| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
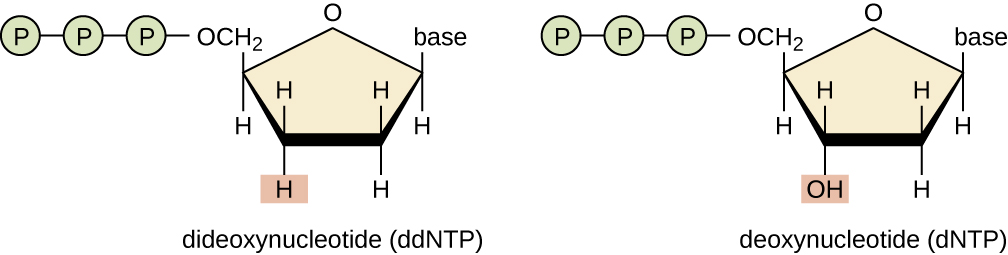
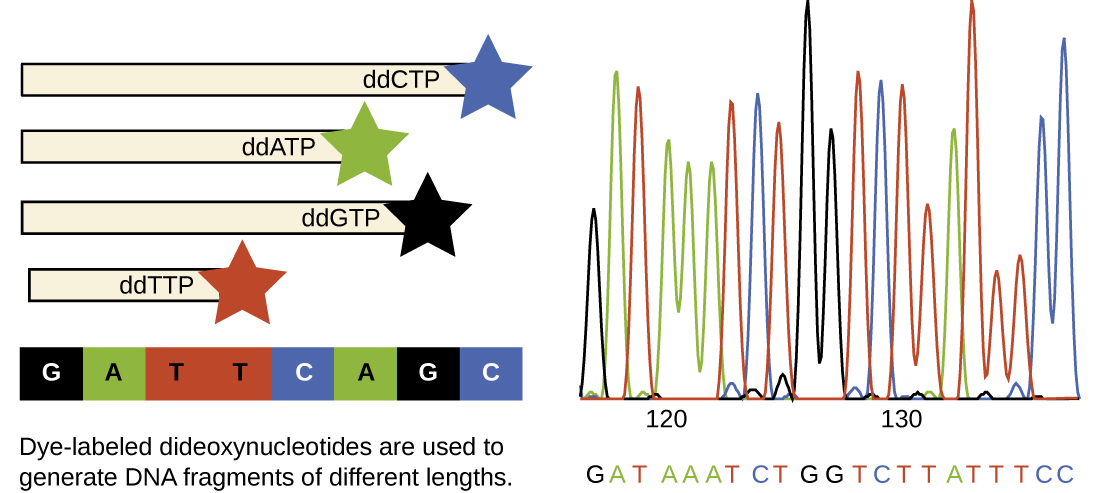
In Sanger’s day, four reactions were set up for each DNA molecule being sequenced, each reaction containing only one of the four possible ddNTPs. Each ddNTP was labeled with a radioactive phosphorus molecule. The products of the four reactions were then run in separate lanes side by side on long, narrow PAGE gels, and the bands of varying lengths were detected by autoradiography. Today, this process has been simplified with the use of ddNTPs, each labeled with a different colored fluorescent dye or fluorochrome ( [link] ), in one sequencing reaction containing all four possible ddNTPs for each DNA molecule being sequenced ( [link] ). These fluorochromes are detected by fluorescence spectroscopy. Determining the fluorescence color of each band as it passes by the detector produces the nucleotide sequence of the template strand.
