| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
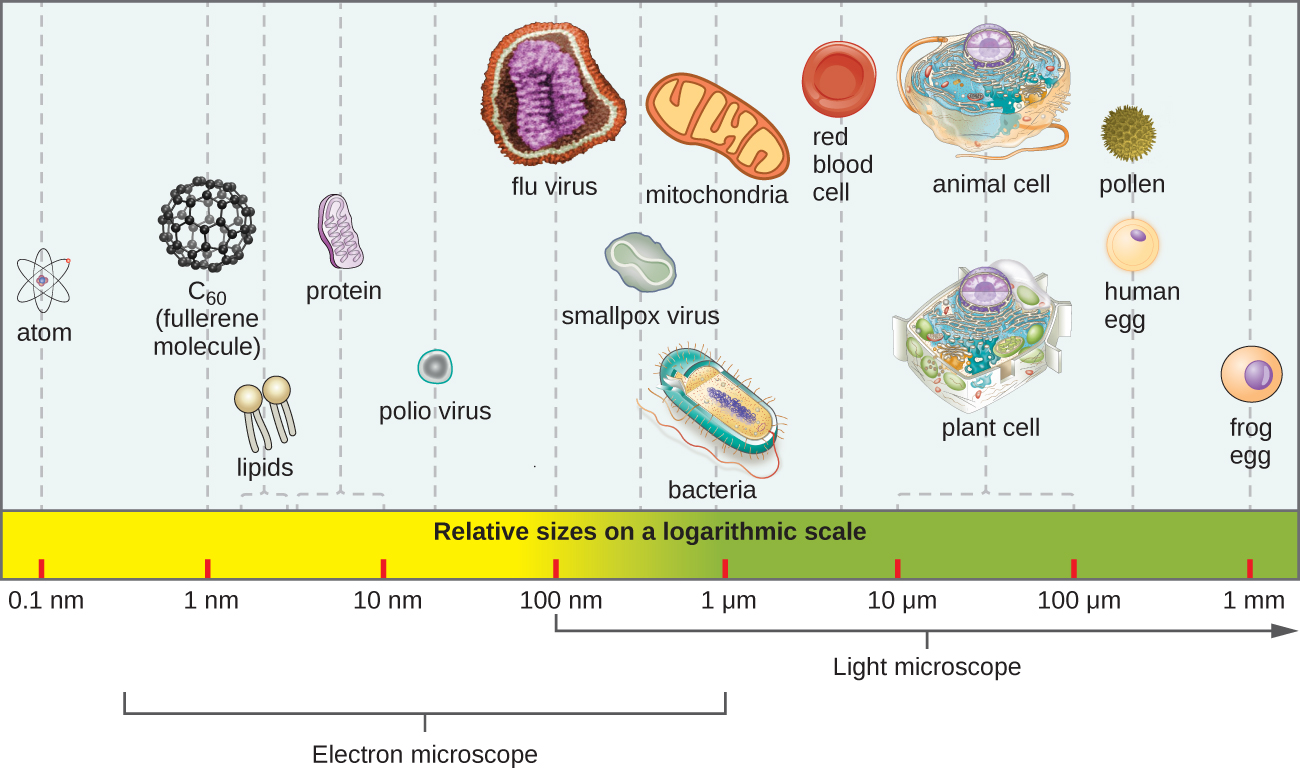
Most microbes are unicellular and small enough that they require artificial magnification to be seen. However, there are some unicellular microbes that are visible to the naked eye, and some multicellular organisms that are microscopic. An object must measure about 100 micrometers (µm) to be visible without a microscope, but most microorganisms are many times smaller than that. For some perspective, consider that a typical animal cell measures roughly 10 µm across but is still microscopic. Bacterial cells are typically about 1 µm, and viruses can be 10 times smaller than bacteria ( [link] ). See [link] for units of length used in microbiology.
| Units of Length Commonly Used in Microbiology | ||
|---|---|---|
| Metric Unit | Meaning of Prefix | Metric Equivalent |
| meter (m) | — | 1 m = 10 0 m |
| decimeter (dm) | 1/10 | 1 dm = 0.1 m = 10 −1 m |
| centimeter (cm) | 1/100 | 1 cm = 0.01 m = 10 −2 m |
| millimeter (mm) | 1/1000 | 1 mm = 0.001 m = 10 −3 m |
| micrometer (μm) | 1/1,000,000 | 1 μm = 0.000001 m = 10 −6 m |
| nanometer (nm) | 1/1,000,000,000 | 1 nm = 0.000000001 m = 10 −9 m |
Microorganisms differ from each other not only in size, but also in structure, habitat, metabolism, and many other characteristics. While we typically think of microorganisms as being unicellular, there are also many multicellular organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope. Some microbes, such as viruses, are even acellular (not composed of cells).
Microorganisms are found in each of the three domains of life: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Microbes within the domains Bacteria and Archaea are all prokaryotes (their cells lack a nucleus), whereas microbes in the domain Eukarya are eukaryotes (their cells have a nucleus). Some microorganisms, such as viruses, do not fall within any of the three domains of life. In this section, we will briefly introduce each of the broad groups of microbes. Later chapters will go into greater depth about the diverse species within each group.

How big is a bacterium or a virus compared to other objects? Check out this interactive website to get a feel for the scale of different microorganisms.
Bacteria are found in nearly every habitat on earth, including within and on humans. Most bacteria are harmless or helpful, but some are pathogen s , causing disease in humans and other animals. Bacteria are prokaryotic because their genetic material (DNA) is not housed within a true nucleus. Most bacteria have cell walls that contain peptidoglycan.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?