| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
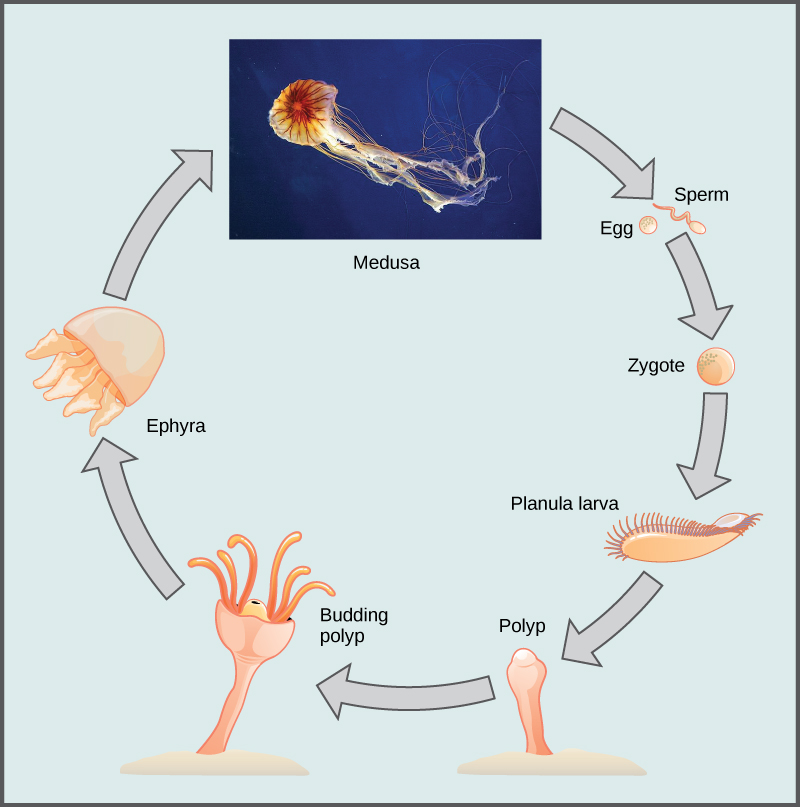
In scyphozoans, nerve cells are scattered all over the body. Neurons may even be present in clusters called rhopalia. These animals possess a ring of muscles lining the dome of the body, which provides the contractile force required to swim through water. Scyphozoans are dioecious animals, that is, the sexes are separate. The gonads are formed from the gastrodermis and gametes are expelled through the mouth. Planula larvae are formed by external fertilization; they settle on a substratum in a polypoid form known as scyphistoma. These forms may produce additional polyps by budding or may transform into the medusoid form. The life cycle ( [link] ) of these animals can be described as polymorphic , because they exhibit both a medusal and polypoid body plan at some point in their life cycle.
Identify the life cycle stages of jellies using this video animation quiz from the New England Aquarium.
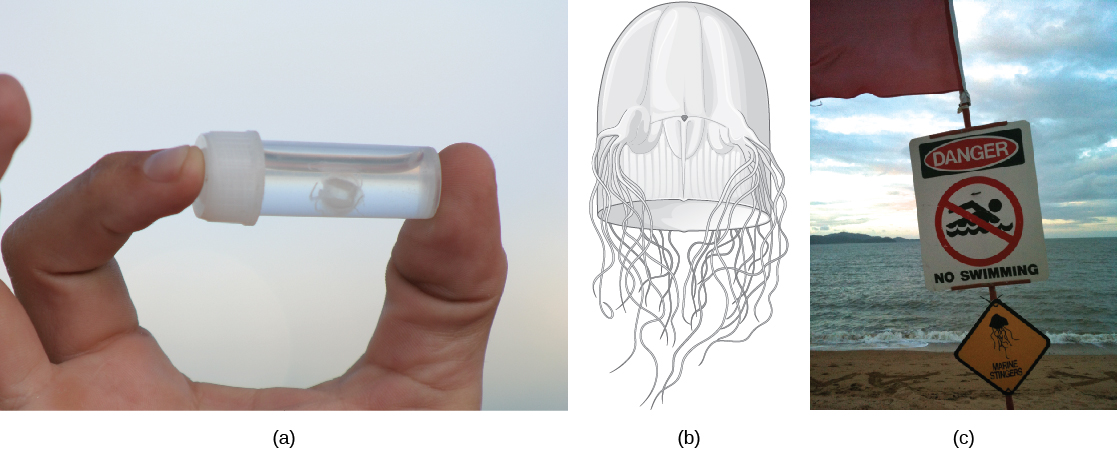
This class includes jellies that have a box-shaped medusa, or a bell that is square in cross-section; hence, are colloquially known as “box jellyfish.” These species may achieve sizes of 15–25 cm. Cubozoans display overall morphological and anatomical characteristics that are similar to those of the scyphozoans. A prominent difference between the two classes is the arrangement of tentacles. This is the most venomous group of all the cnidarians ( [link] ).
The cubozoans contain muscular pads called pedalia at the corners of the square bell canopy, with one or more tentacles attached to each pedalium. These animals are further classified into orders based on the presence of single or multiple tentacles per pedalium. In some cases, the digestive system may extend into the pedalia. Nematocysts may be arranged in a spiral configuration along the tentacles; this arrangement helps to effectively subdue and capture prey. Cubozoans exist in a polypoid form that develops from a planula larva. These polyps show limited mobility along the substratum and, like scyphozoans, may bud to form more polyps to colonize a habitat. Polyp forms then transform into the medusoid forms.
