| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Like the upper limb, the lower limb is divided into three regions. The thigh is that portion of the lower limb located between the hip joint and knee joint. The leg is specifically the region between the knee joint and the ankle joint. Distal to the ankle is the foot . The lower limb contains 30 bones. These are the femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges (see [link] ). The femur is the single bone of the thigh. The patella is the kneecap. The tibia is the larger, weight-bearing bone located on the medial side of the leg, and the fibula is the thin bone of the lateral leg. The bones of the foot are divided into three groups. The ankle portion of the foot is formed by a group of seven bones, each of which is known as a tarsal bone , whereas the mid-foot contains five elongated bones, each of which is a metatarsal bone . The toes contain 14 small bones, each of which is a phalanx bone of the foot .
The femur, or thigh bone, is the single bone of the thigh region ( [link] ). It is the longest and strongest bone of the body, and accounts for approximately one-quarter of a person’s total height. The rounded, proximal end is the head of the femur , which articulates with the acetabulum of the hip bone to form the hip joint .
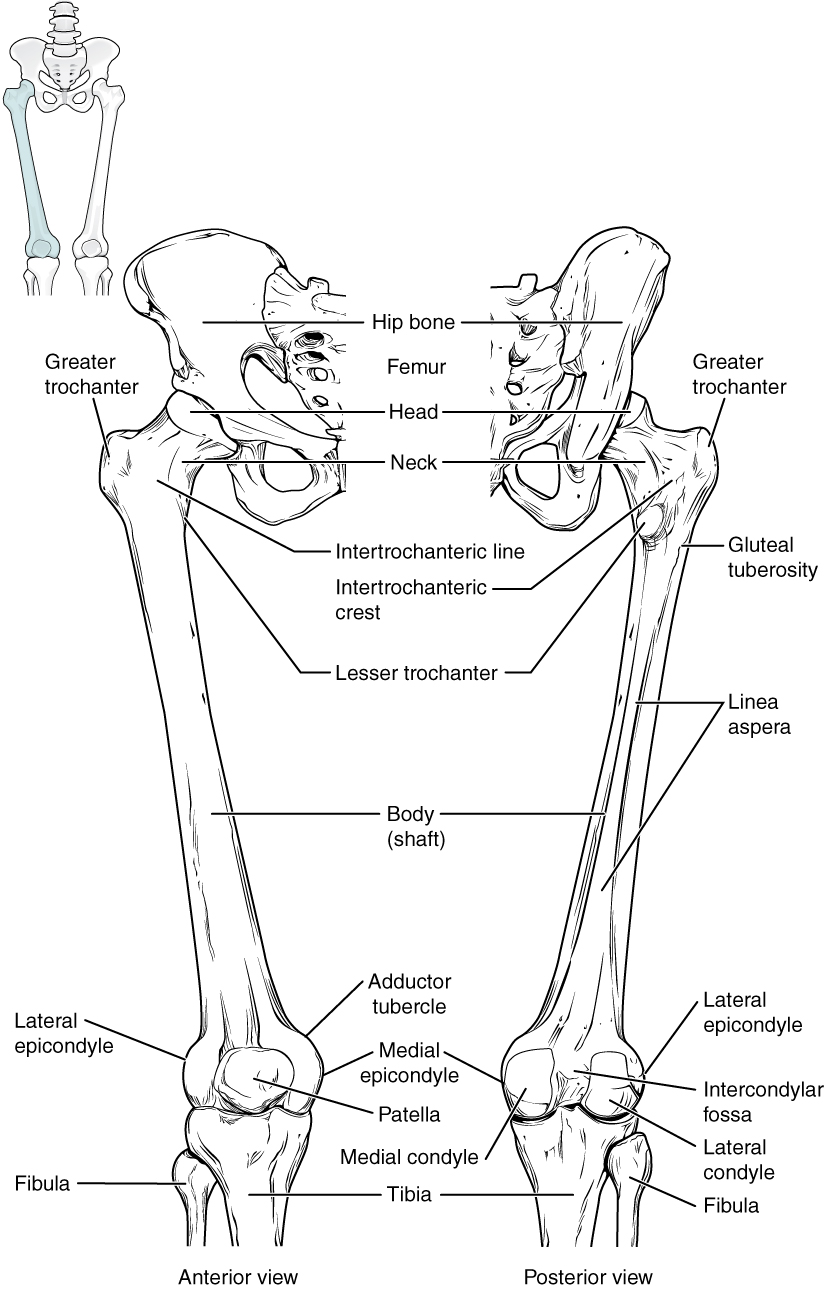
The patella (kneecap) is largest sesamoid bone of the body (see [link] ). A sesamoid bone is a bone that is incorporated into the tendon of a muscle where that tendon crosses a joint. The sesamoid bone articulates with the underlying bones to prevent damage to the muscle tendon due to rubbing against the bones during movements of the joint.
