| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. organisms
environment
non-living
2. producers/manufacturers (food producers)
consumers
herbivores
carnivores
omnivores
3. Location, climate, soil, water, atmospheric gases (more specific factors may also be listed, e.g. slope and south- /east-/ west-/ north-facing instead of location, or temperature, rain and wind instead of climate)
Diagram:
1. All materials are recycled in nature and that is why the resources are not depleted. Whatever is taken from the soil or the air is eventually returned to it.
2. Water: from the soil to plants and animals (and into the air), back to the soil (urine and faeces) or air (perspiration, evaporation).
Carbon dioxide: from the air to the plant, fixed in food, to the animal, released into the air.
Components in the soil to the plant, forming nutrients, to animal that eats the plant, returning to the soil with urine or faeces, or when the plant or animal dies
3. To prevent depletion of natural resources/ substances being used up
You were introduced to the concept of the ecosystem in Grade 6. Let us see how much you can remember:
Complete: An ecosystem is all the living ___________________ that live in a
specific _________________ as well as all the __________________ factors
that determine the nature of the environment.
In an ecosystem, the plants are the ____________________ while the animals
are the _______________________ Animals can be divided into three groups
on the basis of their manner of feeding, namely _______________________,
___________________________ and _______________________________
The non-living factors which determine conditions in the ecosystems are
_______________________________, _____________________________,
_______________________________ and ___________________________ .
An ecosystem can be represented diagrammatically as follows:
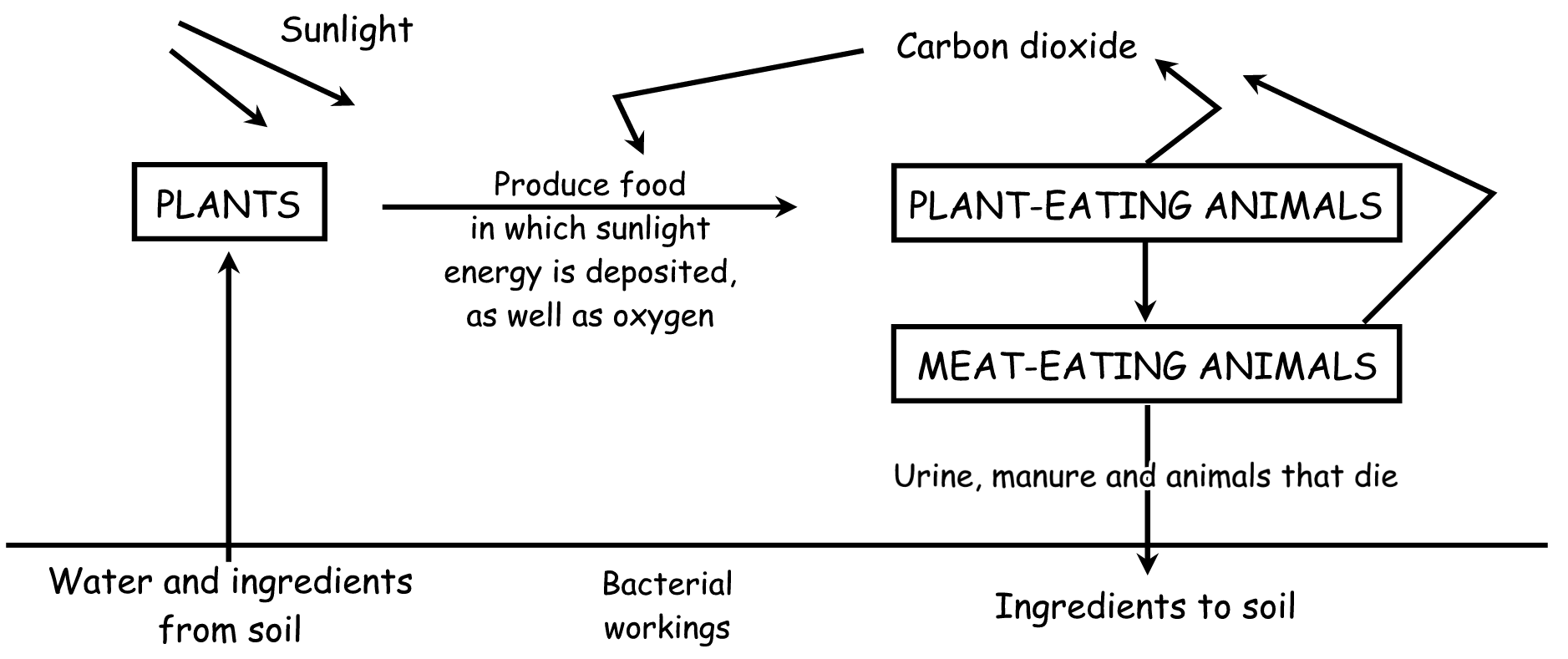
Try to answer the following questions that deal with the diagram:
1. Why is the ecosystem represented as a cycle?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
2. Name three substances/compounds that are circulated in an ecosystem according to the diagram, and give a brief description of each cycle:
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
3. Why is it important for the substances to be circulated?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
Assessment Standard 2.1: We know this when the learner recalls meaningful information (at least definitions and complex facts);
Assessment Standard 2 .3 We know this when the learner interprets information.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?