| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nonspecific innate immunity can be characterized as a multifaceted system of defenses that targets invading pathogens in a nonspecific manner. In this chapter, we have divided the numerous defenses that make up this system into three categories: physical defenses, chemical defenses, and cellular defenses. However, it is important to keep in mind that these defenses do not function independently, and the categories often overlap. [link] provides an overview of the nonspecific defenses discussed in this chapter.
| Overview of Nonspecific Innate Immune Defenses | |
|---|---|
| Physical defenses | Physical barriers |
| Mechanical defenses | |
| Microbiome | |
| Chemical defenses | Chemicals and enzymes in body fluids |
| Antimicrobial peptides | |
| Plasma protein mediators | |
| Cytokines | |
| Inflammation-eliciting mediators | |
| Cellular defenses | Granulocytes |
| Agranulocytes |
Physical defenses provide the body’s most basic form of nonspecific defense. They include physical barriers to microbes, such as the skin and mucous membranes, as well as mechanical defenses that physically remove microbes and debris from areas of the body where they might cause harm or infection. In addition, the microbiome provides a measure of physical protection against disease, as microbes of the normal microbiota compete with pathogens for nutrients and cellular binding sites necessary to cause infection.
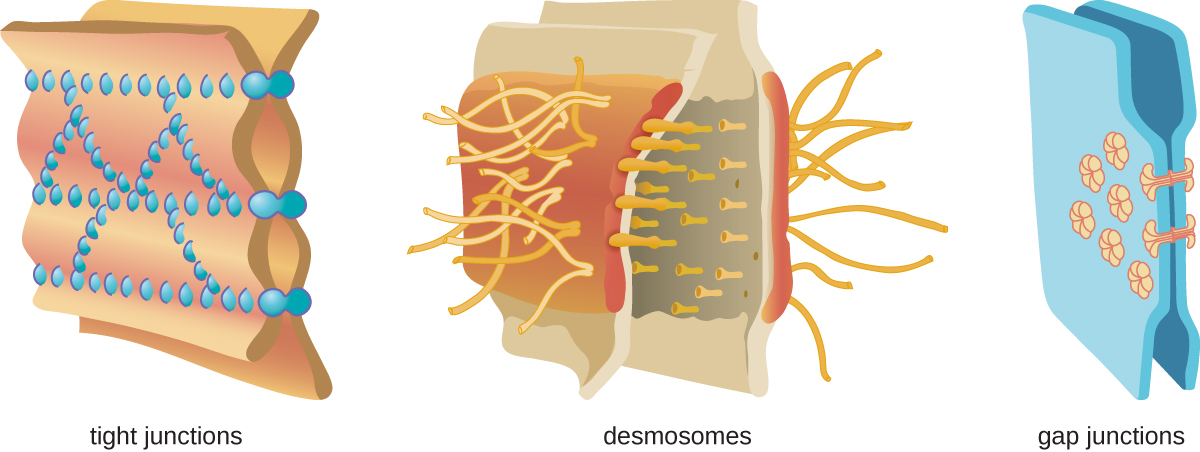
Physical barriers play an important role in preventing microbes from reaching tissues that are susceptible to infection. At the cellular level, barriers consist of cells that are tightly joined to prevent invaders from crossing through to deeper tissue. For example, the endothelial cells that line blood vessels have very tight cell-to-cell junctions, blocking microbes from gaining access to the bloodstream. Cell junctions are generally composed of cell membrane proteins that may connect with the extracellular matrix or with complementary proteins from neighboring cells. Tissues in various parts of the body have different types of cell junctions . These include tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions, as illustrated in [link] . Invading microorganisms may attempt to break down these substances chemically, using enzymes such as proteases that can cause structural damage to create a point of entry for pathogens.
One of the body’s most important physical barriers is the skin barrier , which is composed of three layers of closely packed cells. The thin upper layer is called the epidermis. A second, thicker layer, called the dermis, contains hair follicles, sweat glands, nerves, and blood vessels. A layer of fatty tissue called the hypodermis lies beneath the dermis and contains blood and lymph vessels ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?