our project meant both DTW and HMM-based approaches were impractical, requiring many hundreds more man-hours than was available. We chose to focus on achieving solid results from a more primitive algorithm, the LPC, and work on making it more robust thereafter.
We collected the several hundreds of data samples used to train the library from ourselves.
We featured-matched input and stored data using the Yule-Walker autocorrelation method, minimizing the forward prediction error in the least squares sense. This was done using Matlab’s Yule-Walker AR Estimator.
Testing the algorithm resulted in an abysmal 20-30% accuracy.
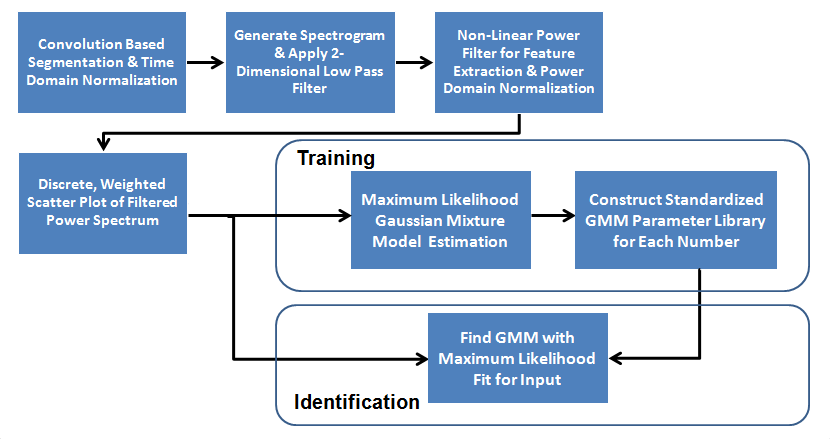
We thought to produce better base accuracy with an algorithm of our own making. Our final results are based upon the following algorithm outlined:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elec 301 project: voice recognition' conversation and receive update notifications?