| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
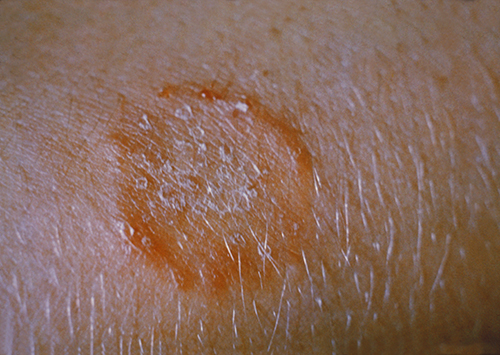
Upon arriving home from school, 7-year-old Sarah complains that a large spot on her arm will not stop itching. She keeps scratching at it, drawing the attention of her parents. Looking more closely, they see that it is a red circular spot with a raised red edge ( [link] ). The next day, Sarah’s parents take her to their doctor, who examines the spot using a Wood’s lamp . A Wood’s lamp produces ultraviolet light that causes the spot on Sarah’s arm to fluoresce, which confirms what the doctor already suspected: Sarah has a case of ringworm .
Sarah’s mother is mortified to hear that her daughter has a “worm.” How could this happen?
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box.
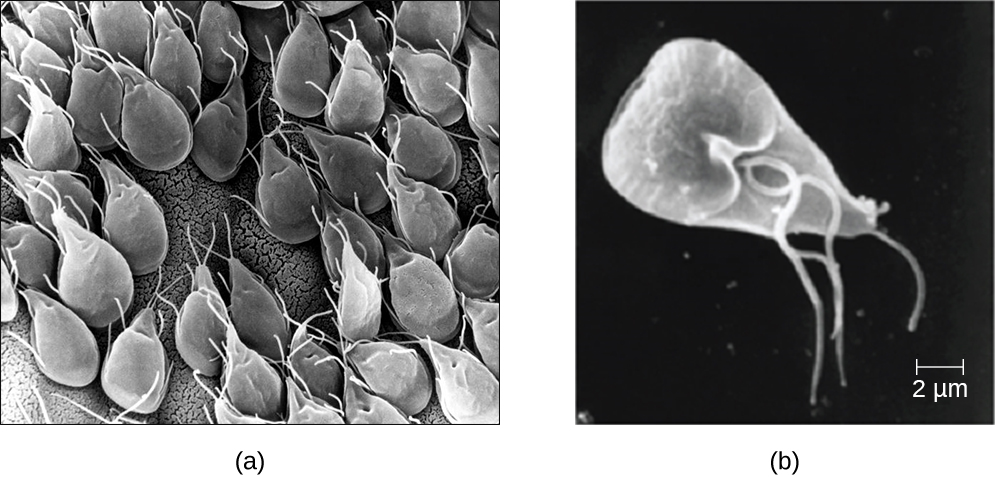
Eukaryotic microbes are an extraordinarily diverse group, including species with a wide range of life cycles, morphological specializations, and nutritional needs. Although more diseases are caused by viruses and bacteria than by microscopic eukaryotes, these eukaryotes are responsible for some diseases of great public health importance. For example, the protozoal disease malaria was responsible for 584,000 deaths worldwide (primarily children in Africa) in 2013, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The protist parasite Giardia causes a diarrheal illness (giardiasis) that is easily transmitted through contaminated water supplies. In the United States, Giardia is the most common human intestinal parasite ( [link] ). Although it may seem surprising, parasitic worms are included within the study of microbiology because identification depends on observation of microscopic adult worms or eggs. Even in developed countries, these worms are important parasites of humans and of domestic animals. There are fewer fungal pathogens, but these are important causes of illness, as well. On the other hand, fungi have been important in producing antimicrobial substances such as penicillin. In this chapter, we will examine characteristics of protists, worms, and fungi while considering their roles in causing disease.
The word protist is a historical term that is now used informally to refer to a diverse group of microscopic eukaryotic organisms. It is not considered a formal taxonomic term because the organisms it describes do not have a shared evolutionary origin. Historically, the protists were informally grouped into the “animal-like” protozoans , the “plant-like” algae , and the “fungus-like” protists such as water molds . These three groups of protists differ greatly in terms of their basic characteristics. For example, algae are photosynthetic organisms that can be unicellular or multicellular. Protozoa, on the other hand, are nonphotosynthetic, motile organisms that are always unicellular. Other informal terms may also be used to describe various groups of protists. For example, microorganisms that drift or float in water, moved by currents, are referred to as plankton . Types of plankton include zooplankton , which are motile and nonphotosynthetic, and phytoplankton , which are photosynthetic.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?