| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Basophils have cytoplasmic granules of varied size and are named for their granules’ ability to absorb the basic dye methylene blue ( [link] ). Their stimulation and degranulation can result from multiple triggering events. Activated complement fragments C3a and C5a, produced in the activation cascades of complement proteins, act as anaphylatoxins by inducing degranulation of basophils and inflammatory responses. This cell type is important in allergic reactions and other responses that involve inflammation. One of the most abundant components of basophil granules is histamine , which is released along with other chemical factors when the basophil is stimulated. These chemicals can be chemotactic and can help to open the gaps between cells in the blood vessels. Other mechanisms for basophil triggering require the assistance of antibodies, as discussed in B Lymphocytes and Humoral Immunity .
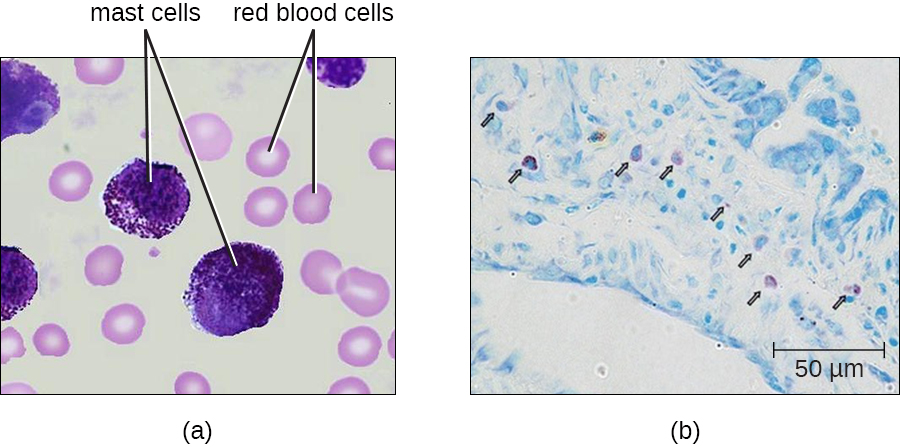
Hematopoiesis also gives rise to mast cells , which appear to be derived from the same common myeloid progenitor cell as neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Functionally, mast cells are very similar to basophils, containing many of the same components in their granules (e.g., histamine ) and playing a similar role in allergic responses and other inflammatory reactions. However, unlike basophils, mast cells leave the circulating blood and are most frequently found residing in tissues. They are often associated with blood vessels and nerves or found close to surfaces that interface with the external environment, such as the skin and mucous membranes in various regions of the body ( [link] ).
Angela’s tests come back negative for all common allergens, and her sputum samples contain no abnormal presence of pathogenic microbes or elevated levels of members of the normal respiratory microbiota. She does, however, have elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines in her blood.
The swelling of her airway has still not responded to treatment with antihistamines or corticosteroids. Additional blood work shows that Angela has a mildly elevated white blood cell count but normal antibody levels. Also, she has a lower-than-normal level of the complement protein C4.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
As their name suggests, agranulocytes lack visible granules in the cytoplasm. Agranulocytes can be categorized as lymphocytes or monocytes ( [link] ). Among the lymphocytes are natural killer cells, which play an important role in nonspecific innate immune defenses. Lymphocytes also include the B cells and T cells, which are discussed in the next chapter because they are central players in the specific adaptive immune defenses. The monocytes differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells , which are collectively referred to as the mononuclear phagocyte system.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?