| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
White phosphorus was originally made commercially for the match industry in the 19 th century, by distilling off phosphorus vapor from precipitated phosphates, mixed with ground coal or charcoal, [link] . The precipitated phosphates were made from ground-up bones that had been de-greased and treated with strong acids. This process is, however, obsolete due to the submerged-arc furnace for phosphorus production was introduced to reduce phosphate rock. Calcium phosphate (phosphate rock) is heated to 1200 - 1500 °C with SiO 2 and coke (impure carbon) to produce vaporized tetraphosphorus, P 4 .
The physical properties of the Group 15 elements ( [link] ) encompasses a gas (N 2 ), a non-metallic solid (P 4 ), metalloids (As and Sb), and a metal (Bi).
| Element | Mp (°C) | Bp (°C) | Density (g/cm 3 ) |
| N | -210.00 | -195.79 | 1.251 g/L (0 °C @ 101.325 kPa) |
| P | 44.2 (white), 610 (black) | 280.5 (white), 416 - 590 (sub., red), 620 (sub, violet) | 1.823 (white), 2.2 - 2.34 (red), 2.36 (violet), 2.69 (black) |
| As | 817 | 615 (sub.) | 5.727 |
| Sb | 630.63 | 1587 | 6.697 (solid), 6.53 (liquid) |
| Bi | 271.5 | 1564 | 9.78 (solid), 10.05 (liquid) |
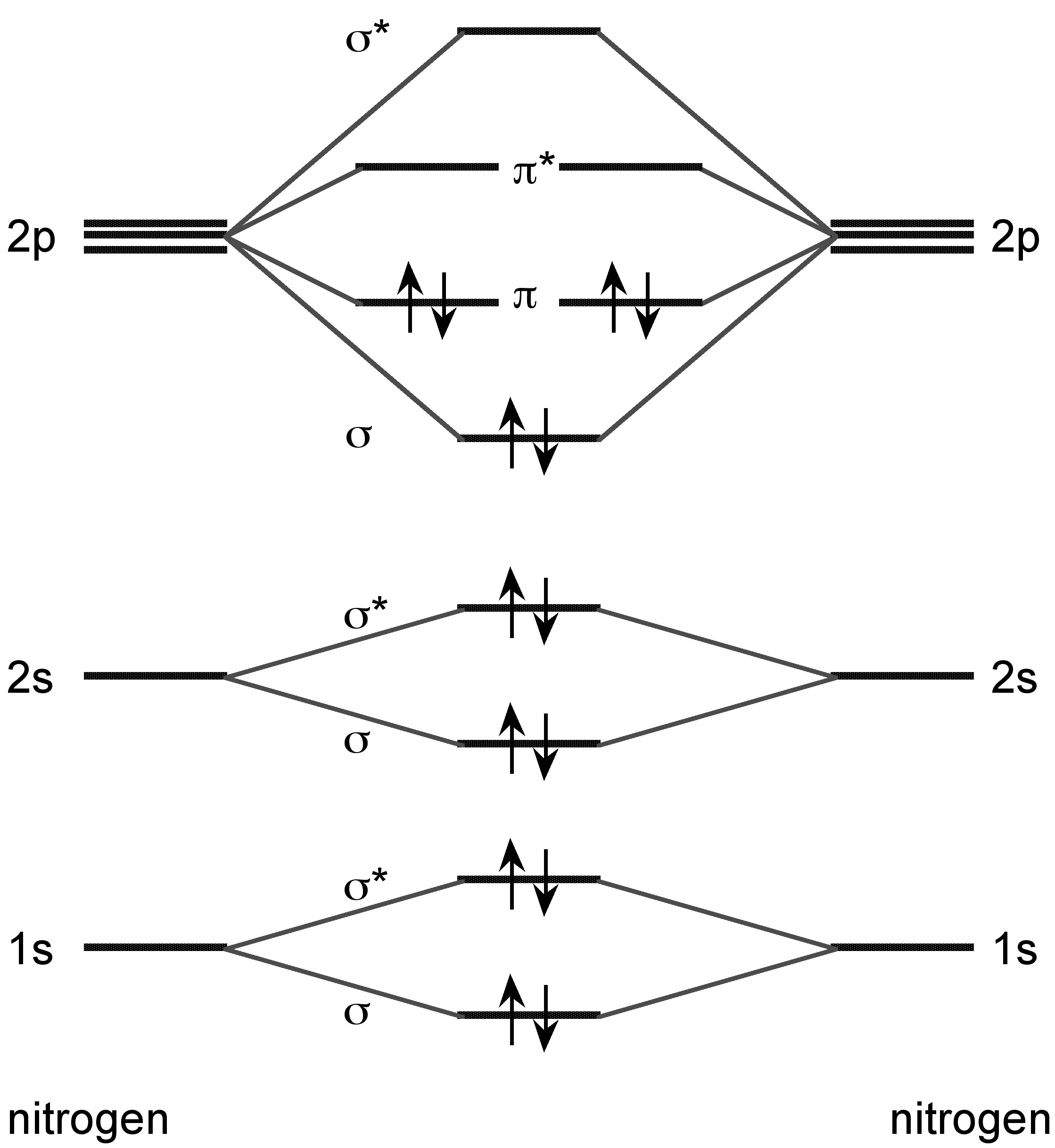
Nitrogen forms a dimer in the vapor phase with a triple bond ( [link] ). In the vapor phase above 800 °C tetraphosphorus (P 4 ) is partially dissociated to P 2 .
