| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Diagnosis of celiac disease is accomplished from serological tests for the presence of primarily IgA antibodies to components of gluten, the transglutinaminase enzyme, and autoantibodies to endomysium , a connective tissue surrounding muscle fibers. Serological tests are typically followed up with endoscopy and biopsy of the duodenal mucosa. Serological screening surveys have found about 1% of individuals in the United Kingdom are positive even though they do not all display symptoms. D.A. Van Heel, J. West. “Recent Advances in Coeliac Disease.” Gut 55 no. 7 (2006):1037—1046. This early recognition allows for more careful monitoring and prevention of severe disease.
Celiac disease is treated with complete removal of gluten-containing foods from the diet, which results in improved symptoms and reduced risk of complications. Other theoretical approaches include breeding grains that do not contain the immunologically reactive components or developing dietary supplements that contain enzymes that break down the protein components that cause the immune response. ibid.
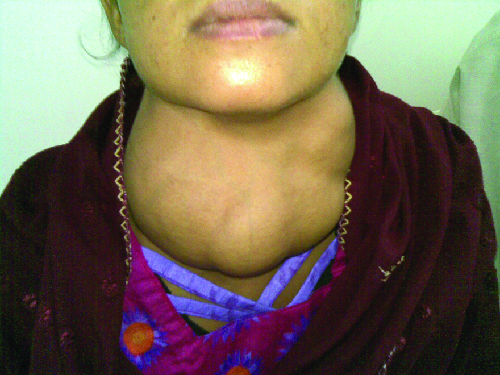
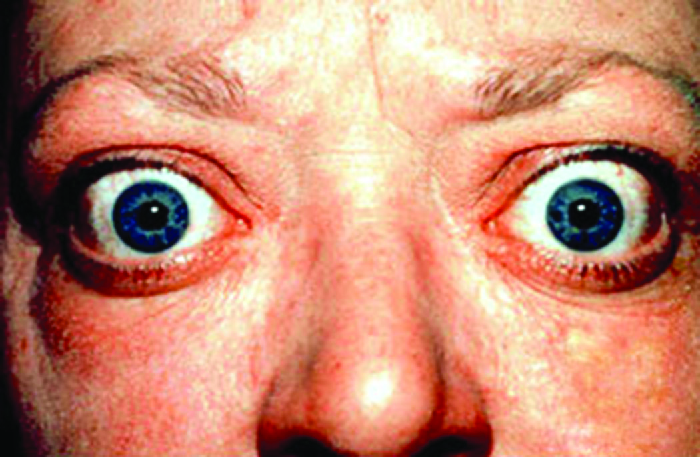
Graves disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Symptoms of Graves disease result from the production of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) also called TSH-receptor antibody . TSI targets and binds to the receptor for thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) , which is naturally produced by the pituitary gland . TSI may cause conflicting symptoms because it may stimulate the thyroid to make too much thyroid hormone or block thyroid hormone production entirely, making diagnosis more difficult. Signs and symptoms of Graves disease include heat intolerance, rapid and irregular heartbeat, weight loss, goiter (a swollen thyroid gland, protruding under the skin of the throat [ [link] ]) and exophthalmia (bulging eyes) often referred to as Graves ophthalmopathy ( [link] ).
The most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States is Hashimoto thyroiditis , also called chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis . Patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis often develop a spectrum of different diseases because they are more likely to develop additional autoimmune diseases such as Addison disease (discussed later in this section), type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and celiac disease. Hashimoto thyroiditis is a T H 1 cell-mediated disease that occurs when the thyroid gland is attacked by cytotoxic lymphocytes, macrophages, and autoantibodies. This autoimmune response leads to numerous symptoms that include goiter ( [link] ), cold intolerance, muscle weakness, painful and stiff joints, depression, and memory loss.
Juvenile diabetes , or type 1 diabetes mellitus , is usually diagnosed in children and young adults. It is a T-cell-dependent autoimmune disease characterized by the selective destruction of the β cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas by CD4 T H 1-mediated CD8 T cells, anti-β-cell antibodies, and macrophage activity. There is also evidence that viral infections can have either a potentiating or inhibitory role in the development of type 1 diabetes (T1D) mellitus. The destruction of the β cells causes a lack of insulin production by the pancreas. In T1D, β-cell destruction may take place over several years, but symptoms of hyperglycemia , extreme increase in thirst and urination, weight loss, and extreme fatigue usually have a sudden onset, and diagnosis usually does not occur until most β cells have already been destroyed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?