| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Plasma membranes must allow certain substances to enter and leave a cell, while preventing harmful material from entering and essential material from leaving. In other words, plasma membranes are selectively permeable —they allow some substances through but not others. If they were to lose this selectivity, the cell would no longer be able to sustain itself, and it would be destroyed. Some cells require larger amounts of specific substances than do other cells; they must have a way of obtaining these materials from the extracellular fluids. This may happen passively, as certain materials move back and forth, or the cell may have special mechanisms that ensure transport.
The most direct forms of membrane transport are passive. Passive transport is a naturally occurring phenomenon and does not require the cell to expend energy to accomplish the movement. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion. A physical space in which there is a different concentration of a single substance is said to have a concentration gradient .
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of perfume in a room filled with people. The perfume is at its highest concentration in the bottle and is at its lowest at the edges of the room. The perfume vapor will diffuse, or spread away, from the bottle, and gradually, more and more people will smell the perfume as it spreads. Materials move within the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion ( [link] ). Diffusion expends no energy. Rather the different concentrations of materials in different areas are a form of potential energy, and diffusion is the dissipation of that potential energy as materials move down their concentration gradients, from high to low.
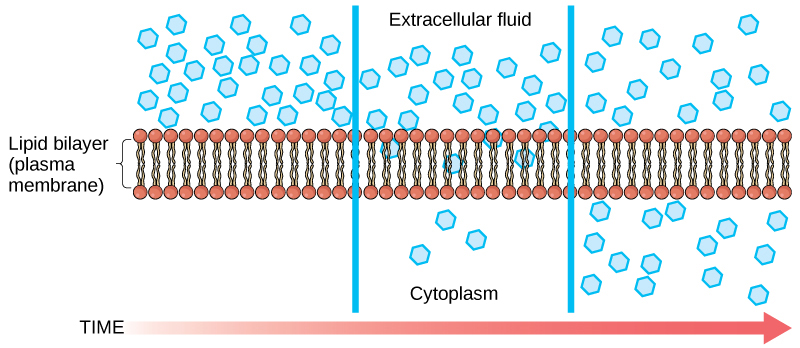
For an animation of the diffusion process in action, view this short video on cell membrane transport.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane according to the concentration gradient of water across the membrane. Whereas diffusion transports material across membranes and within cells, osmosis transports only water across a membrane and the membrane limits the diffusion of solutes in the water. Osmosis is a special case of diffusion. Water, like other substances, moves from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. Imagine a beaker with a semipermeable membrane, separating the two sides or halves ( [link] ). On both sides of the membrane, the water level is the same, but there are different concentrations on each side of a dissolved substance, or solute , that cannot cross the membrane. If the volume of the water is the same, but the concentrations of solute are different, then there are also different concentrations of water, the solvent, on either side of the membrane.
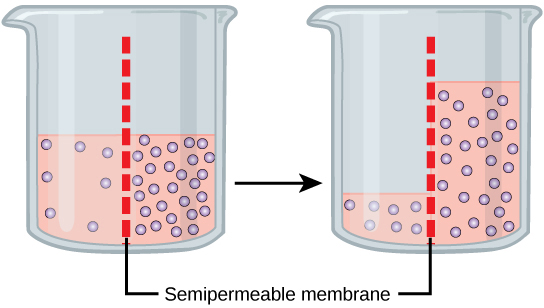
A principle of diffusion is that the molecules move around and will spread evenly throughout the medium if they can. However, only the material capable of getting through the membrane will diffuse through it. In this example, the solute cannot diffuse through the membrane, but the water can. Water has a concentration gradient in this system. Therefore, water will diffuse down its concentration gradient, crossing the membrane to the side where it is less concentrated. This diffusion of water through the membrane—osmosis—will continue until the concentration gradient of water goes to zero. Osmosis proceeds constantly in living systems.
The passive forms of transport, diffusion and osmosis, move material of small molecular weight. Substances diffuse from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, and this process continues until the substance is evenly distributed in a system. In solutions of more than one substance, each type of molecule diffuses according to its own concentration gradient. Many factors can affect the rate of diffusion, including concentration gradient, the sizes of the particles that are diffusing, and the temperature of the system.
In living systems, diffusion of substances into and out of cells is mediated by the plasma membrane. Some materials diffuse readily through the membrane, but others are hindered, and their passage is only made possible by protein channels and carriers. The chemistry of living things occurs in aqueous solutions, and balancing the concentrations of those solutions is an ongoing problem. In living systems, diffusion of some substances would be slow or difficult without membrane proteins.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Environmental biology' conversation and receive update notifications?