| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
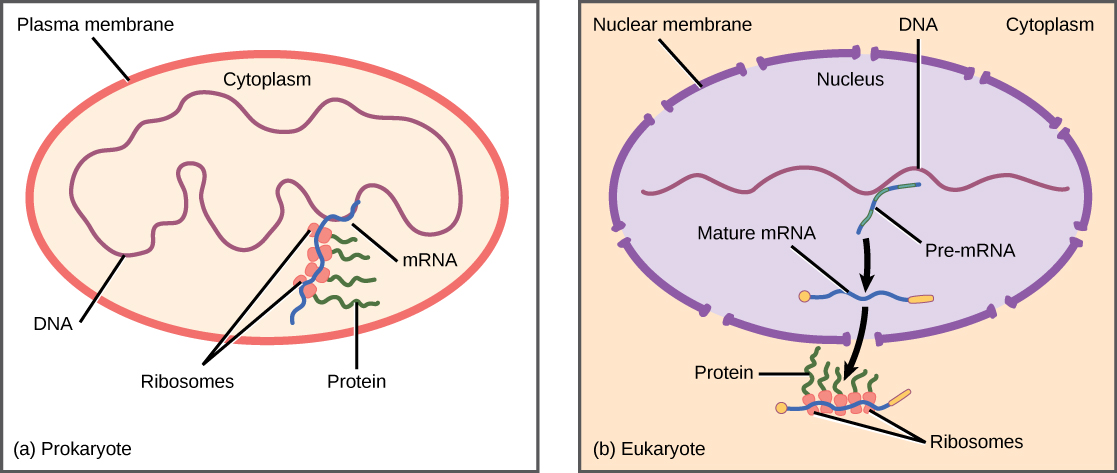
The differences in the regulation of gene expression between prokaryotes and eukaryotes are summarized in [link] . The regulation of gene expression is discussed in detail in subsequent modules.
| Differences in the Regulation of Gene Expression of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Organisms | |
|---|---|
| Prokaryotic organisms | Eukaryotic organisms |
| Lack nucleus | Contain nucleus |
| DNA is found in the cytoplasm | DNA is confined to the nuclear compartment |
| RNA transcription and protein formation occur almost simultaneously | RNA transcription occurs prior to protein formation, and it takes place in the nucleus. Translation of RNA to protein occurs in the cytoplasm. |
| Gene expression is regulated primarily at the transcriptional level | Gene expression is regulated at many levels (epigenetic, transcriptional, nuclear shuttling, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational) |
Some cellular processes arose from the need of the organism to defend itself. Cellular processes such as gene silencing developed to protect the cell from viral or parasitic infections. If the cell could quickly shut off gene expression for a short period of time, it would be able to survive an infection when other organisms could not. Therefore, the organism evolved a new process that helped it survive, and it was able to pass this new development to offspring.
While all somatic cells within an organism contain the same DNA, not all cells within that organism express the same proteins. Prokaryotic organisms express the entire DNA they encode in every cell, but not necessarily all at the same time. Proteins are expressed only when they are needed. Eukaryotic organisms express a subset of the DNA that is encoded in any given cell. In each cell type, the type and amount of protein is regulated by controlling gene expression. To express a protein, the DNA is first transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins. In prokaryotic cells, these processes occur almost simultaneously. In eukaryotic cells, transcription occurs in the nucleus and is separate from the translation that occurs in the cytoplasm. Gene expression in prokaryotes is mostly regulated at the transcriptional level (some epigenetic and post-translational regulation is also present), whereas in eukaryotic cells, gene expression is regulated at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Genetics and evolution' conversation and receive update notifications?