| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The elucidation of the structure of the double helix by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 provided a hint as to how DNA is copied during the process of replication . Separating the strands of the double helix would provide two templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands, but exactly how new DNA molecules were constructed was still unclear. In one model, semiconservative replication , the two strands of the double helix separate during DNA replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied; after replication, each double-stranded DNA includes one parental or “old” strand and one “new” strand. There were two competing models also suggested: conservative and dispersive, which are shown in [link] .
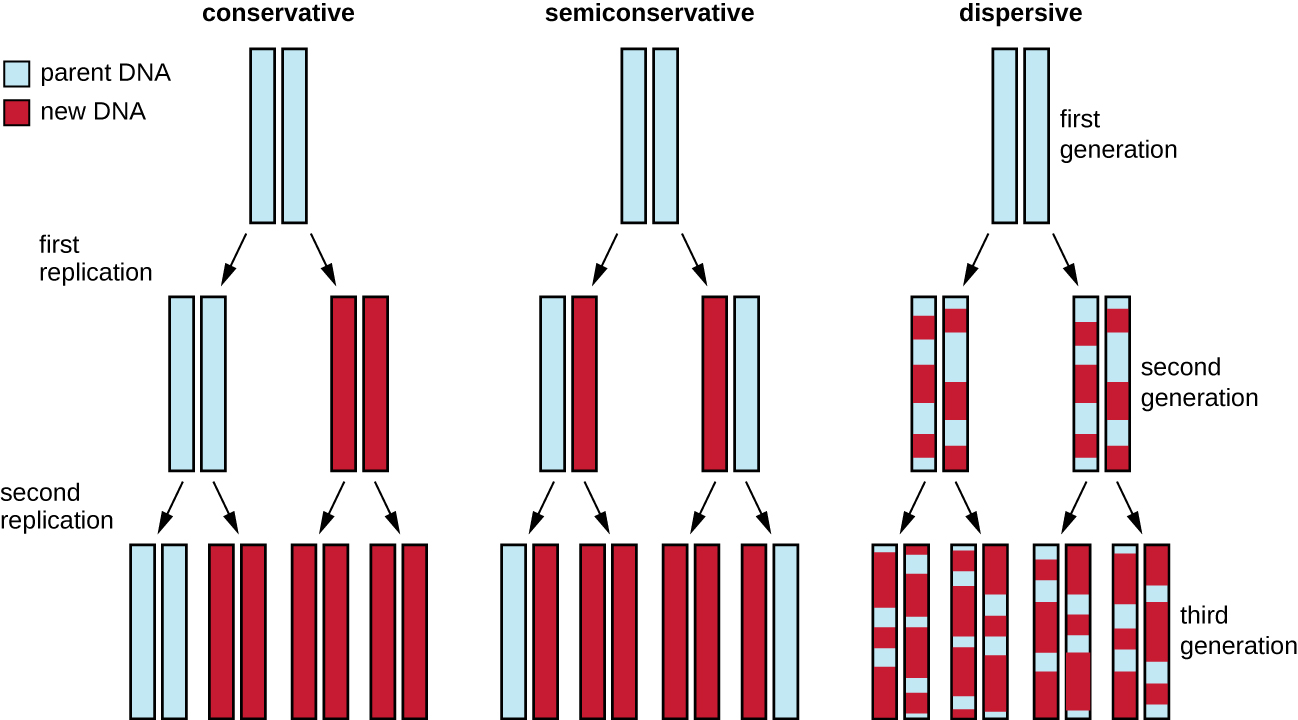
Matthew Meselson (1930–) and Franklin Stahl (1929–) devised an experiment in 1958 to test which of these models correctly represents DNA replication ( [link] ). They grew E. coli for several generations in a medium containing a “heavy” isotope of nitrogen ( 15 N) that was incorporated into nitrogenous bases and, eventually, into the DNA. This labeled the parental DNA. The E. coli culture was then shifted into a medium containing 14 N and allowed to grow for one generation. The cells were harvested and the DNA was isolated. The DNA was separated by ultracentrifugation, during which the DNA formed bands according to its density. DNA grown in 15 N would be expected to form a band at a higher density position than that grown in 14 N. Meselson and Stahl noted that after one generation of growth in 14 N, the single band observed was intermediate in position in between DNA of cells grown exclusively in 15 N or 14 N. This suggested either a semiconservative or dispersive mode of replication. Some cells were allowed to grow for one more generation in 14 N and spun again. The DNA harvested from cells grown for two generations in 14 N formed two bands: one DNA band was at the intermediate position between 15 N and 14 N, and the other corresponded to the band of 14 N DNA. These results could only be explained if DNA replicates in a semiconservative manner. Therefore, the other two models were ruled out. As a result of this experiment, we now know that during DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. The resulting DNA molecules have the same sequence and are divided equally into the two daughter cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?