| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
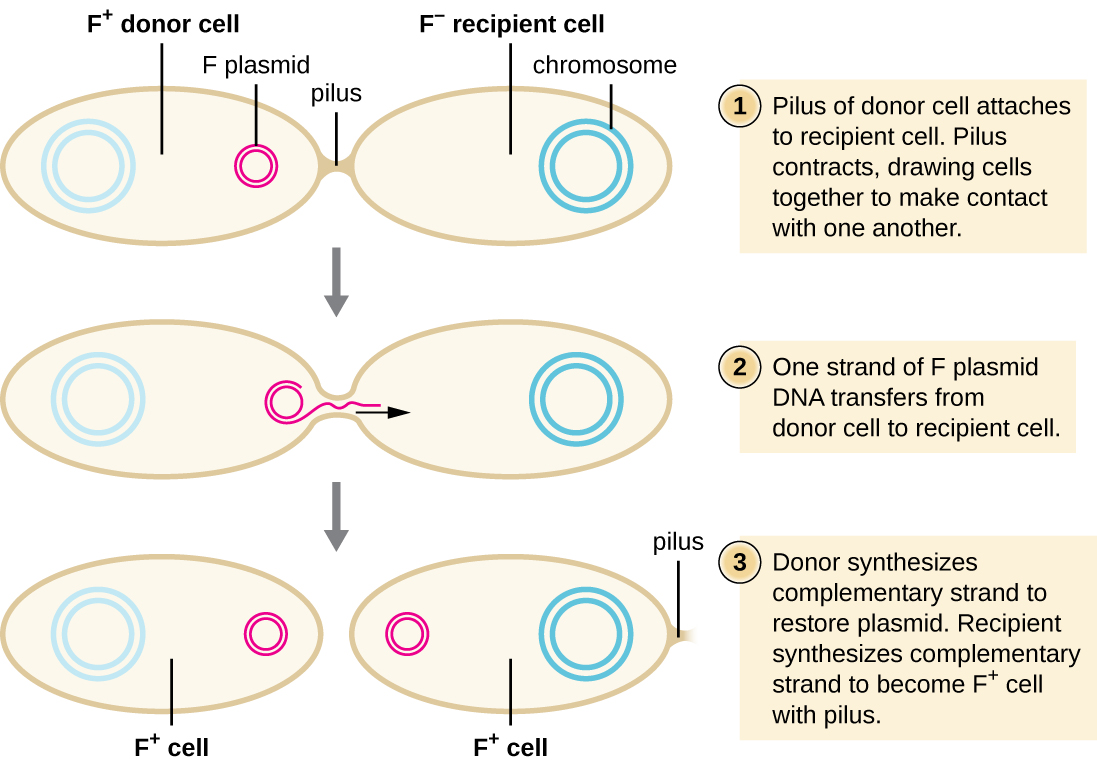
In conjugation , DNA is directly transferred from one prokaryote to another by means of a conjugation pilus , which brings the organisms into contact with one another. In E. coli , the genes encoding the ability to conjugate are located on a bacterial plasmid called the F plasmid , also known as the fertility factor , and the conjugation pilus is called the F pilus . The F-plasmid genes encode both the proteins composing the F pilus and those involved in rolling circle replication of the plasmid. Cells containing the F plasmid, capable of forming an F pilus, are called F + cell s or donor cell s , and those lacking an F plasmid are called F − cell s or recipient cell s .
During typical conjugation in E. coli , the F pilus of an F + cell comes into contact with an F – cell and retracts, bringing the two cell envelopes into contact ( [link] ). Then a cytoplasmic bridge forms between the two cells at the site of the conjugation pilus. As rolling circle replication of the F plasmid occurs in the F + cell, a single-stranded copy of the F plasmid is transferred through the cytoplasmic bridge to the F − cell, which then synthesizes the complementary strand, making it double stranded. The F − cell now becomes an F + cell capable of making its own conjugation pilus. Eventually, in a mixed bacterial population containing both F + and F − cells, all cells will become F + cells. Genes on the E. coli F plasmid also encode proteins preventing conjugation between F + cells.
Although typical conjugation in E. coli results in the transfer of the F-plasmid DNA only, conjugation may also transfer chromosomal DNA. This is because the F plasmid occasionally integrates into the bacterial chromosome through recombination between the plasmid and the chromosome, forming an Hfr cell ( [link] ). “Hfr” refers to the high frequency of recombination seen when recipient F − cells receive genetic information from Hfr cells through conjugation. Similar to the imprecise excision of a prophage during specialized transduction , the integrated F plasmid may also be imprecisely excised from the chromosome, producing an F’ plasmid that carries with it some chromosomal DNA adjacent to the integration site. On conjugation, this DNA is introduced to the recipient cell and may be either maintained as part of the F’ plasmid or be recombined into the recipient cell’s bacterial chromosome.
Hfr cells may also treat the bacterial chromosome like an enormous F plasmid and attempt to transfer a copy of it to a recipient F − cell. Because the bacterial chromosome is so large, transfer of the entire chromosome takes a long time ( [link] ). However, contact between bacterial cells during conjugation is transient, so it is unusual for the entire chromosome to be transferred. Host chromosomal DNA near the integration site of the F plasmid, displaced by the unidirectional process of rolling circle replication, is more likely to be transferred and recombined into a recipient cell’s chromosome than host genes farther away. Thus, the relative location of bacterial genes on the Hfr cell’s genome can be mapped based on when they are transferred through conjugation. As a result, prior to the age of widespread bacterial genome sequencing, distances on prokaryotic genome maps were often measured in minutes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?