| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
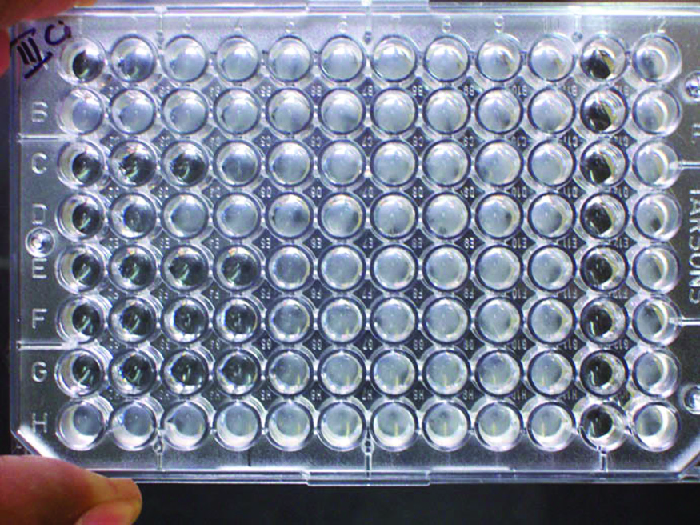
In addition to causing precipitation of soluble molecules and flocculation of molecules in suspension, antibodies can also clump together cells or particles (e.g., antigen-coated latex beads) in a process called agglutination ( [link] ). Agglutination can be used as an indicator of the presence of antibodies against bacteria or red blood cells. Agglutination assays are usually quick and easy to perform on a glass slide or microtiter plate ( [link] ). Microtiter plates have an array of wells to hold small volumes of reagents and to observe reactions (e.g., agglutination) either visually or using a specially designed spectrophotometer. The wells come in many different sizes for assays involving different volumes of reagents.
The use of agglutination tests to identify streptococcal bacteria was developed in the 1920s by Rebecca Lancefield working with her colleagues A.R. Dochez and Oswald Avery . Lancefield, Rebecca C., “The Antigenic Complex of Streptococcus haemoliticus . I. Demonstration of a Type-Specific Substance in Extracts of Streptococcus haemolyticus ,” The Journal of Experimental Medicine 47, no. 1 (1928): 91-103. She used antibodies to identify M protein , a virulence factor on streptococci that is necessary for the bacteria’s ability to cause strep throat. Production of antibodies against M protein is crucial in mounting a protective response against the bacteria.
Lancefield used antisera to show that different strains of the same species of streptococci express different versions of M protein, which explains why children can come down with strep throat repeatedly. Lancefield classified beta-hemolytic streptococci into many groups based on antigenic differences in group-specific polysaccharides located in the bacterial cell wall. The strains are called serovars because they are differentiated using antisera. Identifying the serovars present in a disease outbreak is important because some serovars may cause more severe disease than others.
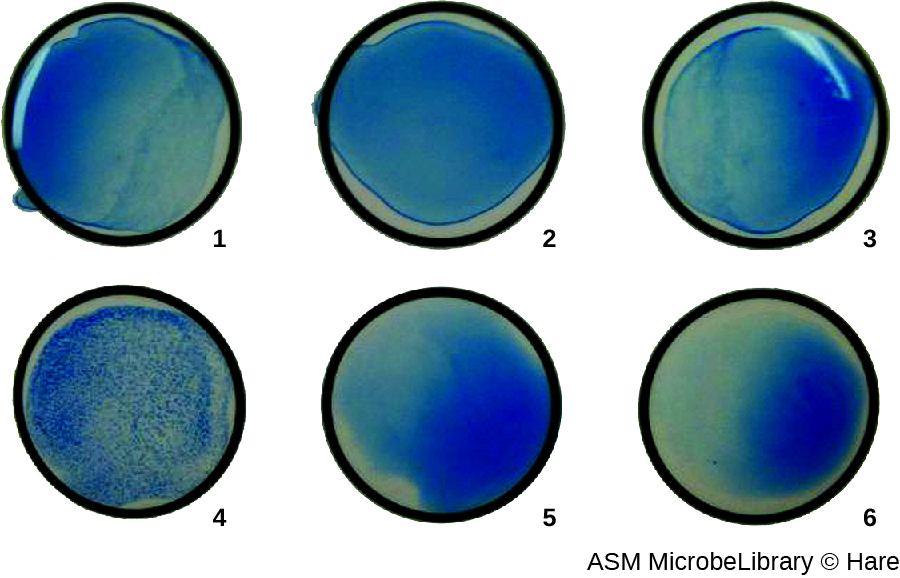
The method developed by Lancefield is a direct agglutination assay , since the bacterial cells themselves agglutinate. A similar strategy is more commonly used today when identifying serovars of bacteria and viruses; however, to improve visualization of the agglutination, the antibodies may be attached to inert latex beads . This technique is called an indirect agglutination assay (or latex fixation assay ), because the agglutination of the beads is a marker for antibody binding to some other antigen ( [link] ). Indirect assays can be used to detect the presence of either antibodies or specific antigens.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?