| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You may have noticed that the nitrite anion in [link] can have two possible structures with the atoms in the same positions. The electrons involved in the N–O double bond, however, are in different positions:
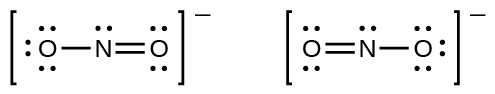
If nitrite ions do indeed contain a single and a double bond, we would expect for the two bond lengths to be different. A double bond between two atoms is shorter (and stronger) than a single bond between the same two atoms. Experiments show, however, that both N–O bonds in have the same strength and length, and are identical in all other properties.
It is not possible to write a single Lewis structure for in which nitrogen has an octet and both bonds are equivalent. Instead, we use the concept of resonance : if two or more Lewis structures with the same arrangement of atoms can be written for a molecule or ion, the actual distribution of electrons is an average of that shown by the various Lewis structures. The actual distribution of electrons in each of the nitrogen-oxygen bonds in is the average of a double bond and a single bond. We call the individual Lewis structures resonance forms . The actual electronic structure of the molecule (the average of the resonance forms) is called a resonance hybrid of the individual resonance forms. A double-headed arrow between Lewis structures indicates that they are resonance forms. Thus, the electronic structure of the ion is shown as:
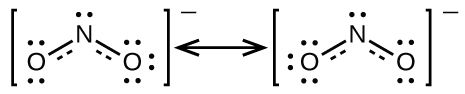
We should remember that a molecule described as a resonance hybrid never possesses an electronic structure described by either resonance form. It does not fluctuate between resonance forms; rather, the actual electronic structure is always the average of that shown by all resonance forms. George Wheland, one of the pioneers of resonance theory, used a historical analogy to describe the relationship between resonance forms and resonance hybrids. A medieval traveler, having never before seen a rhinoceros, described it as a hybrid of a dragon and a unicorn because it had many properties in common with both. Just as a rhinoceros is neither a dragon sometimes nor a unicorn at other times, a resonance hybrid is neither of its resonance forms at any given time. Like a rhinoceros, it is a real entity that experimental evidence has shown to exist. It has some characteristics in common with its resonance forms, but the resonance forms themselves are convenient, imaginary images (like the unicorn and the dragon).
The carbonate anion, provides a second example of resonance:
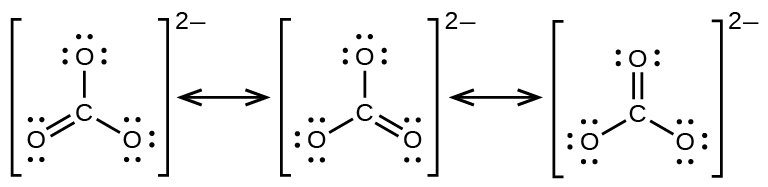
One oxygen atom must have a double bond to carbon to complete the octet on the central atom. All oxygen atoms, however, are equivalent, and the double bond could form from any one of the three atoms. This gives rise to three resonance forms of the carbonate ion. Because we can write three identical resonance structures, we know that the actual arrangement of electrons in the carbonate ion is the average of the three structures. Again, experiments show that all three C–O bonds are exactly the same.
The online Lewis Structure Make includes many examples to practice drawing resonance structures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?