Phosphorus forms a number of allotropes with very different properties ( [link] ). Red phosphorus is an intermediate phase between the white and violet forms. Scarlet phosphorus is obtained by allowing a solution of white phosphorus in carbon disulfide to evaporate in sunlight. Black phosphorus is formed by heating white phosphorus under high pressures ( ca . 12,000 atmospheres).

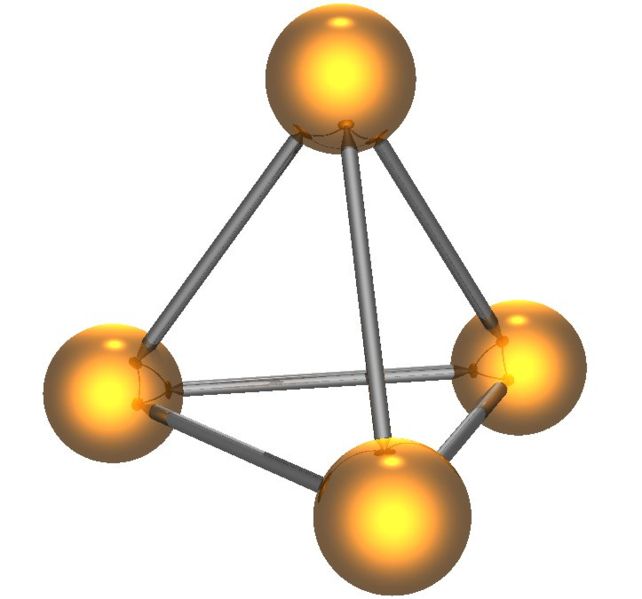
White phosphorus has two forms, low-temperature β form and high-temperature α form; both of which contain the P4 tetrahedron ( [link] ). White phosphorus is the least stable, the most reactive, most volatile, less dense, and most toxic of the allotropes.
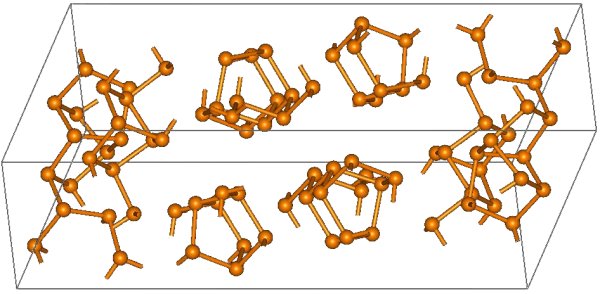
The structural relationship between white and red phosphorus involves breaking one of the P-P bonds in the P 4 unit and forming a bond with a neighboring tetrahedron to give a chain structure ( [link] ). Red phosphorus is formed by heating white phosphorus to 250 °C or by exposing white phosphorus to sunlight. Actually red phosphorus is not a single allotrope, but rather an intermediate phase between the white and violet phosphorus, and most of its properties have a range of values ( [link] ).
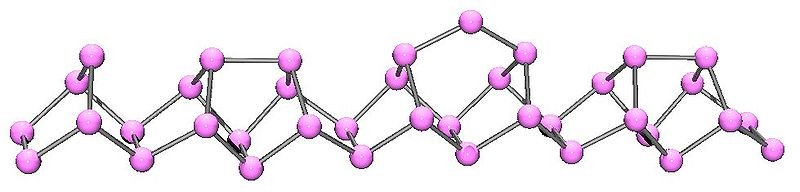
Violet phosphorus ( [link] ) is the thermodynamic stable form of phosphorus that is produced by heating red phosphorus above 550 °C. Due to the synthesis being developed by Johann Hittorf ( [link] ) it is sometimes known as Hittorf's phosphorus .

Black phosphorus is the least reactive allotrope and the thermodynamic stable form below 550 °C. It is also known as β-metallic phosphorus and has a structure somewhat resembling that of graphite ( [link] ).
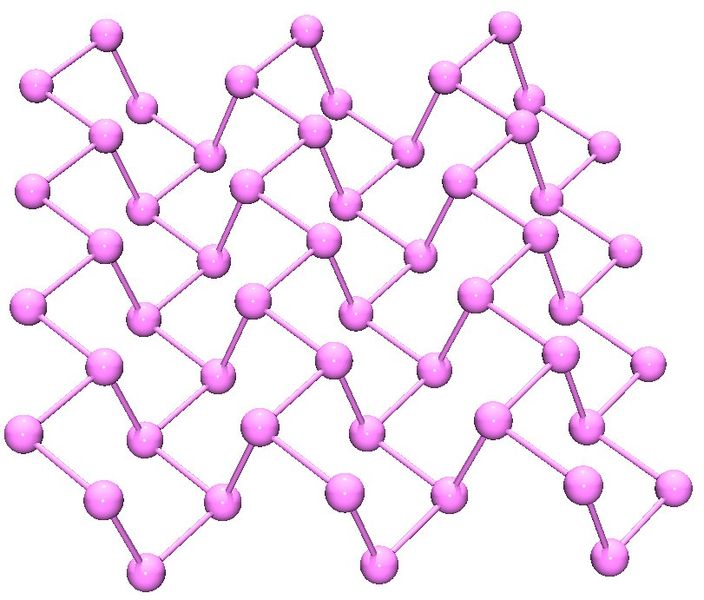
In a similar manner to phosphorus, arsenic has several allotropes some of which a structurally related to those of phosphorus. Grey arsenic has a structure similar to black phosphorus ( [link] ). Yellow arsenic (As 4 ) is soft and waxy with a structure similar to too P 4 ( [link] ). Finally, black arsenic is similar in structure to red phosphorus ( [link] ). Antimony and bismuth are both traditional metals and have trigonal hexagonal structures ( a = 4.299, c = 11.25 Å, and a = 4.537, c = 11.838 Å, respectively).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?