The tibia (shin bone) is the medial bone of the leg and is larger than the fibula, with which it is paired ( [link] ). The tibia is the main weight-bearing bone of the lower leg and the second longest bone of the body, after the femur. The medial side of the tibia is located immediately under the skin and is referred to as the shin.
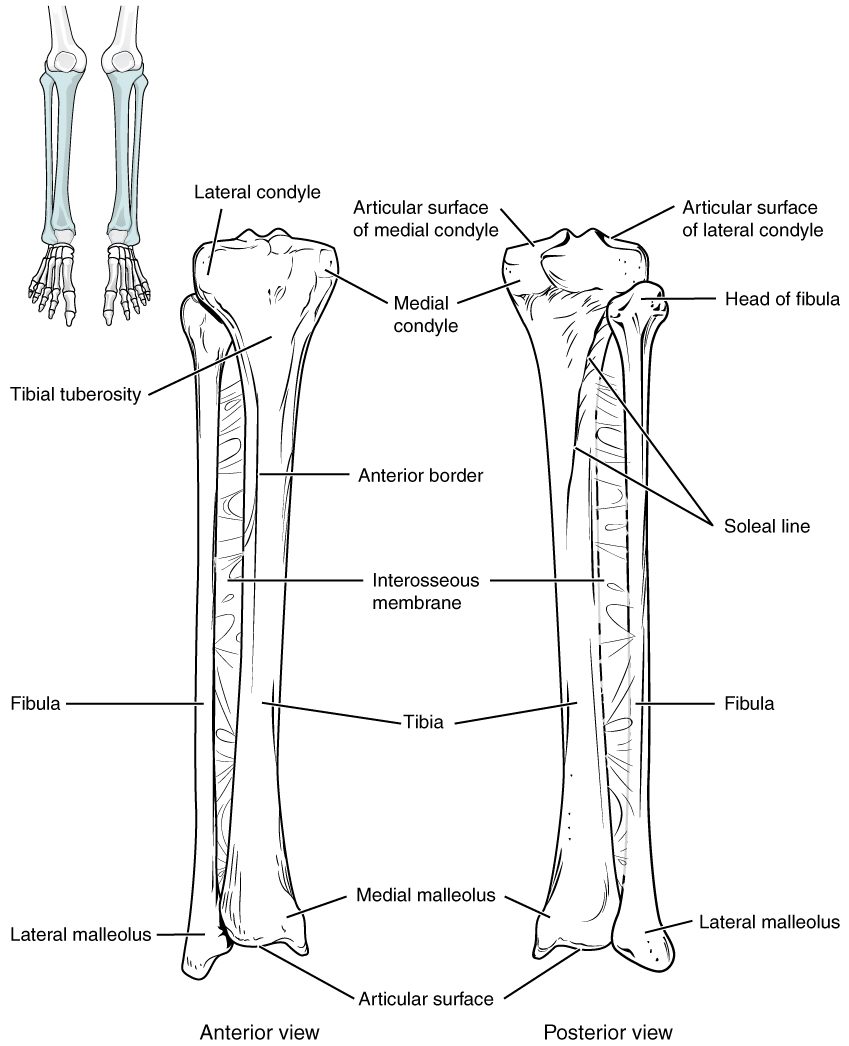
The fibula is the slender bone located on the lateral side of the leg (see [link] ). The fibula does not bear weight. It serves primarily for muscle attachments and thus is largely surrounded by muscles. The bony projections at the bottom of the tibia and fibula are often mistakenly referred to as the ankle bones, but these visible projections are not part of the ankle bones.
