| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
View an animation on DNA structure from the DNA Learning Center to learn more.
DNA stores the information needed to build and control the cell. The transmission of this information from mother to daughter cells is called vertical gene transfer and it occurs through the process of DNA replication. DNA is replicated when a cell makes a duplicate copy of its DNA, then the cell divides, resulting in the correct distribution of one DNA copy to each resulting cell. DNA can also be enzymatically degraded and used as a source of nucleosides and nucleotides for the cell. Unlike other macromolecules, DNA does not serve a structural role in cells.
Historically, women have been underrepresented in the sciences and in medicine, and often their pioneering contributions have gone relatively unnoticed. For example, although Rosalind Franklin performed the X-ray diffraction studies demonstrating the double helical structure of DNA, it is Watson and Crick who became famous for this discovery, building on her data. There still remains great controversy over whether their acquisition of her data was appropriate and whether personality conflicts and gender bias contributed to the delayed recognition of her significant contributions. Similarly, Barbara McClintock did pioneering work in maize (corn) genetics from the 1930s through 1950s, discovering transposons (jumping genes), but she was not recognized until much later, receiving a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1983 ( [link] ).
Today, women still remain underrepresented in many fields of science and medicine. While more than half of the undergraduate degrees in science are awarded to women, only 46% of doctoral degrees in science are awarded to women. In academia, the number of women at each level of career advancement continues to decrease, with women holding less than one-third of the positions of Ph.D.-level scientists in tenure-track positions, and less than one-quarter of the full professorships at 4-year colleges and universities. N.H. Wolfinger “For Female Scientists, There's No Good Time to Have Children.” The Atlantic July 29, 2013. http://www.theatlantic.com/sexes/archive/2013/07/for-female-scientists-theres-no-good-time-to-have-children/278165/. Even in the health professions, like nearly all other fields, women are often underrepresented in many medical careers and earn significantly less than their male counterparts, as shown in a 2013 study published by the Journal of the American Medical Association . S.A. Seabury et al. “Trends in the Earnings of Male and Female Health Care Professionals in the United States, 1987 to 2010.” Journal of the American Medical Association Internal Medicine 173 no. 18 (2013):1748–1750.
Why do such disparities continue to exist and how do we break these cycles? The situation is complex and likely results from the combination of various factors, including how society conditions the behaviors of girls from a young age and supports their interests, both professionally and personally. Some have suggested that women do not belong in the laboratory, including Nobel Prize winner Tim Hunt, whose 2015 public comments suggesting that women are too emotional for science E. Chung. “Tim Hunt, Sexism and Science: The Real 'Trouble With Girls' in Labs.” CBC News Technology and Science , June 12, 2015. http://www.cbc.ca/news/technology/tim-hunt-sexism-and-science-the-real-trouble-with-girls-in-labs-1.3110133. Accessed 8/4/2016. were met with widespread condemnation.
Perhaps girls should be supported more from a young age in the areas of science and math ( [link] ). Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) programs sponsored by the American Association of University Women (AAUW) American Association of University Women. “Building a STEM Pipeline for Girls and Women.” http://www.aauw.org/what-we-do/stem-education/. Accessed June 10, 2016. and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) National Aeronautics and Space Administration. “Outreach Programs: Women and Girls Initiative.” http://women.nasa.gov/outreach-programs/. Accessed June 10, 2016. are excellent examples of programs that offer such support. Contributions by women in science should be made known more widely to the public, and marketing targeted to young girls should include more images of historically and professionally successful female scientists and medical professionals, encouraging all bright young minds, including girls and women, to pursue careers in science and medicine.

Based upon his symptoms, Alex’s physician suspects that he is suffering from a foodborne illness that he acquired during his travels. Possibilities include bacterial infection (e.g., enterotoxigenic E. coli , Vibrio cholerae , Campylobacter jejuni , Salmonella ), viral infection (rotavirus or norovirus), or protozoan infection ( Giardia lamblia , Cryptosporidium parvum , or Entamoeba histolytica ).
