| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
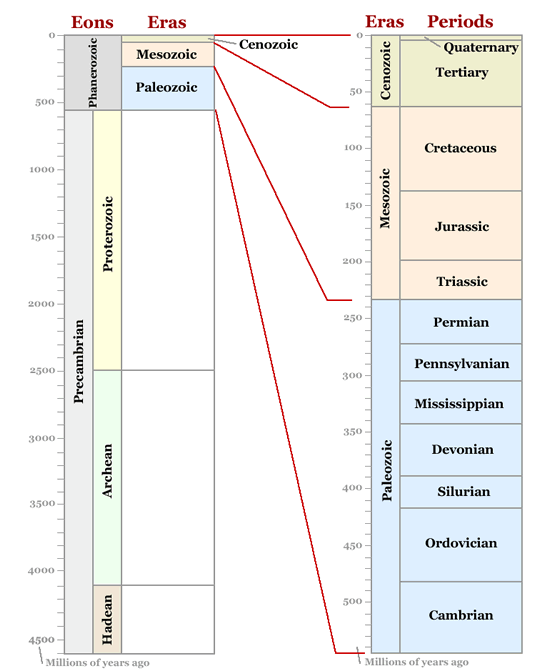
Note that the time scale above shows the Carboniferous period as represented by the Pennsylvanian and Mississippian separately. This is not always done.
Geological time: interactive site: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/variation/time/
Geological time: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/change/deeptime/index.html
The earth’s history can be traced over MANY millions of years, so scientists have developed a geological time scale to help visualize theseperiods. This vast amount of time is divided into eons, eras and periods for easier reference. You MUST know the names of the three ERAS:
So, for example, the most recent eon is divided into 3 eras, called the
Paleozoic (meaning ancient life)
Mesozoic (meaning middle life)
Caenozoic (meaning recent life)
You don’t have to memorize the periods, only the eras . It is important that you become familiar with these names, so that you can use such information in a test or exam. The end of each era is marked by a seriesof catastrophic extinctions, which wiped out many of the previously successful species. Examine the diagram below, showing eras&periods.
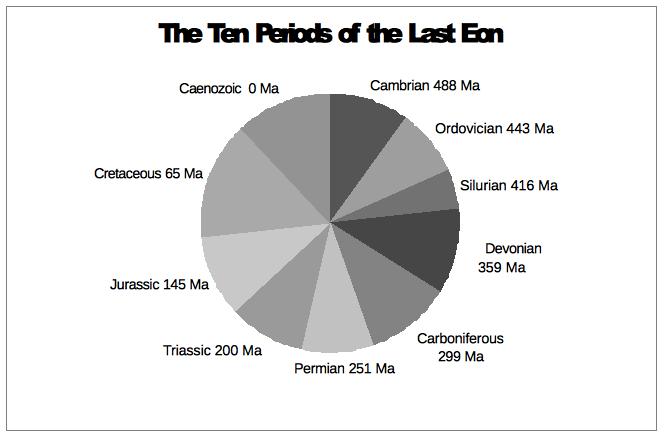
(Ma = million years)
Examine the pie chart and the table, which has the main events of each period
|
PALEOZOIC |
Cambrian period Explosion of multi-cellular life, many trilobites in seas, modern groups develop |
|
Ordovician and Silurian periods Invertebrates with shells, first fish, first plants with vascular tissue | |
|
Devonian period Arthropods on land, first trees, many primitive fish, first amphibians and insects | |
|
Carboniferous period Coal formed, Gondwana is under ice sheets, 1st reptiles develop, many diverse insects | |
|
Permian period Glossopteris trees in Gondwana, many marine Molluscs, mammal-like reptiles | |
|
MESOZOIC |
Triassic period First dinosaurs, first small mammals develop |
|
Jurassic period Dinosaurs develop many forms, 1st birds develop, conifers form, ammonites in seas | |
|
Cretaceous period Flowering plants and insects evolve, more dinosaurs develop, placental mammals | |
|
CAENOZOIC |
Many different forms of mammals and birds develop, the earth cools down after widespread heating, modern animals develop, hominids develop |



Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula: life sciences grade 10' conversation and receive update notifications?