| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
If your answer was yes , explain it briefly in writing. If your answer was no , have a careful look at the following:
Do you know that your body consists of nine different systems? Three of them are the skeleton , the muscle system and the respiratory system .
Assignment

 |
A system is therefore a set of units that work together to perform a certain task.
Example: your skeleton consists of your skull (a unit) and all the other bones in your body (also a unit) that form a strong framework (task) for your body.
In technology we find four systems, namely the electrical , mechanical , hydraulic (fluid pressure) and pneumatic (air pressure) systems.
In this module we look at mechanical systems. An example of a big mechanical system is a bicycle. A mechanical system uses energy to carry out a specific function. This can be to change the speed, the direction or the force applied.
Assignment
Study the illustration with labels and answer the questions that follow:
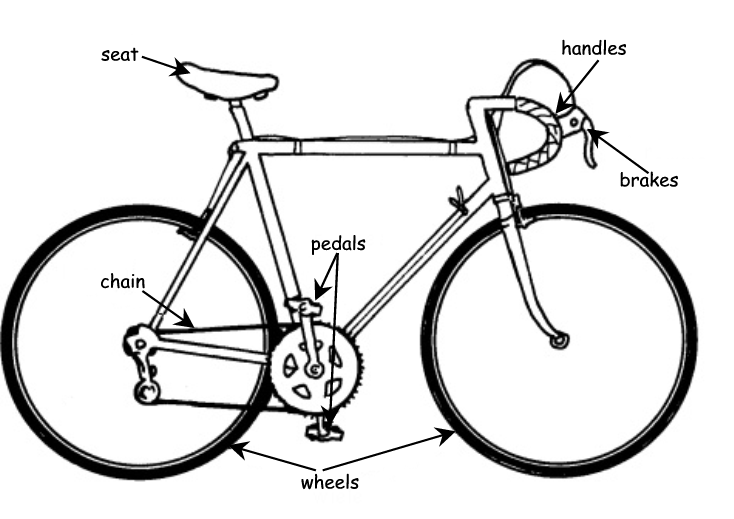
| Part / Parts | Function | |
| a) propulsion unit? | ||
| b) steering unit? | ||
| c) stopping unit? |
[LO 1.2]
If we “break up” the bicycle into different parts according to the task that each one carries out, it is easier to understand how each unit works. Each unit can also be broken up into smaller systems, namely an input , a processing and an output unit.
Assignment
Control can be exercised by means of an open or a closed system. An open system can be controlled, while a closed system works automatically. (You will learn more about this in the higher grades.)
Examples of mechanical systems are depicted in the pictures below, and next to each is the name of the type of mechanical system.
There are mainly four types of movement that a mechanical system can perform if a force is applied to it:
a linear movement (in a straight line and in one direction).
a to-and-fro movement (forwards and backwards in a straight line).
a rotating movement (movement in a circle, like a wheel turning).
a swing movement (a forwards and backwards movement in an arch like a swing).
Assignment
A machine is a combination of different mechanisms/mechanical systems.
[LO 1.3]
The earth’s gravitation causes all objects to be attracted to the earth. However, people have designed mechanical systems to allow machines to move in different directions and at different speeds. Wheels, levers, pulleys and gears make it easier to make a heavy object move.
LO 1
TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SKILLS
The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly, using appropriate information and communication technologies.
We know this when the learner:
Investigates:
1.2 finds out about existing products relevant to a problem, need or opportunity, and identifies some design aspects (e.g. who it is for, what it looks like, what it is for, what it is made of);
1.3.1 planning investigations;
1.3.3 processing and interpreting data;
1.3.4 evaluating and communicating findings.
Makes:
1.7 outlines a plan that shows the steps for making, including drawings or sketches of main parts;
1.8 uses suitable tools and materials to make products by measuring out, cutting or separating, shaping or forming, joining or combining, and finishing the chosen material;
Evaluates:
1.10 evaluates, with assistance, the product according to the design brief and given specifications and constraints (e.g. people, purpose, environment), and suggests improvements and modifications if necessary;
1.11 evaluates the plan of action followed and suggests improvements and modifications if necessary;
Communicates:
LO 2
TECHNOLOGICAL KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING
The learner will be able to understand and apply relevant technological knowledge ethically and responsibly.
We know this when the learner:
Systems and control:
(a)
1. Answers will vary
2. respiratory system skeletal system muscular system
3. nervous system digestive system glandular system
nervous system
e) electrical f) mechanical
(c) Parts Function
1. a) pedals, chain; wheels motion
b) handles; voorwiel change of direction
c) brakes stop
(d)
1. Answers from dictionary of your choice.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?