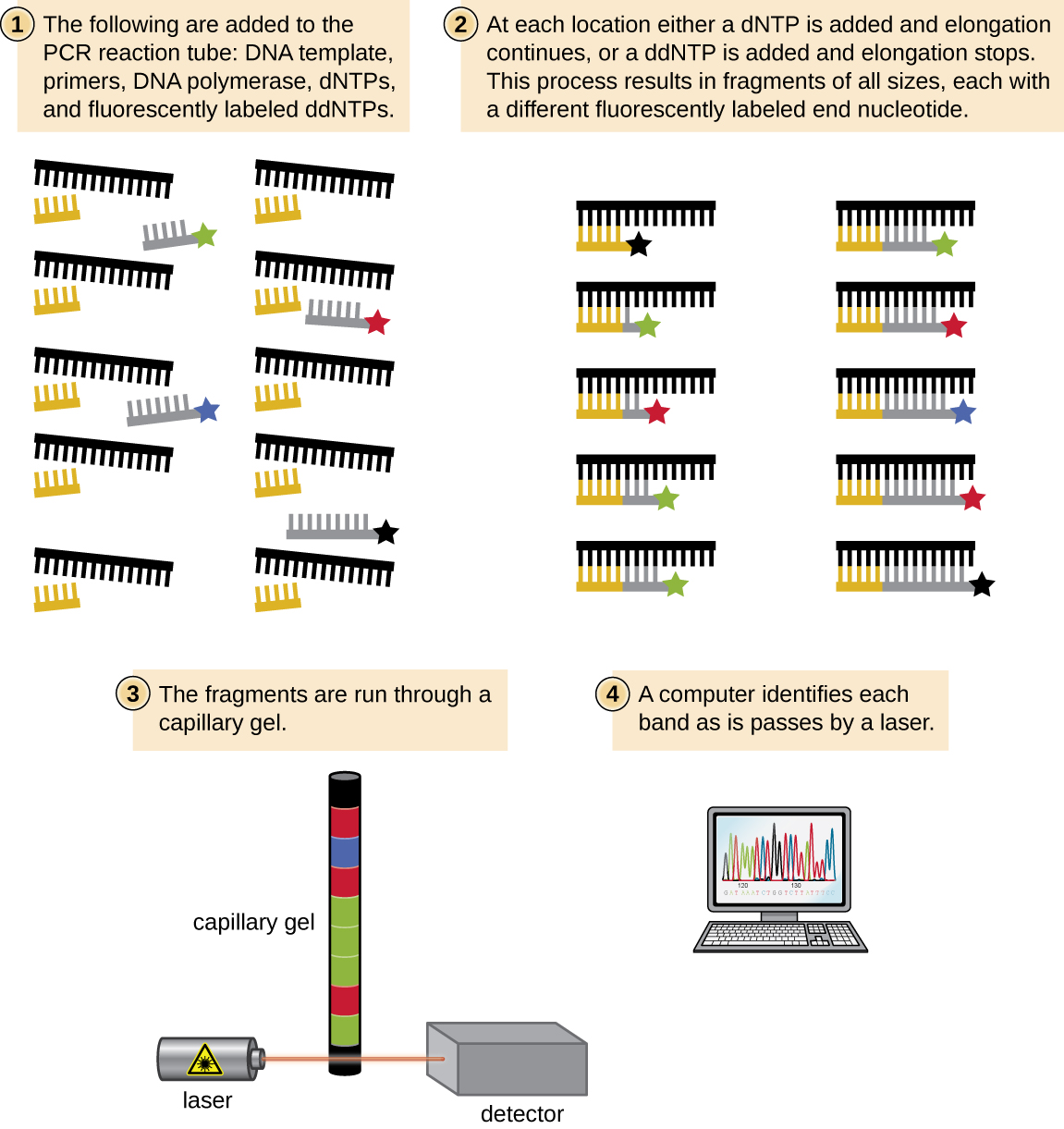
Since 2005, automated sequencing techniques used by laboratories fall under the umbrella of next generation sequencing , which is a group of automated techniques used for rapid DNA sequencing. These methods have revolutionized the field of molecular genetics because the low-cost sequencers can generate sequences of hundreds of thousands or millions of short fragments (25 to 600 base pairs) just in one day. Although several variants of next generation sequencing technologies are made by different companies (for example, 454 Life Sciences’ pyrosequencing and Illumina’s Solexa technology), they all allow millions of bases to be sequenced quickly, making the sequencing of entire genomes relatively easy, inexpensive, and commonplace. In 454 sequencing (pyrosequencing) , for example, a DNA sample is fragmented into 400–600-bp single-strand fragments, modified with the addition of DNA adapters to both ends of each fragment. Each DNA fragment is then immobilized on a bead and amplified by PCR, using primers designed to anneal to the adapters, creating a bead containing many copies of that DNA fragment. Each bead is then put into a separate well containing sequencing enzymes. To the well, each of the four nucleotides is added one after the other; when each one is incorporated, pyrophosphate is released as a byproduct of polymerization, emitting a small flash of light that is recorded by a detector. This provides the order of nucleotides incorporated as a new strand of DNA is made and is an example of synthesis sequencing. Next generation sequencers use sophisticated software to get through the cumbersome process of putting all the fragments in order. Overall, these technologies continue to advance rapidly, decreasing the cost of sequencing and increasing the availability of sequence data from a wide variety of organisms quickly.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?