| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[link] illustrates a hypothetical and simplified balance sheet for the Safe and Secure Bank. Because of the two-column format of the balance sheet, with the T-shape formed by the vertical line down the middle and the horizontal line under “Assets” and “Liabilities,” it is sometimes called a T-account .
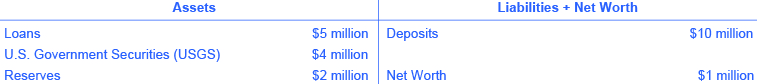
The “T” in a T-account separates the assets of a firm, on the left, from its liabilities, on the right. All firms use T-accounts, though most are much more complex. For a bank, the assets are the financial instruments that either the bank is holding (its reserves) or those instruments where other parties owe money to the bank—like loans made by the bank and U.S. Government Securities, such as U.S. treasury bonds purchased by the bank. Liabilities are what the bank owes to others. Specifically, the bank owes any deposits made in the bank to those who have made them. The net worth of the bank is the total assets minus total liabilities. Net worth is included on the liabilities side to have the T account balance to zero. For a healthy business, net worth will be positive. For a bankrupt firm, net worth will be negative. In either case, on a bank’s T-account, assets will always equal liabilities plus net worth.
When bank customers deposit money into a checking account, savings account, or a certificate of deposit, the bank views these deposits as liabilities. After all, the bank owes these deposits to its customers, when the customers wish to withdraw their money. In the example shown in [link] , the Safe and Secure Bank holds $10 million in deposits.
Loans are the first category of bank assets shown in [link] . Say that a family takes out a 30-year mortgage loan to purchase a house, which means that the borrower will repay the loan over the next 30 years. This loan is clearly an asset from the bank’s perspective, because the borrower has a legal obligation to make payments to the bank over time. But in practical terms, how can the value of the mortgage loan that is being paid over 30 years be measured in the present? One way of measuring the value of something—whether a loan or anything else—is by estimating what another party in the market is willing to pay for it. Many banks issue home loans, and charge various handling and processing fees for doing so, but then sell the loans to other banks or financial institutions who collect the loan payments. The market where loans are made to borrowers is called the primary loan market , while the market in which these loans are bought and sold by financial institutions is the secondary loan market.
One key factor that affects what financial institutions are willing to pay for a loan, when they buy it in the secondary loan market, is the perceived riskiness of the loan: that is, given the characteristics of the borrower, such as income level and whether the local economy is performing strongly, what proportion of loans of this type will be repaid? The greater the risk that a loan will not be repaid, the less that any financial institution will pay to acquire the loan. Another key factor is to compare the interest rate charged on the original loan with the current interest rate in the economy. If the original loan made at some point in the past requires the borrower to pay a low interest rate, but current interest rates are relatively high, then a financial institution will pay less to acquire the loan. In contrast, if the original loan requires the borrower to pay a high interest rate, while current interest rates are relatively low, then a financial institution will pay more to acquire the loan. For the Safe and Secure Bank in this example, the total value of its loans if they were sold to other financial institutions in the secondary market is $5 million.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?