His physician orders a stool sample to identify possible causative agents (e.g., bacteria, cysts) and to look for the presence of blood because certain types of infectious agents (like C. jejuni , Salmonella , and E. histolytica ) are associated with the production of bloody stools.
Alex’s stool sample showed neither blood nor cysts. Following analysis of his stool sample and based upon his recent travel history, the hospital physician suspected that Alex was suffering from traveler’s diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic E. coli ( ETEC ), the causative agent of most traveler’s diarrhea. To verify the diagnosis and rule out other possibilities, Alex’s physician ordered a diagnostic lab test of his stool sample to look for DNA sequences encoding specific virulence factors of ETEC. The physician instructed Alex to drink lots of fluids to replace what he was losing and discharged him from the hospital.
ETEC produces several plasmid-encoded virulence factors that make it pathogenic compared with typical E. coli . These include the secreted toxins heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) and heat-stabile enterotoxin (ST) , as well as colonization factor (CF) . Both LT and ST cause the excretion of chloride ions from intestinal cells to the intestinal lumen, causing a consequent loss of water from intestinal cells, resulting in diarrhea. CF encodes a bacterial protein that aids in allowing the bacterium to adhere to the lining of the small intestine.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
The end of a nucleic acid strand with a free phosphate group is called the ________.
5ʹ end
The work of Rosalind Franklin and R.G. Gosling was important in demonstrating the helical nature of DNA.
True
The A-T base pair has more hydrogen bonding than the C-G base pair.
False
What is the role of phosphodiester bonds within the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA?
What is meant by the term “antiparallel?”
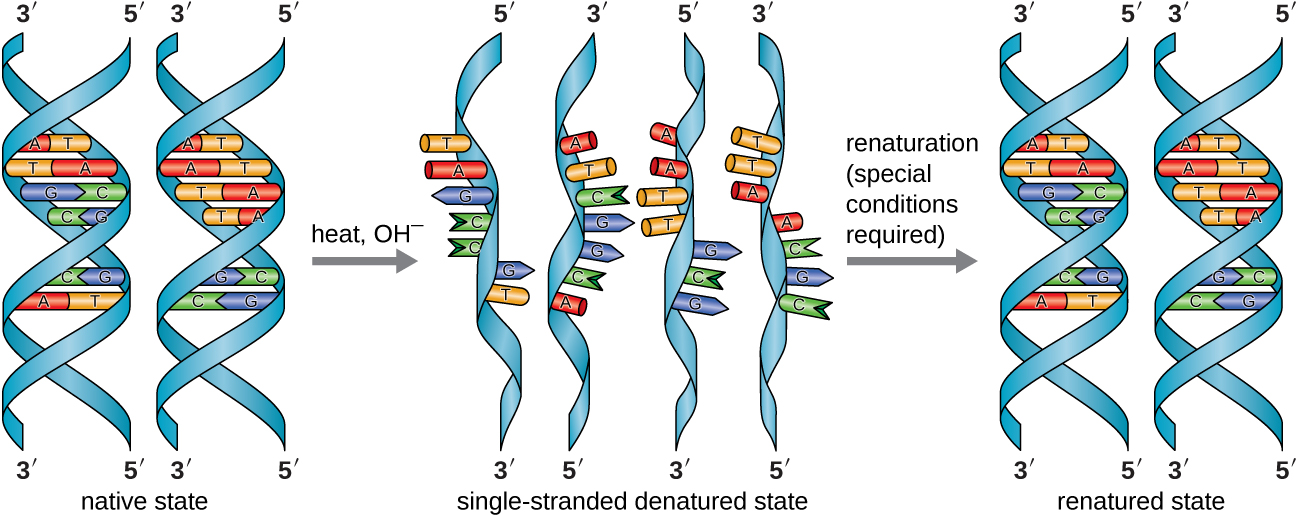
Why is DNA with a high GC content more difficult to denature than that with a low GC content?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?