| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
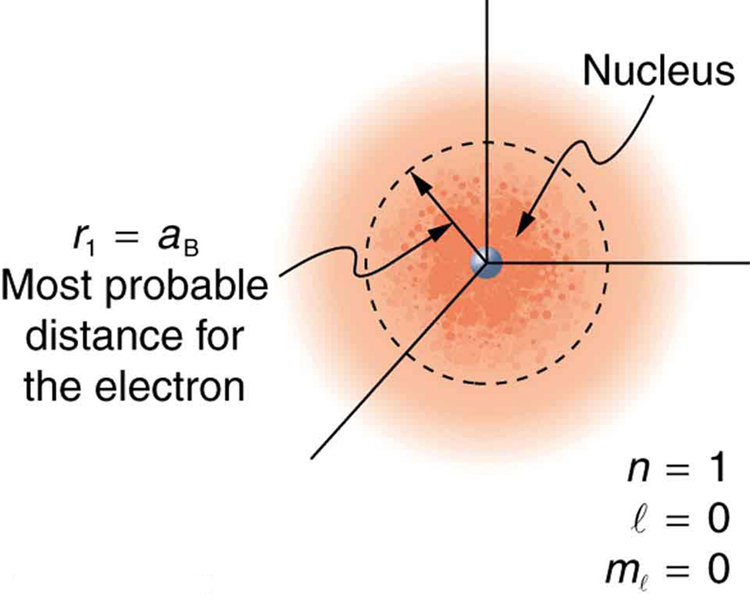
Because of the wave character of matter, the idea of well-defined orbits gives way to a model in which there is a cloud of probability, consistent with Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. [link] shows how this applies to the ground state of hydrogen. If you try to follow the electron in some well-defined orbit using a probe that has a small enough wavelength to get some details, you will instead knock the electron out of its orbit. Each measurement of the electron’s position will find it to be in a definite location somewhere near the nucleus. Repeated measurements reveal a cloud of probability like that in the figure, with each speck the location determined by a single measurement. There is not a well-defined, circular-orbit type of distribution. Nature again proves to be different on a small scale than on a macroscopic scale.
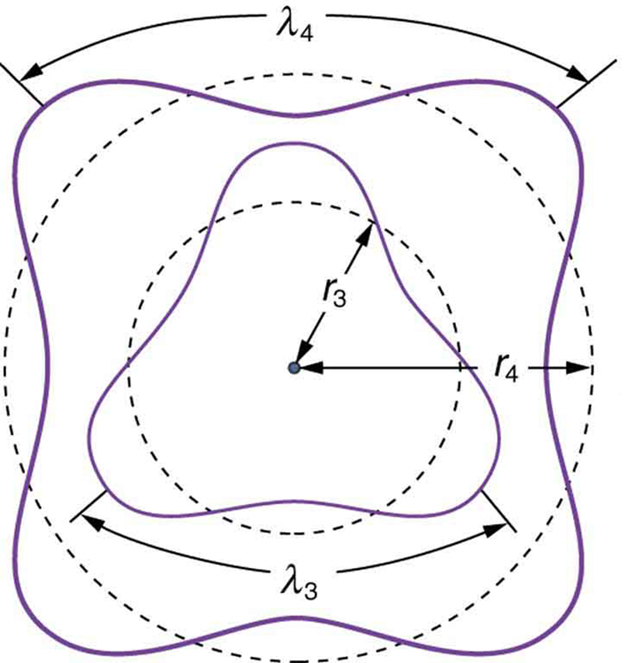
There are many examples in which the wave nature of matter causes quantization in bound systems such as the atom. Whenever a particle is confined or bound to a small space, its allowed wavelengths are those which fit into that space. For example, the particle in a box model describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. This is true in blackbody radiators (atoms and molecules) as well as in atomic and molecular spectra. Various atoms and molecules will have different sets of electron orbits, depending on the size and complexity of the system. When a system is large, such as a grain of sand, the tiny particle waves in it can fit in so many ways that it becomes impossible to see that the allowed states are discrete. Thus the correspondence principle is satisfied. As systems become large, they gradually look less grainy, and quantization becomes less evident. Unbound systems (small or not), such as an electron freed from an atom, do not have quantized energies, since their wavelengths are not constrained to fit in a certain volume.
When do photons, electrons, and atoms behave like particles and when do they behave like waves? Watch waves spread out and interfere as they pass through a double slit, then get detected on a screen as tiny dots. Use quantum detectors to explore how measurements change the waves and the patterns they produce on the screen.

How is the de Broglie wavelength of electrons related to the quantization of their orbits in atoms and molecules?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?