| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In addition to physical methods of microbial control, chemicals are also used to control microbial growth. A wide variety of chemicals can be used as disinfectants or antiseptics. When choosing which to use, it is important to consider the type of microbe targeted; how clean the item needs to be; the disinfectant’s effect on the item’s integrity; its safety to animals, humans, and the environment; its expense; and its ease of use. This section describes the variety of chemicals used as disinfectants and antiseptics, including their mechanisms of action and common uses.
In the 1800s, scientists began experimenting with a variety of chemicals for disinfection. In the 1860s, British surgeon Joseph Lister (1827–1912) began using carbolic acid, known as phenol , as a disinfectant for the treatment of surgical wounds (see Foundations of Modern Cell Theory ). In 1879, Lister’s work inspired the American chemist Joseph Lawrence (1836–1909) to develop Listerine, an alcohol-based mixture of several related compounds that is still used today as an oral antiseptic. Today, carbolic acid is no longer used as a surgical disinfectant because it is a skin irritant, but the chemical compounds found in antiseptic mouthwashes and throat lozenges are called phenolics .
Chemically, phenol consists of a benzene ring with an –OH group, and phenolics are compounds that have this group as part of their chemical structure ( [link] ). Phenolics such as thymol and eucalyptol occur naturally in plants. Other phenolics can be derived from creosote, a component of coal tar. Phenolics tend to be stable, persistent on surfaces, and less toxic than phenol. They inhibit microbial growth by denaturing proteins and disrupting membranes.
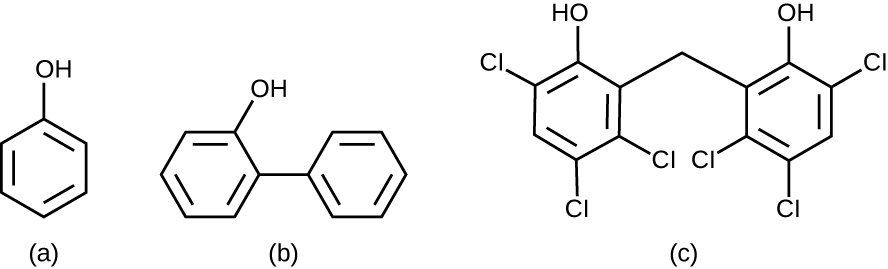
Since Lister’s time, several phenolic compounds have been used to control microbial growth. Phenolics like cresols (methylated phenols) and o-phenylphenol were active ingredients in various formulations of Lysol since its invention in 1889. o-Phenylphenol was also commonly used in agriculture to control bacterial and fungal growth on harvested crops, especially citrus fruits, but its use in the United States is now far more limited. The bisphenol hexachlorophene , a disinfectant, is the active ingredient in pHisoHex, a topical cleansing detergent widely used for handwashing in hospital settings. pHisoHex is particularly effective against gram-positive bacteria, including those causing staphylococcal and streptococcal skin infections. pHisoHex was formerly used for bathing infants, but this practice has been discontinued because it has been shown that exposure to hexachlorophene can lead to neurological problems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?