| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Several other heavy metals also exhibit antimicrobial activity. Copper sulfate is a common algicide used to control algal growth in swimming pools and fish tanks. The use of metallic copper to minimize microbial growth is also becoming more widespread. Copper linings in incubators help reduce contamination of cell cultures. The use of copper pots for water storage in underdeveloped countries is being investigated as a way to combat diarrheal diseases. Copper coatings are also becoming popular for frequently handled objects such as doorknobs, cabinet hardware, and other fixtures in health-care facilities in an attempt to reduce the spread of microbes.
Nickel and zinc coatings are now being used in a similar way. Other forms of zinc, including zinc chloride and zinc oxide , are also used commercially. Zinc chloride is quite safe for humans and is commonly found in mouthwashes, substantially increasing their length of effectiveness. Zinc oxide is found in a variety of products, including topical antiseptic creams such as calamine lotion, diaper ointments, baby powder, and dandruff shampoos.
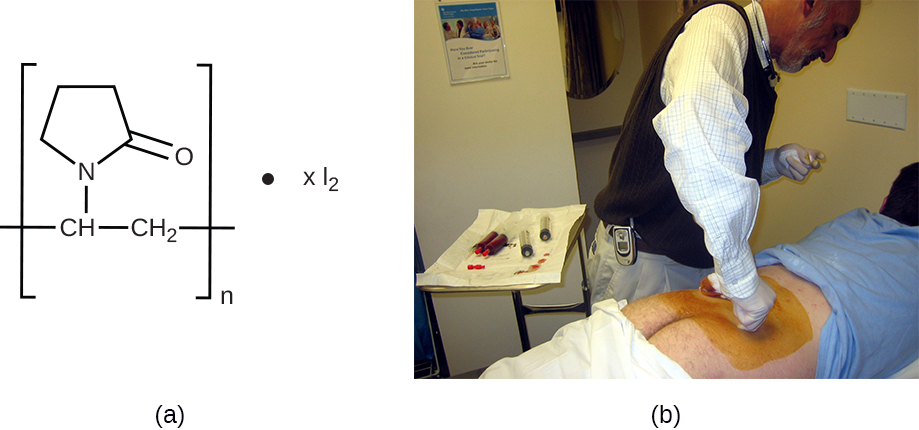
Other chemicals commonly used for disinfection are the halogens iodine , chlorine , and fluorine . Iodine works by oxidizing cellular components, including sulfur-containing amino acids, nucleotides, and fatty acids, and destabilizing the macromolecules that contain these molecules. It is often used as a topical tincture, but it may cause staining or skin irritation. An iodophor is a compound of iodine complexed with an organic molecule, thereby increasing iodine’s stability and, in turn, its efficacy. One common iodophor is povidone-iodine , which includes a wetting agent that releases iodine relatively slowly. Betadine is a brand of povidone-iodine commonly used as a hand scrub by medical personnel before surgery and for topical antisepsis of a patient’s skin before incision ( [link] ).
Chlorine is another halogen commonly used for disinfection. When chlorine gas is mixed with water, it produces a strong oxidant called hypochlorous acid, which is uncharged and enters cells easily. Chlorine gas is commonly used in municipal drinking water and wastewater treatment plants, with the resulting hypochlorous acid producing the actual antimicrobial effect. Those working at water treatment facilities need to take great care to minimize personal exposure to chlorine gas. Sodium hypochlorite is the chemical component of common household bleach , and it is also used for a wide variety of disinfecting purposes. Hypochlorite salts, including sodium and calcium hypochlorites, are used to disinfect swimming pools. Chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, and calcium hypochlorite are also commonly used disinfectants in the food processing and restaurant industries to reduce the spread of foodborne diseases. Workers in these industries also need to take care to use these products correctly to ensure their own safety as well as the safety of consumers. A recent joint statement published by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations and WHO indicated that none of the many beneficial uses of chlorine products in food processing to reduce the spread of foodborne illness posed risks to consumers. World Health Organization. “Benefits and Risks of the Use of Chlorine-Containing Disinfectants in Food Production and Food Processing: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Meeting.” Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2009.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?