| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Prior to Darwin’s time, classification was merely cataloging, and the cataloging system used morphology as the key characteristic for determining relationships. There is no theoretical basis for preferring one morphological cataloging scheme over another, however. The concept of evolution, and its prediction of common descent, provided that theoretical basis. Relationships, based on common ancestry, should provide a more accurate taxonomy. Besides being similar in size or shape, two organisms that were most closely related should have a common ancestor in the more recent past than would be the case for two less closely related organisms. The evolutionary history of the taxa was valuable and necessary information in this approach. The word for the determination of the evolutionary history of a species or group of species is phylogenetics , and the hypothesized evolutionary history and relationships of a species or group of species is a phylogeny . It quickly became clear that a taxonomic scheme that reflected phylogeny would be better than the arbitrary morphology-based schemes of the past. However, at the time of Darwin, and for many years thereafter, it was not exactly easy to discern the evolutionary history of organisms. So the development of a true phylogenetic taxonomy took a long time to develop, and, indeed, it is still being developed.
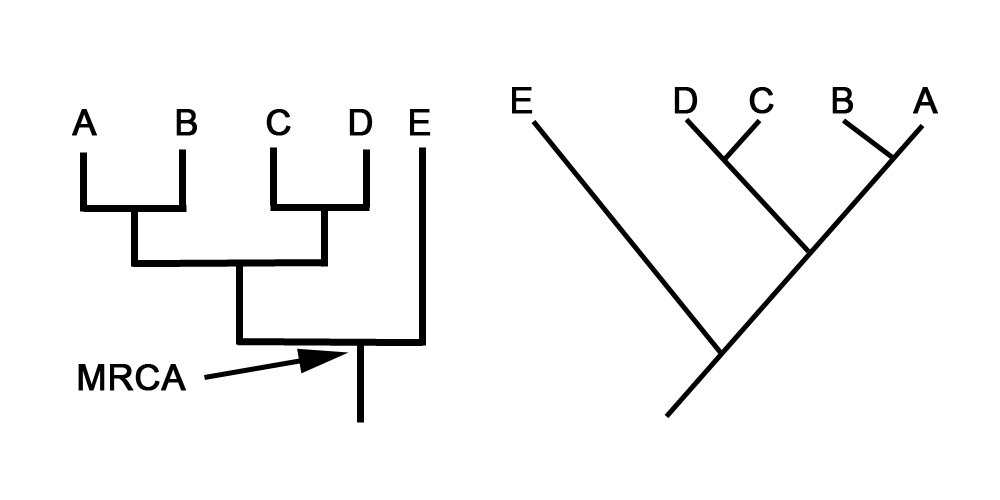
The current approach to determining relationships between two (or more) groups of organisms is the construction of what are called phylogenetic trees . Phylogenetic trees are hypothesized reconstructions of evolutionary history. They depict arrays of extant (currently living) organisms at the tips of the branches, and branch points that indicate a common ancestor. ( [link] ). A, B, C, D, and E in this diagram are the species being considered. The vertical axis represents the passage of time. The branch points represent organisms that are putative common ancestors of the organisms on the branches above. In some cases these ancestors are known species from the fossil record. In most cases they are not. A common ancestor for all of these organisms is the branch point above the root of the tree, known as the most recent common ancestor (MRCA). These trees can be horizontal and vertical arrangements, or diagonal arrangements, both of which are shown here. The two arrangements, in this case, represent identical trees in terms of the hypothesized relationships of species A, B, C, D , and E.
Another critical point about these trees is that if you rotate the structures, using one of the branch points as a pivot, you don’t change the relationships. So just like the two trees above, which show the same relationships even though they are formatted differently, all of the trees in Figure 4.3 ( [link] ) are essentially identical in terms of depicting the relationships between the species A, B, C, and D. If you don’t see how that is true, just concentrate on the relationships and the branch points rather than on the sequence of species (A,B, C and D) shown across the tops of these diagrams. That sequence is not important; the branch structure underlying the sequence is what you will need to focus on.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?