| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The quadratic formula not only generates the solutions to a quadratic equation, it tells us about the nature of the solutions when we consider the discriminant , or the expression under the radical, The discriminant tells us whether the solutions are real numbers or complex numbers, and how many solutions of each type to expect. [link] relates the value of the discriminant to the solutions of a quadratic equation.
| Value of Discriminant | Results |
|---|---|
| One rational solution (double solution) | |
| perfect square | Two rational solutions |
| not a perfect square | Two irrational solutions |
| Two complex solutions |
For where and are real numbers, the discriminant is the expression under the radical in the quadratic formula: It tells us whether the solutions are real numbers or complex numbers and how many solutions of each type to expect.
Use the discriminant to find the nature of the solutions to the following quadratic equations:
Calculate the discriminant for each equation and state the expected type of solutions.
There will be one rational double solution.
As is a perfect square, there will be two rational solutions.
As is a perfect square, there will be two rational solutions.
There will be two complex solutions.
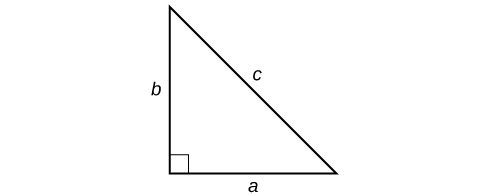
One of the most famous formulas in mathematics is the Pythagorean Theorem . It is based on a right triangle, and states the relationship among the lengths of the sides as where and refer to the legs of a right triangle adjacent to the angle, and refers to the hypotenuse. It has immeasurable uses in architecture, engineering, the sciences, geometry, trigonometry, and algebra, and in everyday applications.
We use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the length of one side of a triangle when we have the lengths of the other two. Because each of the terms is squared in the theorem, when we are solving for a side of a triangle, we have a quadratic equation. We can use the methods for solving quadratic equations that we learned in this section to solve for the missing side.
The Pythagorean Theorem is given as
where and refer to the legs of a right triangle adjacent to the angle, and refers to the hypotenuse, as shown in [link] .
Find the length of the missing side of the right triangle in [link] .
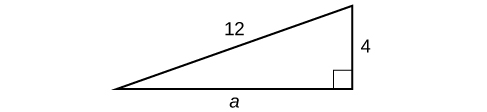
As we have measurements for side b and the hypotenuse, the missing side is a.
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve the right triangle problem: Leg a measures 4 units, leg b measures 3 units. Find the length of the hypotenuse.
units
Access these online resources for additional instruction and practice with quadratic equations.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?