| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The website of the U.S. Congress Visitor Center contains a number of interesting online exhibits and informational tidbits about the U.S. government’s “first branch” (so called because it is described in Article I of the Constitution).
The Constitution specifies that every state will have two senators who each serve a six-year term. Therefore, with fifty states in the Union, there are currently one hundred seats in the U.S. Senate. Senators were originally appointed by state legislatures, but in 1913, the Seventeenth Amendment was approved, which allowed for senators to be elected by popular vote in each state. Seats in the House of Representatives are distributed among the states based on each state’s population and each member of the House is elected by voters in a specific congressional district. Each state is guaranteed at least one seat in the House ( [link] ).
| The 114th Congress | ||
|---|---|---|
| House of Representatives | Senate | |
| Total Number of Members | 435 | 100 |
| Number of Members per State | 1 or more, based on population | 2 |
| Length of Term of Office | 2 years | 6 years |
| Minimum Age Requirement | 25 | 30 |
Congressional apportionment today is achieved through the equal proportions method , which uses a mathematical formula to allocate seats based on U.S. Census Bureau population data, gathered every ten years as required by the Constitution. At the close of the first U.S. Congress in 1791, there were sixty-five representatives, each representing approximately thirty thousand citizens. Then, as the territory of the United States expanded, sometimes by leaps and bounds, the population requirement for each new district increased as well. Adjustments were made, but the roster of the House of Representatives continued to grow until it reached 435 members after the 1910 census. Ten years later, following the 1920 census and with urbanization changing populations across the country, Congress failed to reapportion membership because it became deadlocked on the issue. In 1929, an agreement was reached to permanently cap the number of seats in the House at 435.
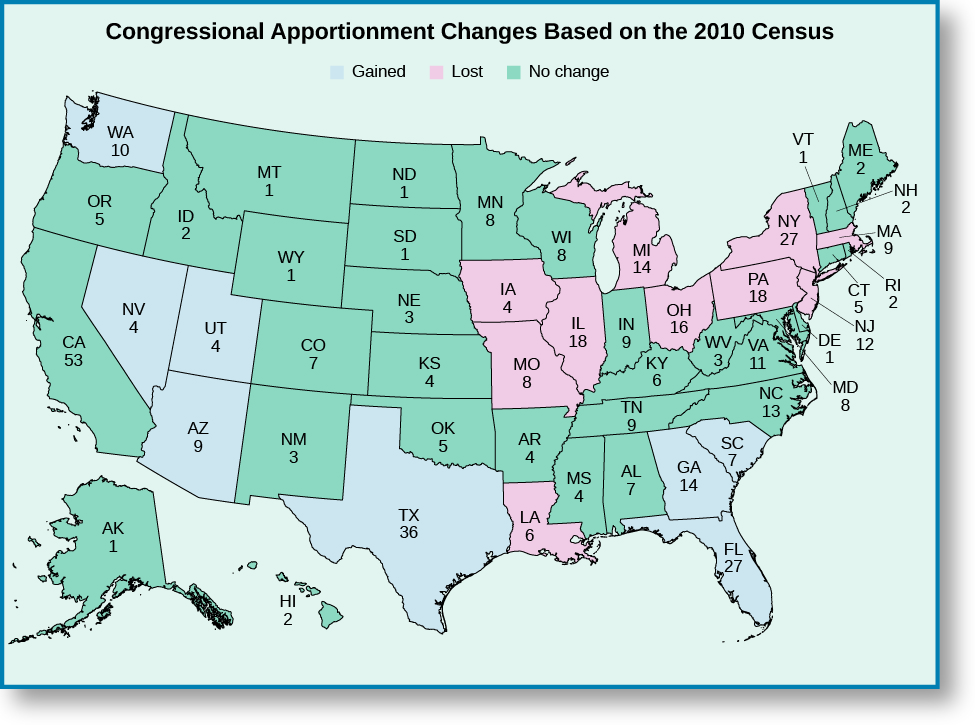
Redistricting occurs every ten years, after the U.S. Census has established how many persons live in the United States and where. The boundaries of legislative districts are redrawn as needed to maintain similar numbers of voters in each while still maintaining a total number of 435 districts. Because local areas can see their population grow as well as decline over time, these adjustments in district boundaries are typically needed after ten years have passed. Currently, there are seven states with only one representative (Alaska, Delaware, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Vermont, and Wyoming), whereas the most populous state, California, has a total of fifty-three congressional districts ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'American government' conversation and receive update notifications?