| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
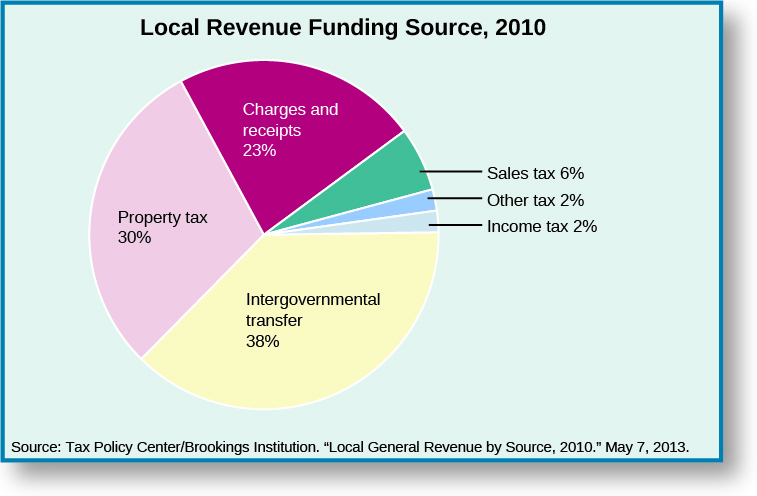
Property taxes can be assessed on homes, land, and businesses. The local government’s reliance on
property tax revenue can be problematic for a number of reasons. First, unlike sales tax, the collection of which is spaced out in small increments across multiple transactions, property tax is collected in one or two lump sums and is therefore highly visible and unpopular.
Another drawback to local governments’ reliance on property tax is that property values vary with the economic health of a given area, the quality of school districts, and the overall desirability of a state, municipality, or county. Significant parcels of land in many cities are also tax-exempt, including property occupied by colleges, churches, and other nonprofit organizations. Boston is a good example as almost 50 percent of the assessed value of property is tax-exempt.
When the mortgage crisis began in 2007, property values decreased in many areas of the country, and many homeowners defaulted on their mortgages because their homes were now worth less than they had borrowed to buy them. With the decline in property values, local governments faced a loss in tax revenue at the same time states were cutting back on aid; tax collections were also down because of economic conditions and the inability to derive income tax from internet sales. A number of municipalities filed for bankruptcy in the face of fiscal distress during the economic recession. Perhaps the best known municipality was Detroit, Michigan, which filed for Chapter 9 bankruptcy in 2013 ( [link] ).

Detroit filed for bankruptcy due to massive debt obligations and demands for repayment that it could not meet due to a perfect storm of economic and democratic factors. The city owed money to investors who had loaned it money, and it had liabilities resulting from its failure to fulfill its pension and healthcare obligations to city workers. The bankruptcy allowed the city time to develop an exit strategy and negotiate with creditors and union representatives in an effort to restructure its debt load.
Detroit’s fiscal condition only highlights the unique challenges municipalities face. Local governments have to provide many of the same services as state and national governments, but they are often constrained by the boundaries the state prescribes. They may not have the authority to raise revenue above a certain threshold, and they do not have the ability to pass expenses on to another level of government because they lack sovereignty.
The power structure of government established in the Articles of Confederation was rebalanced in the Constitution to ensure that both the central and the regional governments had some degree of authority and autonomy. Federal and state governments have managed to work out sharing power throughout history, with the federal government often using fiscal policy to encourage compliance from the states. The taxing power of local governments means they face unique pressures during economic downturns.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'American government' conversation and receive update notifications?