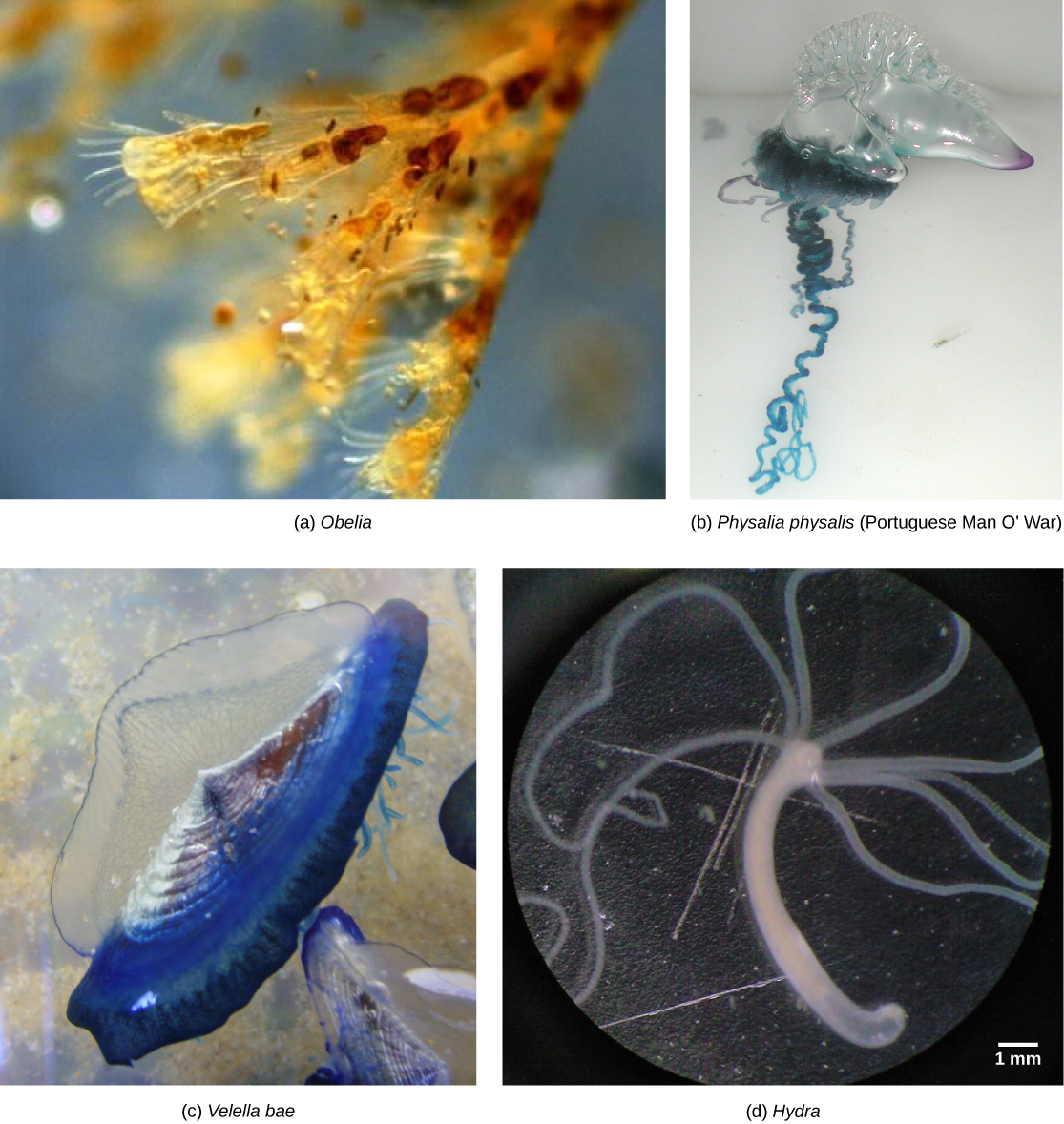
Hydrozoa includes nearly 3,200 species; most are marine, although some freshwater species are known ( [link] ). Animals in this class are polymorphs, and most exhibit both polypoid and medusoid forms in their lifecycle, although this is variable.
The polyp form in these animals often shows a cylindrical morphology with a central gastrovascular cavity lined by the gastrodermis. The gastrodermis and epidermis have a simple layer of mesoglea sandwiched between them. A mouth opening, surrounded by tentacles, is present at the oral end of the animal. Many hydrozoans form colonies that are composed of a branched colony of specialized polyps that share a gastrovascular cavity, such as in the colonial hydroid Obelia . Colonies may also be free-floating and contain medusoid and polypoid individuals in the colony as in Physalia (the Portuguese Man O’ War) or Velella (By-the-wind sailor). Even other species are solitary polyps ( Hydra ) or solitary medusae ( Gonionemus ). The true characteristic shared by all of these diverse species is that their gonads for sexual reproduction are derived from epidermal tissue, whereas in all other cnidarians they are derived from gastrodermal tissue.
Cnidarians represent a more complex level of organization than Porifera. They possess outer and inner tissue layers that sandwich a noncellular mesoglea. Cnidarians possess a well-formed digestive system and carry out extracellular digestion. The cnidocyte is a specialized cell for delivering toxins to prey as well as warning off predators. Cnidarians have separate sexes and have a lifecycle that involves morphologically distinct forms. These animals also show two distinct morphological forms—medusoid and polypoid—at various stages in their lifecycle.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?