| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A general schematic diagram of the stages involving the nanoparticles formation is shown in [link] . As seen, first step is the M-atom generation by dissociation of the metal-precursor. Next step is the M-complex formulation, which is carried out before the actual particle assembly stage. Between this step and the final particle formulation, oxidation of the activated complex occurs upon interaction with an oxidant substance. The x-axis is a function of temperature or time or both depending on the synthesis procedure.
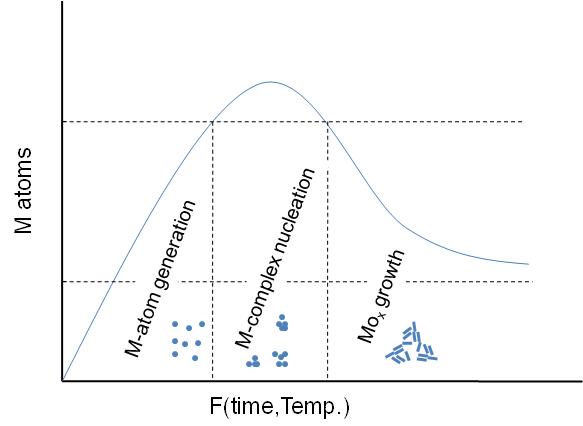
In all cases, the particles synthesized consist of MO x nanoparticle structures stabilized by one or more types of ligand(s) as seen in [link] . The ligands are usually long-chained organic molecules that have one more functional groups. These molecules protect the nanoparticles from attracting each other under van der Waals forces and therefore prevent them from aggregating.
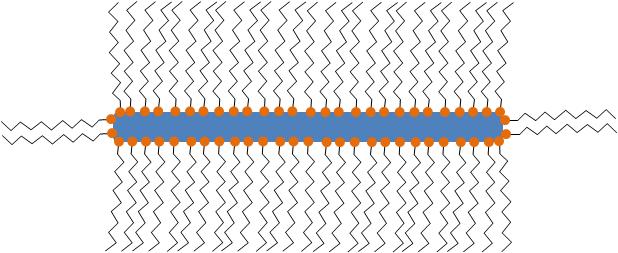
Even though often not referred to specifically, all particles synthesized are stabilized by organic (hydrophilic, hydrophobic or amphoteric) ligands. The detection and the understanding of the structure of these ligands can be of critical importance for understanding the controlling the properties of the synthesized nanoparticles.
In this work, we refer to MO x nanoparticles synthesized via slow decomposition of a metal complex. In [link] , a number of different MO x nanoparticles are presented, synthesized via metal complex dissociation. Metal–MO x and mixed MO x nanoparticles are not discussed here.
| Metal oxide | Shape | Size (approx.) |
| Cerium oxide | dots | 5-20 nm |
