| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Where do weather forecasters get their information?
They get the information from weather satellites, weather balloons and earth stations. Metsat is the name of a weather satellite that orbits the earth.
A camera on Metsat is used for taking photographs of clouds and snow and it also shows approaching storms. The photographs can also be used to identify warm and cold areas of the earth.
Information is collected about the temperature, humidity (this is the moisture in the air), wind speeds and directions, the types of clouds, air pressure (atmospheric pressure) and rainfall. All the information is sent to a weather station where it is fed into a computer for processing.
After this has been done, a weather chart is drawn and sent to all the media (television, radio and newspapers).

Which one of you would like to present today’s weather to the class as it is presented on television?
Try to get hold of a newspaper that has a weather chart each day. Cut it out and study the key that indicates the different types of weather carefully.
Look at the following example:
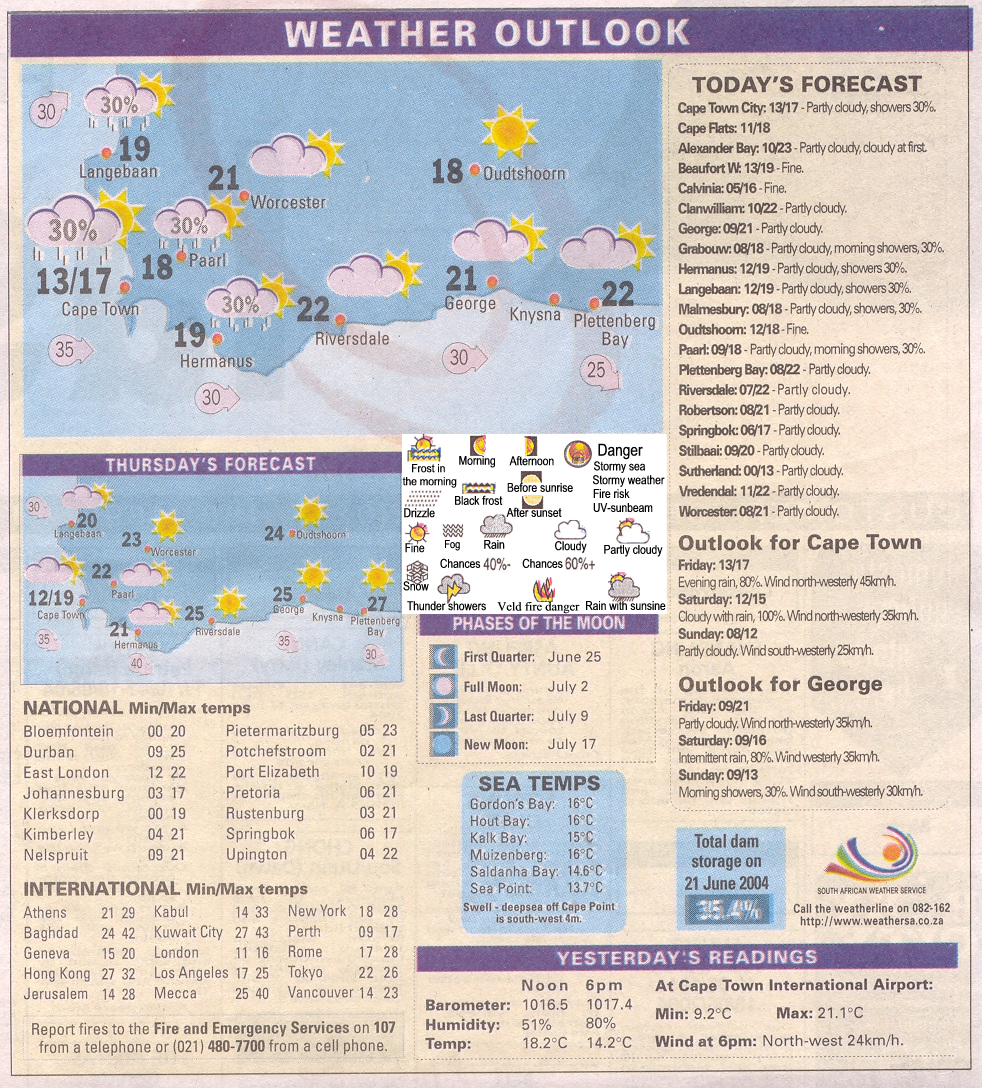
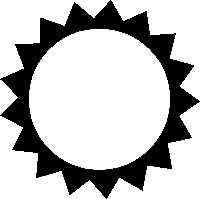
Study the key and write down the correct names of the signs:



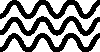





Draw a picture to show your favourite kind of weather.


