| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
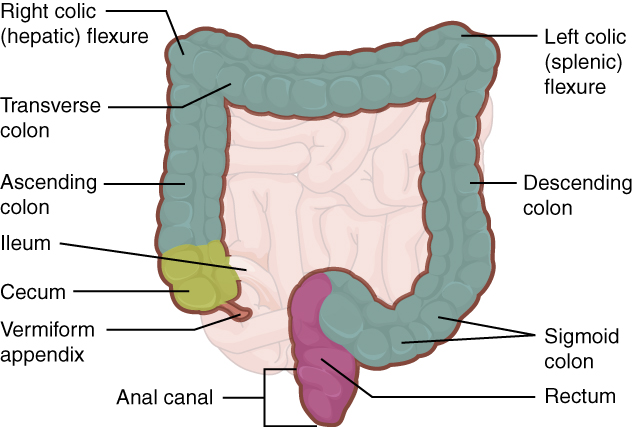
The cecum blends seamlessly with the colon . Upon entering the colon, the food residue first travels up the ascending colon on the right side of the abdomen. At the inferior surface of the liver, the colon bends to form the right colic flexure (hepatic flexure) and becomes the transverse colon . The region defined as hindgut begins with the last third of the transverse colon and continues on. Food residue passing through the transverse colon travels across to the left side of the abdomen, where the colon angles sharply immediately inferior to the spleen, at the left colic flexure (splenic flexure). From there, food residue passes through the descending colon , which runs down the left side of the posterior abdominal wall. After entering the pelvis inferiorly, it becomes the s-shaped sigmoid colon , which extends medially to the midline ( [link] ). The ascending and descending colon, and the rectum (discussed next) are located in the retroperitoneum. The transverse and sigmoid colon are tethered to the posterior abdominal wall by the mesocolon.
Colorectal cancer may be signaled by constipation or diarrhea, cramping, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding. Bleeding from the rectum may be either obvious or occult (hidden in feces). Since most colon cancers arise from benign mucosal growths called polyps, cancer prevention is focused on identifying these polyps. The colonoscopy is both diagnostic and therapeutic. Colonoscopy not only allows identification of precancerous polyps, the procedure also enables them to be removed before they become malignant. Screening for fecal occult blood tests and colonoscopy is recommended for those over 50 years of age.
Food residue leaving the sigmoid colon enters the rectum in the pelvis, near the third sacral vertebra. The final 20.3 cm (8 in) of the alimentary canal, the rectum extends anterior to the sacrum and coccyx. Even though rectum is Latin for “straight,” this structure follows the curved contour of the sacrum and has three lateral bends that create a trio of internal transverse folds called the rectal valves . These valves help separate the feces from gas to prevent the simultaneous passage of feces and gas.
Finally, food residue reaches the last part of the large intestine, the anal canal , which is located in the perineum, completely outside of the abdominopelvic cavity. This 3.8–5 cm (1.5–2 in) long structure opens to the exterior of the body at the anus. The anal canal includes two sphincters. The internal anal sphincter is made of smooth muscle, and its contractions are involuntary. The external anal sphincter is made of skeletal muscle, which is under voluntary control. Except when defecating, both usually remain closed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?