| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Trichinellosis, also called trichinosis , caused by Trichinella spiralis , is contracted by consuming undercooked meat, which releases the larvae and allows them to encyst in muscles. Infection can cause fever, muscle pains, and digestive system problems; severe infections can lead to lack of coordination, breathing and heart problems, and even death. Finally, heartworm in dogs and other animals is caused by the nematode Dirofilaria immitis , which is transmitted by mosquitoes. Symptoms include fatigue and cough; when left untreated, death may result.
The physician explains to Sarah’s mother that ringworm can be transferred between people through touch. “It’s common in school children, because they often come in close contact with each other, but anyone can become infected,” he adds. “Because you can transfer it through objects, locker rooms and public pools are also a potential source of infection. It’s very common among wrestlers and athletes in other contact sports.”
Looking very uncomfortable, Sarah says to her mother “I want this worm out of me.”
The doctor laughs and says, “Sarah, you’re in luck because ringworm is just a name; it is not an actual worm. You have nothing wriggling around under your skin.”
“Then what is it?” asks Sarah.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
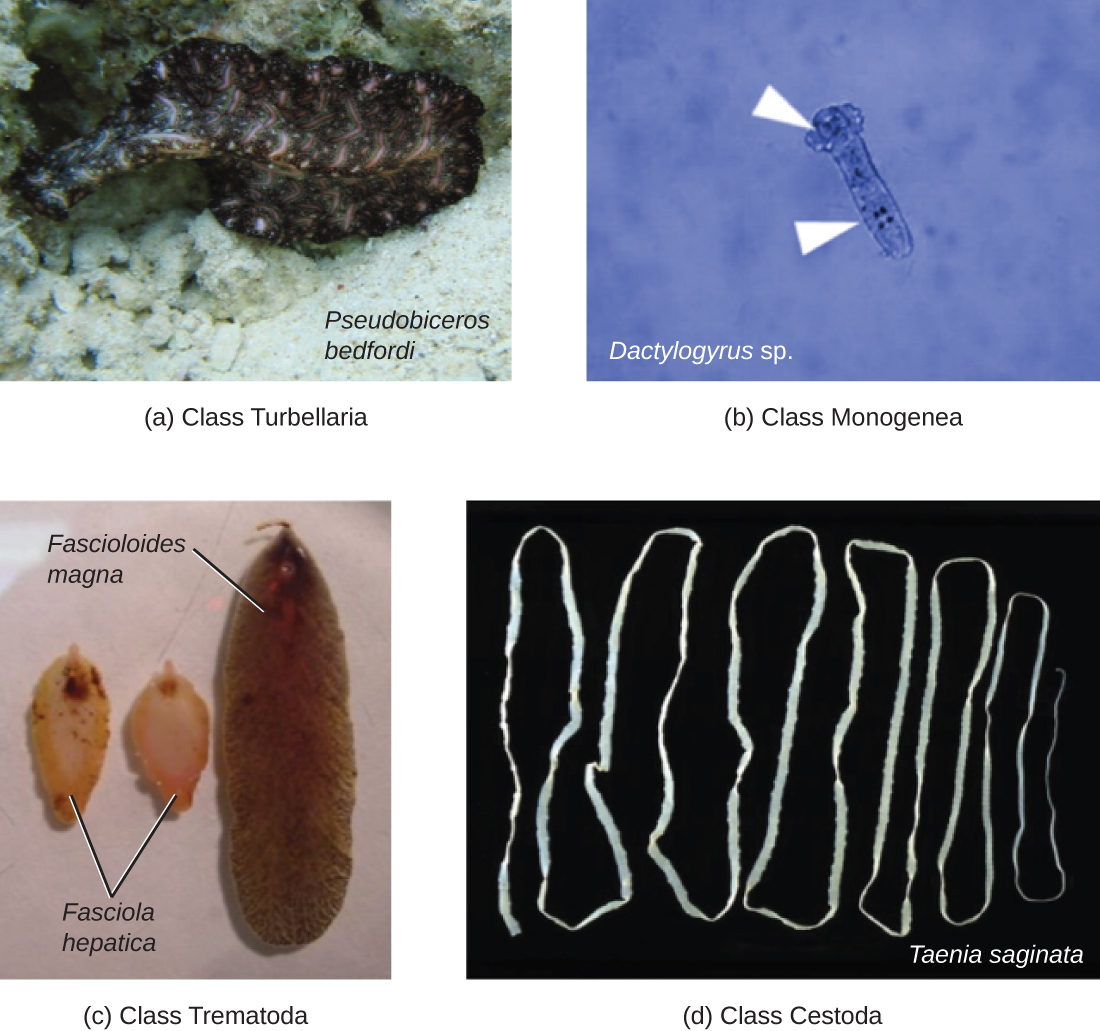
Phylum Platyhelminthes (the platyhelminths) are flatworms . This group includes the flukes, tapeworms, and the turbellarians, which include planarians. The flukes and tapeworms are medically important parasites ( [link] ).
The flukes ( trematodes ) are nonsegmented flatworms that have an oral sucker ( [link] ) (and sometimes a second ventral sucker) and attach to the inner walls of intestines, lungs, large blood vessels, or the liver. Trematodes have complex life cycles, often with multiple hosts. Several important examples are the liver flukes ( Clonorchis and Opisthorchis ), the intestinal fluke ( Fasciolopsis buski ), and the oriental lung fluke ( Paragonimus westermani ). Schistosomiasis is a serious parasitic disease, considered second in the scale of its impact on human populations only to malaria. The parasites Schistosoma mansoni, S. haematobium , and S. japonicum , which are found in freshwater snails, are responsible for schistosomiasis ( [link] ). Immature forms burrow through the skin into the blood. They migrate to the lungs, then to the liver and, later, other organs. Symptoms include anemia, malnutrition, fever, abdominal pain, fluid buildup, and sometimes death.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?