| Iron oxide | dots, cubes | 8.5-23.4 nm |
| Manganese oxide | Multipods | >50 nm |
| Zinc oxide | Hexagonal pyramid | 15-25 nm |
| Cobalt oxide | dots | ~ 10 nm |
| Chromium oxide | dots | 12 nm |
| Vanadium oxide | dots | 9-15 nm |
| Molybdenum oxide | dots | 5 nm |
| Rhodium oxide | dots,rods | 16 nm |
| Palladium oxide | dots | 18 nm |
| Ruthenium oxide | dots | 9-14 nm |
| Zirconium oxide | rods | 7x30 nm |
| Barium oxide | dots | 20 nm |
| Magnesium oxide | dots | 4-8 nm |
| Calcium oxide | dots, rods | 7-12 nm |
| Nickel oxide | dots | 8-15 nm |
| Titanium oxide | dots and rods | 2.3-30 nm |
| Tin oxide | dots | 2.0-5.0 nm |
| Indium oxide | dots | ~ 5 nm |
| Samaria | Square | ~ 10 nm |
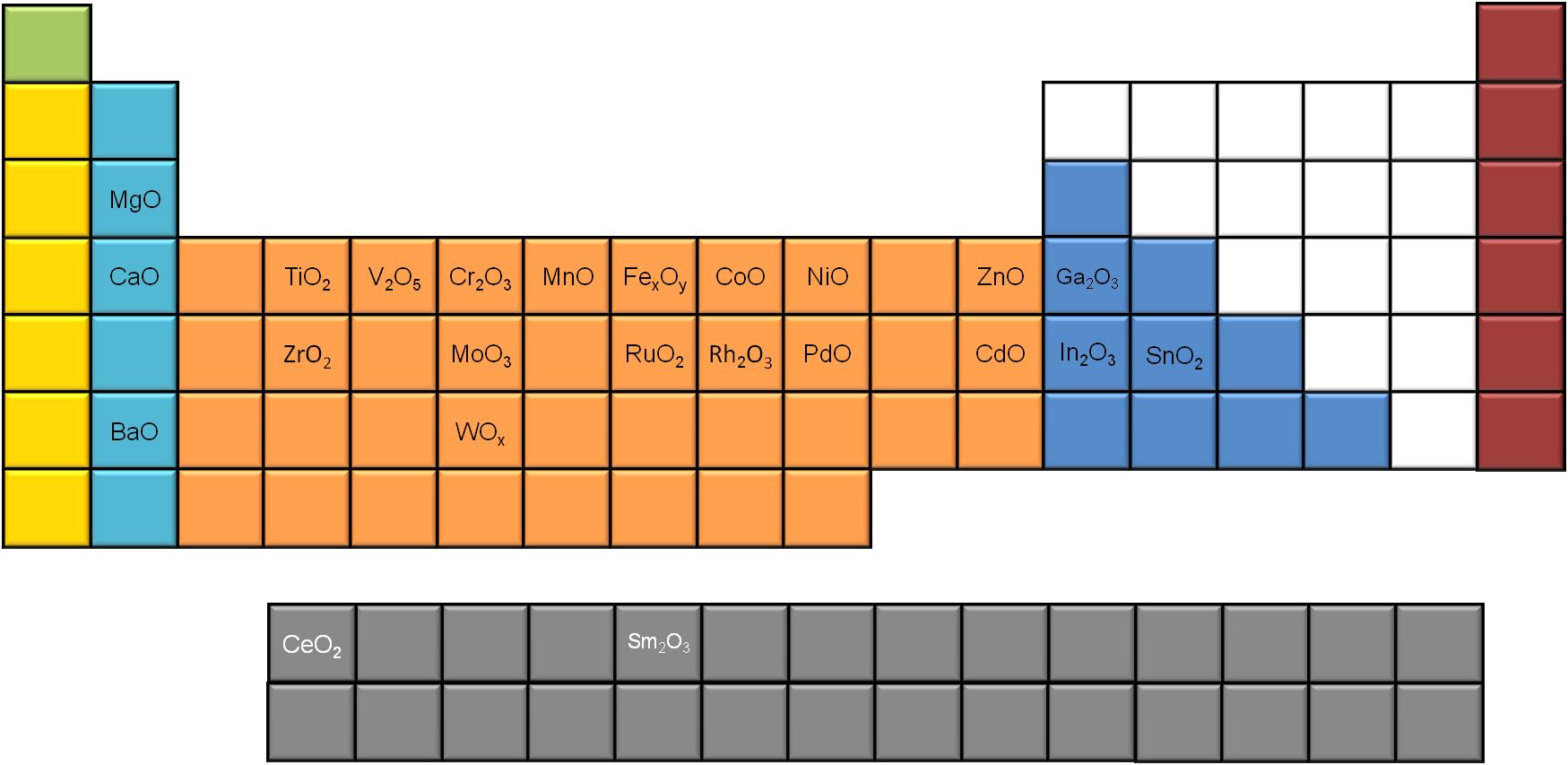
A significant number of metal oxides synthesized using slow decomposition is reported in literature. If we use the periodic table to map the different MO x nanoparticles ( [link] ), we notice that most of the alkali and transition metals generate MO x nanoparticles, while only a few of the poor metals seem to do so, using this synthetic route. Moreover, two of the rare earth metals (Ce and Sm) have been reported to successfully give metal oxide nanoparticles via slow decomposition.
Among the different characterization techniques used for defining these structures, transition electron microscopy (TEM) holds the lion’s share. Nevertheless, most of the modern characterization methods are more important when it comes to understanding the properties of nanoparticles. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), IR spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) methods are systematically used for characterization.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?