| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Reproductive cloning is a method used to make a clone or an identical copy of an entire multicellular organism. Most multicellular organisms undergo reproduction by sexual means, which involves the contribution of DNA from two individuals (parents), making it impossible to generate an identical copy or a clone of either parent. Recent advances in biotechnology have made it possible to reproductively clone mammals in the laboratory.
Natural sexual reproduction involves the union, during fertilization, of a sperm and an egg. Each of these gametes is haploid, meaning they contain one set of chromosomes in their nuclei. The resulting cell, or zygote, is then diploid and contains two sets of chromosomes. This cell divides mitotically to produce a multicellular organism. However, the union of just any two cells cannot produce a viable zygote; there are components in the cytoplasm of the egg cell that are essential for the early development of the embryo during its first few cell divisions. Without these provisions, there would be no subsequent development. Therefore, to produce a new individual, both a diploid genetic complement and an egg cytoplasm are required. The approach to producing an artificially cloned individual is to take the egg cell of one individual and to remove the haploid nucleus. Then a diploid nucleus from a body cell of a second individual, the donor, is put into the egg cell. The egg is then stimulated to divide so that development proceeds. This sounds simple, but in fact it takes many attempts before each of the steps is completed successfully.
The first cloned agricultural animal was Dolly, a sheep who was born in 1996. The success rate of reproductive cloning at the time was very low. Dolly lived for six years and died of a lung tumor ( [link] ). There was speculation that because the cell DNA that gave rise to Dolly came from an older individual, the age of the DNA may have affected her life expectancy. Since Dolly, several species of animals (such as horses, bulls, and goats) have been successfully cloned.
There have been attempts at producing cloned human embryos as sources of embryonic stem cells. In the procedure, the DNA from an adult human is introduced into a human egg cell, which is then stimulated to divide. The technology is similar to the technology that was used to produce Dolly, but the embryo is never implanted into a surrogate mother. The cells produced are called embryonic stem cells because they have the capacity to develop into many different kinds of cells, such as muscle or nerve cells. The stem cells could be used to research and ultimately provide therapeutic applications, such as replacing damaged tissues. The benefit of cloning in this instance is that the cells used to regenerate new tissues would be a perfect match to the donor of the original DNA. For example, a leukemia patient would not require a sibling with a tissue match for a bone-marrow transplant.
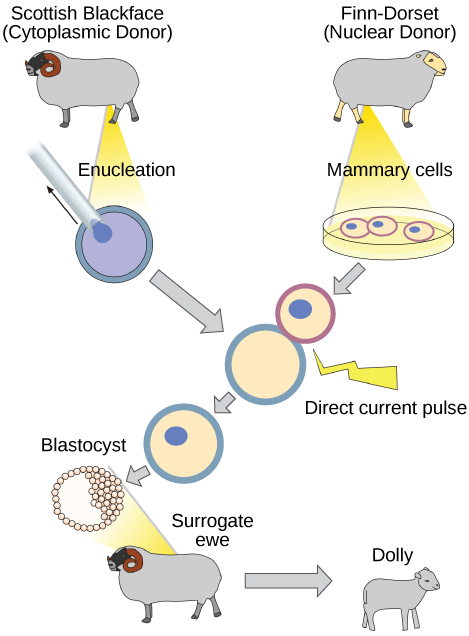
Why was Dolly a Finn-Dorset and not a Scottish Blackface sheep?
Using recombinant DNA technology to modify an organism’s DNA to achieve desirable traits is called genetic engineering . Addition of foreign DNA in the form of recombinant DNA vectors that are generated by molecular cloning is the most common method of genetic engineering. An organism that receives the recombinant DNA is called a genetically modified organism (GMO). If the foreign DNA that is introduced comes from a different species, the host organism is called transgenic . Bacteria, plants, and animals have been genetically modified since the early 1970s for academic, medical, agricultural, and industrial purposes. These applications will be examined in more detail in the next module.
Watch this short video explaining how scientists create a transgenic animal.
Although the classic methods of studying the function of genes began with a given phenotype and determined the genetic basis of that phenotype, modern techniques allow researchers to start at the DNA sequence level and ask: "What does this gene or DNA element do?" This technique, called reverse genetics , has resulted in reversing the classical genetic methodology. One example of this method is analogous to damaging a body part to determine its function. An insect that loses a wing cannot fly, which means that the wing’s function is flight. The classic genetic method compares insects that cannot fly with insects that can fly, and observes that the non-flying insects have lost wings. Similarly in a reverse genetics approach, mutating or deleting genes provides researchers with clues about gene function. Alternately, reverse genetics can be used to cause a gene to overexpress itself to determine what phenotypic effects may occur.
Nucleic acids can be isolated from cells for the purposes of further analysis by breaking open the cells and enzymatically destroying all other major macromolecules. Fragmented or whole chromosomes can be separated on the basis of size by gel electrophoresis. Short stretches of DNA can be amplified by PCR. DNA can be cut (and subsequently re-spliced together) using restriction enzymes. The molecular and cellular techniques of biotechnology allow researchers to genetically engineer organisms, modifying them to achieve desirable traits.
Cloning may involve cloning small DNA fragments (molecular cloning), or cloning entire organisms (reproductive cloning). In molecular cloning with bacteria, a desired DNA fragment is inserted into a bacterial plasmid using restriction enzymes and the plasmid is taken up by a bacterium, which will then express the foreign DNA. Using other techniques, foreign genes can be inserted into eukaryotic organisms. In each case, the organisms are called transgenic organisms. In reproductive cloning, a donor nucleus is put into an enucleated egg cell, which is then stimulated to divide and develop into an organism.
In reverse genetics methods, a gene is mutated or removed in some way to identify its effect on the phenotype of the whole organism as a way to determine its function.
[link] Why was Dolly a Finn-Dorset and not a Scottish Blackface sheep?
[link] Because even though the original cell came from a Scottish Blackface sheep and the surrogate mother was a Scottish Blackface, the DNA came from a Finn-Dorset.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?