| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Uniform circular motion, on the other hand, involves an acceleration, which is not one dimensional. It is constant in magnitude, but keeps changing direction along the line connecting the center of the circle and the particle. The main point is that acceleration in uniform circular motion is two dimensional unlike projectile motion in which acceleration (due to gravity) is one dimensional. As a more generalized case, we can think of circular motion in which both magnitude and direction of acceleration is changing. Such would be the case when particle moves with varying speed along the circular path.
In the nutshell, we can conclude that two dimensional motion types (circular motion, elliptical motion and other non-linear motion) involve varying acceleration in two dimensions. In order to facilitate study of general class of motion in two dimensions, we introduce the concept of components of acceleration in two specific directions. Notably, these directions are not same as the coordinate directions (“x” and “y”). One of the component acceleration is called “tangential acceleration”, which is directed along the tangent to the path of motion and the other is called “normal acceleration”, which is perpendicular to the tangent to the path of motion. Two accelerations are perpendicular to each other. The acceleration (sometimes also referred as total acceleration) is the vector sum of two mutually perpendicular component accelerations,
Two dimensional acceleration
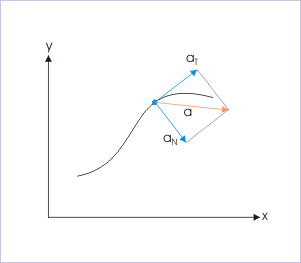
The normal acceleration is also known as radial or centripetal acceleration, , particularly in reference of circular motion.
Tangential acceleration is directed tangentially to the path of motion. Since velocity is also tangential to the path of motion, it is imperative that tangential acceleration is directed in the direction of velocity. This leads to an important meaning. We recall that it is only the component of force in the direction of velocity that changes the magnitude of velocity. This means that component of acceleration in the tangential direction represents the change in the magnitude of velocity (read speed). In non-uniform circular motion, the tangential acceleration accounts for the change in the speed (we shall study non-uniform circular motion in detail in a separate module).
By logical extension, we can define that tangential acceleration is time rate of change of "speed". The speed is highlighted here to underscore the character of tangential acceleration. Mathematically,
This insight into the motion should resolve the differences that we had highlighted earlier, emphasizing that rate of change in the magnitude of velocity (dv/dt) is not equal to the magnitude of rate of change of velocity (|d v /dt|). What we see now that rate of change in the magnitude of velocity (dv/dt) is actually just a component of total acceleration (d v /dt).
It is easy to realize that tangential acceleration comes into picture only when there is change in the magnitude of velocity. For example, uniform circular motion does not involve change in the magnitude of velocity (i.e. speed is constant). There is, therefore, no tangential acceleration involved in uniform circular motion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?