| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Cora, a 41-year-old lawyer and mother of two, has recently been experiencing severe headaches, a high fever, and a stiff neck. Her husband, who has accompanied Cora to see a doctor, reports that Cora also seems confused at times and unusually drowsy. Based on these symptoms, the doctor suspects that Cora may have meningitis, a potentially life-threatening infection of the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
Meningitis has several potential causes. It can be brought on by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or even a reaction to medication or exposure to heavy metals. Although people with viral meningitis usually heal on their own, bacterial and fungal meningitis are quite serious and require treatment.
Cora’s doctor orders a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to take three samples of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from around the spinal cord ( [link] ). The samples will be sent to laboratories in three different departments for testing: clinical chemistry, microbiology, and hematology. The samples will first be visually examined to determine whether the CSF is abnormally colored or cloudy; then the CSF will be examined under a microscope to see if it contains a normal number of red and white blood cells and to check for any abnormal cell types. In the microbiology lab, the specimen will be centrifuged to concentrate any cells in a sediment; this sediment will be smeared on a slide and stained with a Gram stain. Gram staining is a procedure used to differentiate between two different types of bacteria (gram-positive and gram-negative).
About 80% of patients with bacterial meningitis will show bacteria in their CSF with a Gram stain. Rebecca Buxton. “Examination of Gram Stains of Spinal Fluid—Bacterial Meningitis.” American Society for Microbiology . 2007. http://www.microbelibrary.org/library/gram-stain/3065-examination-of-gram-stains-of-spinal-fluid-bacterial-meningitis Cora’s Gram stain did not show any bacteria, but her doctor decides to prescribe her antibiotics just in case. Part of the CSF sample will be cultured—put in special dishes to see if bacteria or fungi will grow. It takes some time for most microorganisms to reproduce in sufficient quantities to be detected and analyzed.
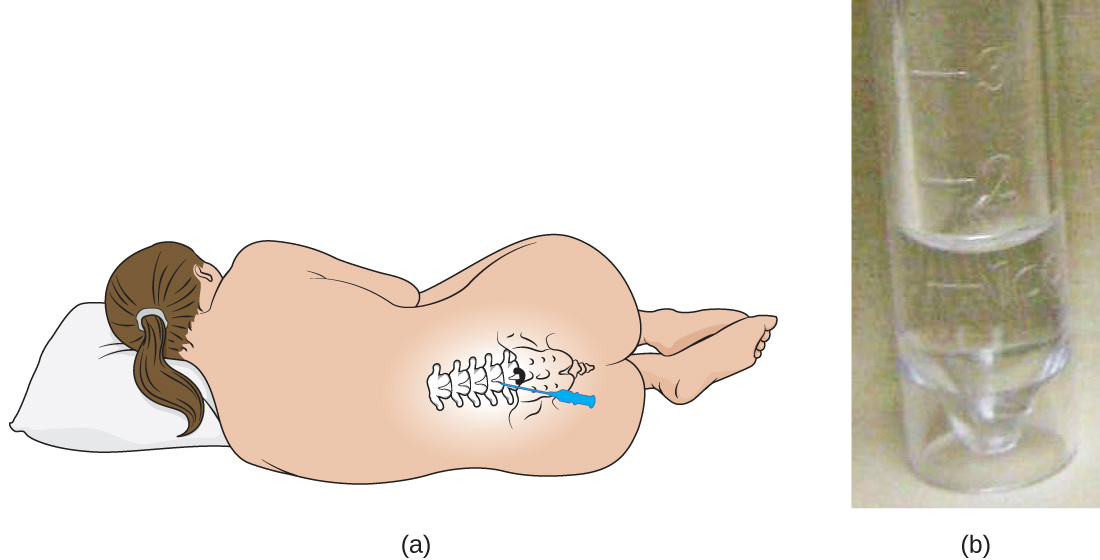
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?