| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Several viruses can cause serious problems for the human reproductive system. Most of these viral infections are incurable, increasing the risk of persistent sexual transmission. In addition, such viral infections are very common in the United States. For example, human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common STI in the country, with an estimated prevalence of 79.1 million infections in 2008; herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV-2) is the next most prevalent STI at 24.1 million infections. Catherine Lindsey Satterwhite, Elizabeth Torrone, Elissa Meites, Eileen F. Dunne, Reena Mahajan, M. Cheryl Bañez Ocfemia, John Su, Fujie Xu, and Hillard Weinstock. “Sexually Transmitted Infections Among US Women and Men: Prevalence and Incidence Estimates, 2008.” Sexually Transmitted Diseases 40, no. 3 (2013): 187–193. In this section, we will examine these and other major viral infections of the reproductive system.
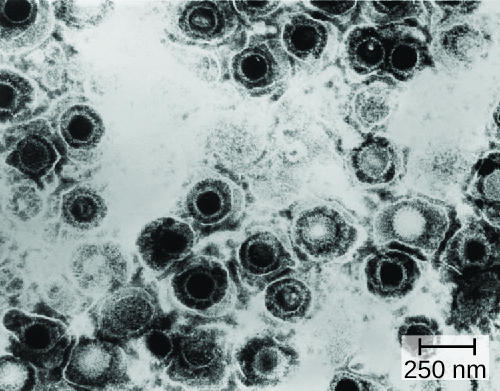
Genital herpes is a common condition caused by the herpes simplex virus ( [link] ), an enveloped, double-stranded DNA virus that is classified into two distinct types. Herpes simplex virus has several virulence factors, including infected cell protein (ICP) 34.5, which helps in replication and inhibits the maturation of dendritic cells as a mechanism of avoiding elimination by the immune system. In addition, surface glycoproteins on the viral envelope promote the coating of herpes simplex virus with antibodies and complement factors, allowing the virus to appear as “self” and prevent immune system activation and elimination.
There are two herpes simplex virus types. While herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is generally associated with oral lesions like cold sores or fever blisters (see Viral Infections of the Skin and Eyes ), herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) is usually associated with genital herpes. However, both viruses can infect either location as well as other parts of the body. Oral-genital contact can spread either virus from the mouth to the genital region or vice versa.
Many infected individuals do not develop symptoms, and thus do not realize that they carry the virus. However, in some infected individuals, fever, chills, malaise, swollen lymph nodes, and pain precede the development of fluid-filled vesicles that may be irritating and uncomfortable. When these vesicles burst, they release infectious fluid and allow transmission of HSV. In addition, open herpes lesions can increase the risk of spreading or acquiring HIV.
In men, the herpes lesions typically develop on the penis and may be accompanied by a watery discharge. In women, the vesicles develop most commonly on the vulva, but may also develop on the vagina or cervix ( [link] ). The symptoms are typically mild, although the lesions may be irritating or accompanied by urinary discomfort. Use of condoms may not always be an effective means of preventing transmission of genital herpes since the lesions can occur on areas other than the genitals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?