SUN
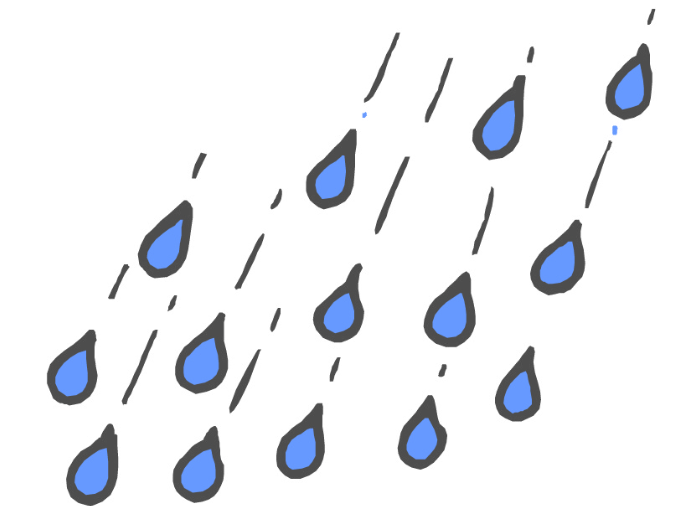

RAIN
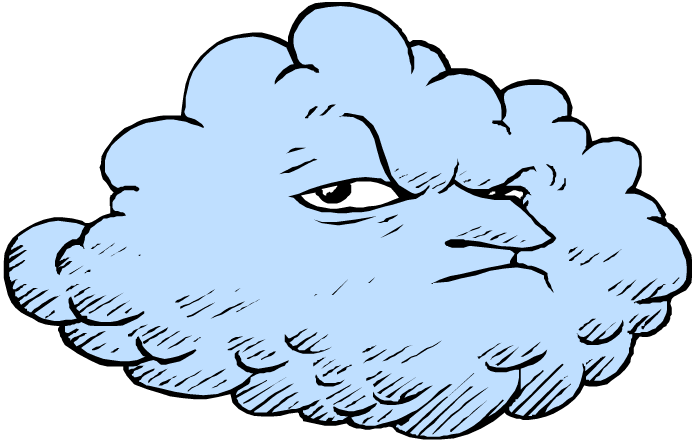

OVERCAST
Keep your own weather chart for one week. Draw the sun, raindrops or a cloud in the weather column, and fill in the wind speed and temperature.
DayWeatherWind speedTemperatureMondayTuesdayWednesdayThursdayFridaySaturdaySunday
LEARNING OUTCOME 1 : SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATIONS
The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard
We know this when the learner
1.1 plans investigations;
1.2 leads investigations and collects data;
1.3 evaluates data and provides feedback on observations.
LEARNING OUTCOME 2 : CONSTRUCTING SCIENCE KNOWLEDGE The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
Assessment Standard
We know this when the learner
2.1 recalls significant information.
LEARNING OUTCOME 3 : SCIENCE, SOCIETY AND THE ENVIRONMENT The learner will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships between science and technology, society and the environment.
Assessment Standard
We know this when the learner
3.1 understands science and technology in the context of history and personal knowledge.
Mr Brain Cell:
Study the key and write down the correct names: see key on map.
Mr Brain Cell:
High pressure: When a high-pressure system moves over the land, it normally means that it is going to be a fine day. Cold air moves out and down and becomes warmer.
Low pressure: A low-pressure system normally brings rain and cloudy conditions. Cold air moves in and up and becomes cold.
Front: We frequently see a front approaching the land. This is only the direction in which the cold or warm air moves.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?