The ankle is formed by seven tarsal bones ( [link] ). The most superior bone is the talus . This has a relatively square-shaped, upper surface that articulates with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint . Inferiorly, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone), the largest bone of the foot, which forms the heel.
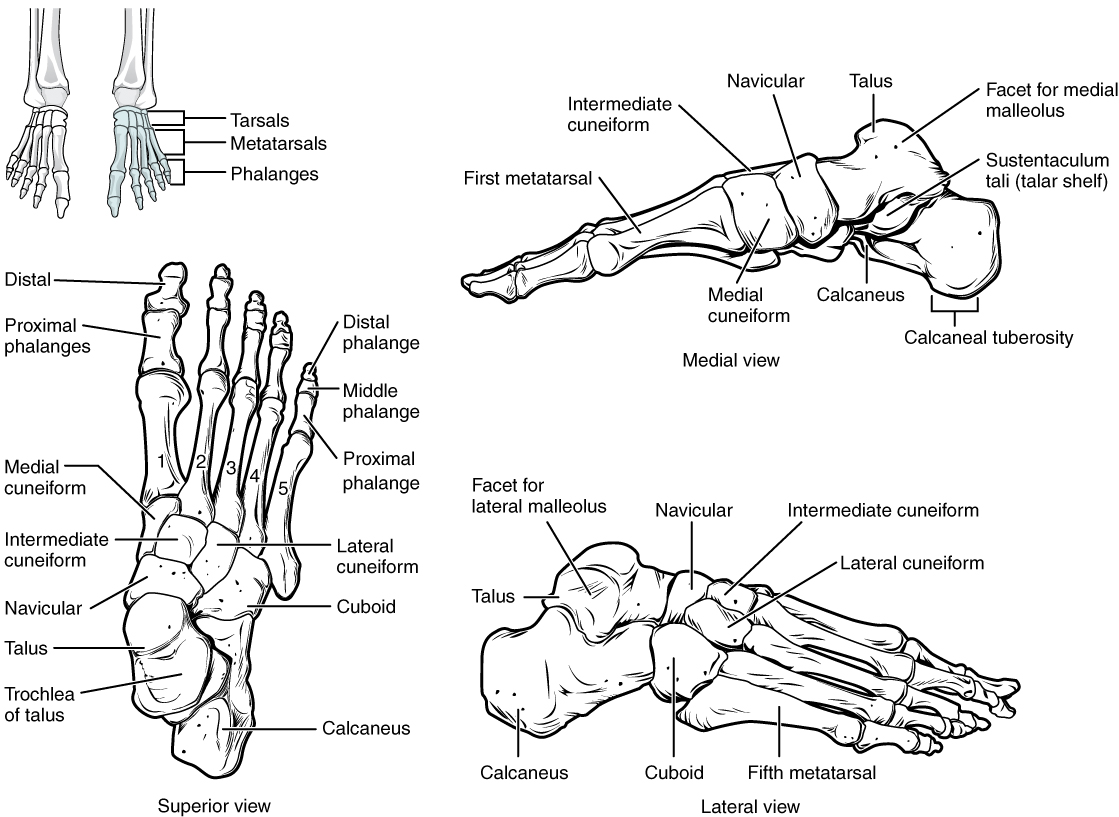
The anterior half of the foot is formed by the five metatarsal bones, which are located between the tarsal bones of the posterior foot and the phalanges of the toes (see [link] ). The first metatarsal bone is shorter and thicker than the others. The second metatarsal is the longest. The heads of the metatarsal bones also rest on the ground and form the ball (anterior end) of the foot.
The toes contain a total of 14 phalanx bones (phalanges), arranged in a similar manner as the phalanges of the fingers (see [link] ). The big toe has two phalanx bones. The remaining toes all have 3 phalanges.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Skeletal system' conversation and receive update notifications?